And here we go for another episode of the series: "Unlock your [….] data with Red Hat JBoss Data Virtualization." Through this blog series, we will look at how to connect Red Hat JBoss Data Virtualization (JDV) to different and heterogeneous data sources.
JDV is a lean, virtual data integration solution that unlocks trapped data and delivers it as easily consumable, unified, and actionable information. It makes data spread across physically diverse systems — such as multiple databases, XML files, and Hadoop systems — appear as a set of tables in a local database. By providing the following functionality, JDV enables agile data use:
- Connect: Access data from multiple, heterogeneous data sources.
- Compose: Easily combine and transform data into reusable, business-friendly virtual data models and views.
- Consume: Makes unified data easily consumable through open standards interfaces.
It hides complexities, like the true locations of data or the mechanisms required to access or merge it. Data becomes easier for developers and users to work with. This post will guide you step-by-step on how to connect JDV to a PostgreSQL database using Teiid Designer. We will connect to a PostgreSQL database using the PostgreSQL JDBC driver.
Prerequisites
-
JDV 6.3 Environment
Download: http://developers.redhat.com/products/datavirt/download
Install: http://developers.redhat.com/products/datavirt/get-started/#Step1We will refer to the installation directory of JDV 6.3 as $JDV_HOME.
-
Red Hat JBoss Developer Studio (JBDS) 9.1.0 with Teiid Designer plugins
Download: https://developers.redhat.com/download-manager/file/jboss-devstudio-9.1.0.GA-installer-eap.jar
Install: http://developers.redhat.com/products/datavirt/get-started/#Step2 -
PostgreSQL Database
Download: https://www.postgresql.org/download
Install: Follow the installation instructions.In this example, we will connect to a database called "unlockdata" with the username/password "postgresql_dev/postgresql_dev".
Note: If you are running on RHEL, be aware that PostgreSQL is available via Software Collection. -
PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
JDV requires access to the following jar file to successfully use the PostgreSQL JDBC driver to connect to PostgreSQL database; you can download it from the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver and extract it.
We will refer to the directory with this jar file as $DRIVER_HOME.
Install & Configure the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver on JDV
-
Create a JBoss module directory for the PostgreSQL JDBC driver
$ mkdir -p $JDV_HOME/modules/system/layers/dv/org/postgresql/main
-
Copy the PostgreSQL JDBC jar file into the new JBoss module directory created
$ cp $DRIVER_HOME/postgresql-9.4.1212.jar $JDV_HOME/modules/system/layers/dv/org/postgresql/main
-
Create a module.xml file with content seen below, in the new JBoss modules directory created
<?xml version="1.0"?> <module xmlns="urn:jboss:module:1.1" name="org.postgresql"> <resources> <resource-root path="postgresql-9.4.1212.jar"/> </resources> <dependencies> <module name="javax.api"/> <module name="javax.transaction.api"/> </dependencies> </module> -
Start your local JDV 6.3 environment
$ $JDV_HOME/bin/standalone.sh
-
Add PostgreSQL JDBC driver
$ $JDV_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect [standalone@localhost:9999 /] /subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=postgresql:add(driver-name=postgresql,driver-module-name=org.postgresql,driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.postgresql.xa.PGXADataSource)
-
Add PostgreSQL Datasource and enable it
[standalone@localhost:9999 /] data-source add --name=UnlockData_PostgreSQL_DS --jndi-name=java:/UnlockData_PostgreSQL_DS --connection-url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/unlockdata --driver-name=postgresql --user-name=postgresql_dev --password=postgresql_dev [standalone@localhost:9999 /] data-source enable --name=UnlockData_PostgreSQL_DS
What about automating configuration ? (Optional)
A question you might ask: Can we automate the above configuration steps? The answer is yes. We can, with Ansible, by Red Hat.
Ansible is a radically simple IT automation engine that automates cloud provisioning, configuration management, application deployment, intra-service orchestration, and many other IT needs. It uses no agents and no additional custom security infrastructure, so it’s easy to deploy – and most importantly, it uses a very simple language (YAML, in the form of Ansible Playbooks) that allow you to describe your automation jobs in a way that approaches plain English. For your convenience most of the steps are automated in an ansible playbook called postgresql on github and to run you only need to run one command and you should see similar output as shown below:
$ cd unlock-your-data/postgresql $ ansible-playbook local.yml PLAY [Configure local JBoss Data Virtualization with PostgreSQL JDBC driver] *** TASK [setup] ******************************************************************* ok: [localhost] TASK [Create JBoss module directory for the PostgreSQL JDBC driver] ************ changed: [localhost] TASK [Download the PostgreSQL JDBC jar file] *********************************** changed: [localhost] TASK [Copy module.xml into JBoss modules directory] **************************** changed: [localhost] TASK [Execute Management CLI file(s)] ****************************************** changed: [localhost] => (item=add_datasource.cli) changed: [localhost] => (item=add_driver.cli) PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************* localhost : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0
Note: See https://github.com/cvanball/unlock-your-data/tree/master/postgresql for more information.
Start Your Development Environment
-
-
Start your local JDV 6.3 environment
$ $JDV_HOME/bin/standalone.sh
-
Start your local JBDS environment
Start JBDS 9.1.0 and open the Teiid Designer Perspective as shown below:
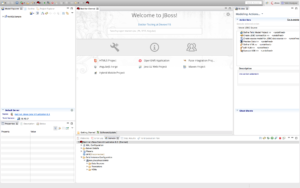
Note: Use the following menu options "Window" > "Perspective" > "Open Perspective" > "Other..." > "Teiid Designer" to set JBDS in Teiid Designer perspective
-
Create Your Teiid Project
-
-
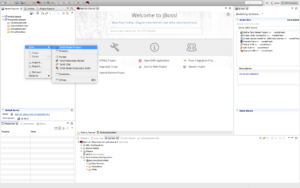
Create Teiid Model Project called "PostgreSQLSample"
Create a new Teiid Model project using right-click "New" > "Teiid Model Project" in the Model Explorer window as shown below:
-
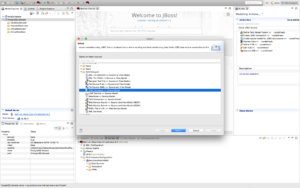
Import Metadata using JDBC importer
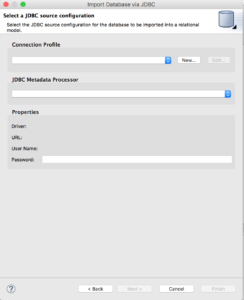
We are now going to use the PostgreSQL JDBC driver directly and import metadata directly using the JDBC importer. Right-click the project "PostgreSQLSample" and select Import and select "JDBC Database >> Source Model" as shown above and click "Next >".
-
Create Your Connection Profile
-
Create the connection profile
On the first page of the wizard, click "New..." to create a new Connection Profile. Before we can proceed we need to setup a new connection profile to be able to connect to the PostgreSQL database using the JDBC jar previously downloaded.
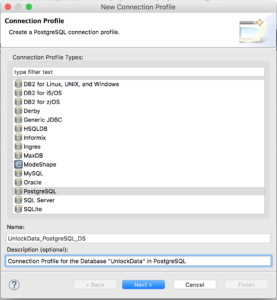
Select "PostgreSQL" for the Connection Profile Type and name the Connection Profile “UnlockData_PostgreSQL_DS”. Click "Next >".
-
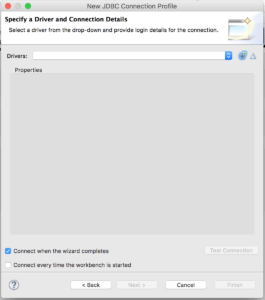
Add and configure the JDBC driver
Click the “Add Driver Definition” button.
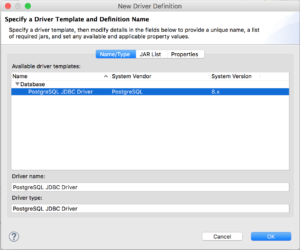
In the "Name/Type" tab, select the right driver template.
In the "JAR List" tab, click "Clear All" and click "Add JAR/Zip..." to add the JDBC driver jar file, $DRIVER_HOME/postgresql-9.4.1212.jar.
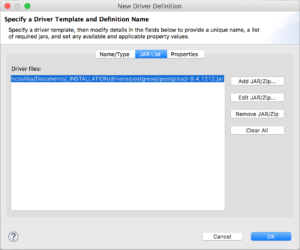
Click "Ok" and now we are ready to connect to the PostgreSQL database by providing the correct connection details.The PostgreSQL JDBC URL is a string with the following syntax:
jdbc:postgresql://host:port/database
where
host
is the host name of the server.
port
is the port number the server is listening on. The default port number is 5432.
database
is the database name.
Here we will use the following connection details:
Username = postgresql_dev Password = postgresql_dev Database = unlockdata URL = jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/unlockdata
Check “Save password” box and Click "Test Connection" to validate if the connection to the server can ping successfully.
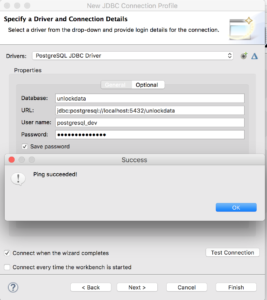
Since the connection can ping successfully we are ready to select tables from the PostgreSQL database and create a source model out of it. Click "OK" then "Finish".
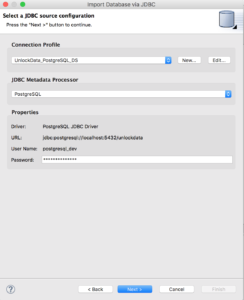
Create Your Source Model
-
Import the metadata from the database
Click "Next >" twice to select database objects.
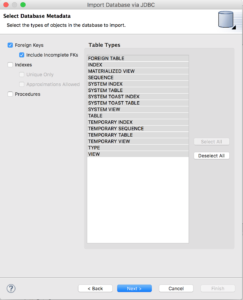
Select all tables in the 'public' schema and click "Next >"
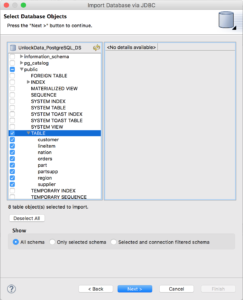
Specify the target folder for the source models (here "PostgreSQLSample/DataSourceLayer"). Make sure that the JNDI name corresponds to the one we created in the JDV environment (Hint: UnlockData_PostgreSQL_DS) and that Auto-create Data Source is not selected. Click “Finish” to create the source models.
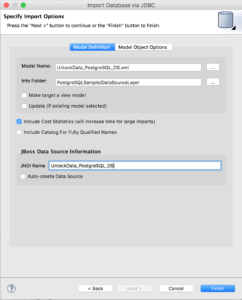
-
Preview the data through JDV
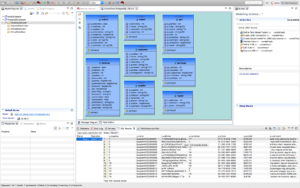
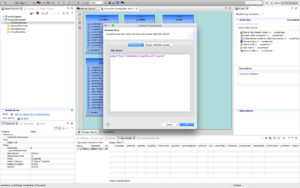
Select any model and click the running man icon
 to preview the data as depicted below:
to preview the data as depicted below:
Conclusion
In this post we've shown the configuration steps needed to perform in order to unlock your PostgreSQL data using PostgreSQL JDBC driver with Red Hat JBoss Data Virtualization.
Now we are ready to federate this data with other data-sources from physically distinct systems into such as other SQL databases, XML/Excel files, NoSQL databases, enterprise applications and web-services etc.
For more information about PostgreSQL and Red Hat JBoss Data Virtualization please refer to the following websites:
Last updated: November 9, 2023