This article describes how to run a client-server application for JBoss Data Grid on Openshift using Red Hat Container Development Kit 3.0 Beta and Minishift. This environment for this tutorial can be set up quickly following up this previous post on the Developer Blog.
First of all, you need to make sure you have available the ImageStreams and Templates, in order to run JBoss Data Grid in your Openshift Paas. You can check that your environment contains both of them through the oc command as follows:
$ oc get is -n openshift | grep datagrid
jboss-datagrid65-openshift registry.access.redhat.com/jboss-datagrid-6/datagrid65-openshift 1.2,1.2-13,1.2-18 + 2 more... 2 weeks ago
$ oc get templates -n openshift | grep datagrid
datagrid65-basic Application template for JDG 6.5 applications.
If you don’t have ImageStreams and Templates loaded yet then you can quickly download them from the official repository available at https://github.com/openshift/library/tree/master/official/datagrid.
Now, you can create both resources as follows:
# create imagestream
$ oc create -f Jboss-datagrid65-openshift-rhel7.json
# create template
$ oc create -f datagrid65-basic.json
Ok, now we’re ready to rock. As an example, we will create a new project named “jdg-demo” which will contain the JBoss DataGrid Service, which will be invoked from a client application running in an EAP 6 Service.
By the way, as mentioned from the Documentation, at the moment Client-Server mode is the only native option to access JBoss Data Grid in a PaaS since Library Mode is not supported.
In order to create your project, enter the following commands from a shell:
$ oc new-project jdg-demo
Now using project "jdg-demo" on server "https://192.168.42.149:8443"
The New step will be adding a new application to it, using the datagrid65-basic template:
$ oc new-app datagrid65-basic --name datagrid
Deploying template "datagrid65-basic" in project "openshift"
datagrid65-basic
---------
Application template for JDG 6.5 applications.
* With parameters:
* APPLICATION_NAME=datagrid-app
* HOSTNAME_HTTP=
* USERNAME=
* PASSWORD=
* IMAGE_STREAM_NAMESPACE=openshift
* INFINISPAN_CONNECTORS=hotrod,memcached,rest
* CACHE_NAMES=
* ENCRYPTION_REQUIRE_SSL_CLIENT_AUTH=
* MEMCACHED_CACHE=default
* REST_SECURITY_DOMAIN=
* JGROUPS_CLUSTER_PASSWORD=sKPBot52 # generated
Creating resources with label app=datagrid ...
service "datagrid-app" created
service "datagrid-app-memcached" created
service "datagrid-app-hotrod" created
route "datagrid-app" created
deploymentconfig "datagrid-app" created
Success
Run 'oc status' to view your app.
As you could see from the output, a set of services has been created in order to expose the service to the cluster. In particular, we’re interested in the service "datagrid-app-hotrod" which will be contacted by our EAP client application. To confirm our services are ok, we will execute the following check:
$ oc get svc
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
datagrid-app 172.30.139.80 <none> 8080/TCP 15s
datagrid-app-hotrod 172.30.10.134 <none> 11333/TCP 15s
datagrid-app-memcached 172.30.198.163 <none> 11211/TCP 15s
Ok, we’re almost done. Although we will not explore cluster capabilities in this article, in order to use them the Kubernetes' PING protocol, which is used to look up other nodes in the Infinispan cluster, needs to be enabled. This can be done using the default Service Account as follows:
$ oc policy add-role-to-user view system:serviceaccount:$(oc project -q):default -n $(oc project -q)
We are done with JBoss data Grid, and our Web console should reflect the status of your available services and route:
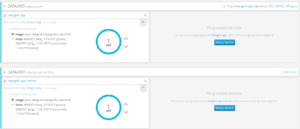
Now let’s add another application, which is based on the jboss-eap64 template and does S2I of a simple web application hosted at https://github.com/fmarchioni/ in the Web Context eap-hotrod:
$ oc new-app jboss-eap64-openshift~https://github.com/fmarchioni/ocpdemos --name eap-hotrod --context-dir=eap-hotrod -e HOTROD_SERVICE=datagrid-app-hotrod -e HOTROD_SERVICE_PORT=11333
Creating resources with label app=eap-hotrod ...
imagestream "eap-hotrod" created
buildconfig "eap-hotrod" created
deploymentconfig "eap-hotrod" created
service "eap-hotrod" created
Success
Build scheduled, use 'oc logs -f bc/eap-hotrod' to track its progress.
Run 'oc status' to view your app.
As you could see, we have passed some environment variables to our application. These variables are used to solve the name of JDG Hot Rod service and its port. As you can see from the minimal Servlet contained in it, we abstract from the Hostname and Port where the Hot Rod service is running and just use the name of Openshift Service (and its port) passed as Environment variable:
package infinispan;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.infinispan.client.hotrod.RemoteCache;
import org.infinispan.client.hotrod.RemoteCacheManager;
import org.infinispan.client.hotrod.configuration.ConfigurationBuilder;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
@WebServlet(value = "/test")
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
private RemoteCacheManager cacheManager;
private RemoteCache < String, Object > cache;
@Override
public void init() {
ConfigurationBuilder builder = new ConfigurationBuilder();
builder.addServer().host(System.getenv("HOTROD_SERVICE"))
.port(Integer.parseInt(System.getenv("HOTROD_SERVICE_PORT")));
cacheManager = new RemoteCacheManager(builder.build());
cache = cacheManager.getCache("default");
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) {
doPost(req, res);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) {
res.setContentType("text/html");
String name = req.getParameter("name");
String surname = req.getParameter("surname");
String teamName = req.getParameter("teamname");
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
out = res.getWriter();
Player player = new Player();
player.setName(name);
player.setSurname(surname);
player.setTeamName(teamName);
String randomId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
cache.put(randomId, player);
out.println("Added Player: " + cache.get(randomId));
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
You can complete the example by exposing the EAP route as follows:
$ oc expose service eap-hotrod
route "eap-hotrod" exposed
In a couple of minutes, your service should be available as you can see from the Web console:
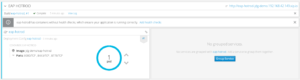
Clicking on the Service’s route, you will be redirected to the welcome page, which is a simple JSP frontend to the Servlet. Add some data in it to test it:
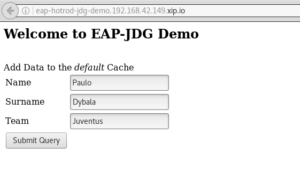
Finally, when you are done with experimenting, you can remove everything using 'oc delete' command:
$ oc delete all -l "app=eap-hotrod"
$ oc delete all -l "app=datagrid"
About the Author:
Francesco Marchioni is a Senior Technical Account Manager on Middleware products based in Rome (Italy). Some of its contributions to the Community of JBoss developers are available on the site http://www.mastertheboss.com
Click here to download JBoss Data Grid.
Last updated: July 27, 2023