Microservices is the architecture design favored in new software projects; however, getting the most from this type of approach requires overcoming several previous requirements. As the evolution from a monolithic to a distributed system takes place not only in the application space but also at the data store, managing your data becomes one of the hardest challenges. This article examines some of the considerations for implementing data as a service.
When following microservices design guidelines, we find references to data handling at several points. Some of those common directions include:
- Use private databases per service for loose coupling.
- Embrace eventual consistency.
- Implement saga pattern for eventual consistency transactions.
- Use Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) and API composition.
With these points in mind, when targeting loose coupling as an essential piece in the architecture, shared databases now become an antipattern, making transactions and querying increase in difficulty. The use of datastores per service requires encapsulated data, whereas the interaction with other domains of the architecture should happen only at the API level, encouraging us to hide data implementation details. As a result, using lightweight frameworks like Spring Boot is just one of the first steps in the microservices journey.
The query challenge
Because we have data store per service, we need to make it available for consumption by other services becoming the entry point for this domain. As all the data calls happen at the service level and according to their domain, when a view of composite data is required, a traditional “table join” is no longer an option like we used to have in the shared database implementation. Additionally, we can not write a service that queries the private data stores and aggregates the data because it violates the encapsulation design.
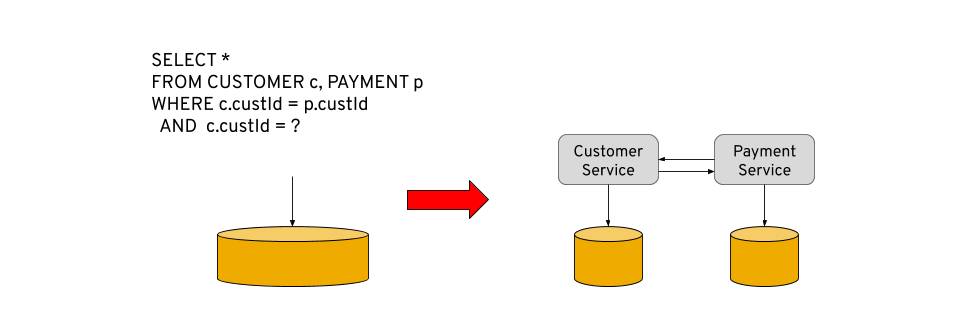
To solve the previous challenge, we need to bring back to the microservices architecture the use of well-established Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIP) like content enrichment and aggregator. Most of the time, these patterns have been rebranded as API composition pattern and commonly implemented in components like the API gateway.
In general, the API composition pattern involves the addition of another service, which makes the calls to the underlying data services with the required information to compose the required data view. As seen in the image below, it will first query the Customer Service for the basic information and then use that information to retrieve the history for this customer from the Payment Service.
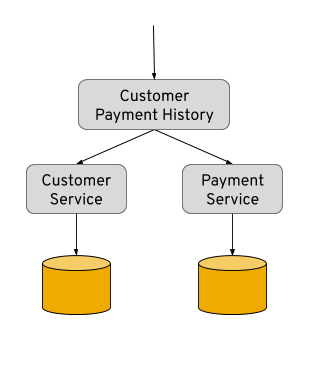
At first glance, this looks like a simple composition task; however, the business typically requires more and more control of how the data is consumed and more logic is added to this type of services. Restrictions on the amount of data to be retrieved, permissions of the consuming end user, etc., are common business requirements, making the implementation of this type of service a full-time maintenance task.
On the other hand, the Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) tries to tackle the query challenge focusing on maintaining one or more materialized sets of data aggregated from multiple source events. As a result, the complexity of the system increases as an event bus is now a requirement. We will talk about this pattern in future articles.
Distributed data integration
As has been discussed before, the distributed nature of microservices makes service-to-service communications and service composition vital for a successful implementation. Trying to implement every service from the ground up in an ad hoc fashion, even though possible, is not always recommended, especially when specialized tools exist already and help us simplify the work.
In fact, making data available for external consumption through services is one example where coding everything from scratch is avoidable. We can expose data resting in different stores, not only relational databases using existing frameworks that help us implement the API composition pattern but also simple data-as-a-microservice services.
A distributed data-focused integration provides integrated access to data in any of its store implementations through a single uniform API. Data integration allows joining and unioning data even if the information resides in more than one type of sources beyond SQL or JDBC. Contrary to a database management system, it should not store any data but act as a “single point” interface to optimally access data sources.
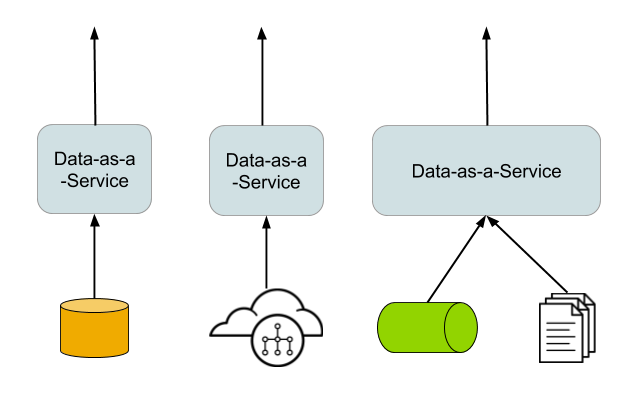
Markedly, this type of framework should be compatible with the distributed nature of microservices. Hence, the engine and implementation should be lightweight and be able to be deployed as a container in cloud environments. Correspondingly, you should have the flexibility to execute standalone the components in runtimes like Spring Boot or embed it in your application.
Summary
All things considered, going beyond building services in a microservice architecture involves the use of generally established practices like Enterprise Integration Patterns and Data Integration techniques. The ability to query different data sources and join them to expose meaningful information while providing a secure access layer in a lightweight and distributed way, can simplify your applications. And, as Christian Posta said in his article, "data, data integration, data boundaries, enterprise usage patterns, distributed systems theory, timing, etc, are all the hard parts of microservices (since microservices is really just distributed systems!).”
Last updated: February 6, 2024