Virtual machines (VMs) remain a cornerstone of many enterprise IT environments, hosting critical applications and services. However, as organizations accelerate their cloud-native journey, the challenge often becomes about how to modernize these traditional workloads, providing them with the agility, observability, and resilience typically associated with cloud-native applications.
One answer lies with Red Hat OpenShift. It empowers VMs to become fully integrated components in a cloud-native world, starting with Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization, and further enhancing their capabilities with Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh and Red Hat OpenShift GitOps. This article examines how these powerful OpenShift features can enhance your virtual machine operations.
Bring VMs into the Kubernetes ecosystem
At its core, OpenShift Virtualization extends the power of Kubernetes to manage VMs alongside your containers. This means you can use familiar Kubernetes commands and concepts to deploy, scale, and monitor your VMs, eliminating the need for disparate management tools.
Consider a virtual machine in your environment running a web server or a database. With OpenShift Virtualization, you can seamlessly view its health, details, and metrics directly through the OpenShift console like any other application on the platform.
A key advantage is how easily these VM workloads can communicate. OpenShift provides built-in mechanisms for internal load balancing and service discovery, allowing VMs to connect effortlessly with other services on the platform. For external access, OpenShift provides straightforward methods to make VM-backed services accessible from outside your environment, all without requiring complex firewall rules or external DNS configurations. This immediate integration helps unlock the cloud-native potential for your existing VM fleet.
Achieve elasticity in a hybrid environment
Elasticity is a key characteristic of cloud-native applications, and with OpenShift Virtualization, virtual machines (VMs) are no exception. You can achieve robust, on-demand scaling for your virtualized workloads as follows:
- Scaling up (vertical scaling): For VMs that require more processing power, OpenShift Virtualization allows you to easily increase allocated CPU and memory resources directly from the console. The platform handles the underlying changes, even supporting live migration to ensure minimal disruption.
- Scaling out (horizontal scaling): Distributing workloads across multiple VM instances enhances both performance and availability. OpenShift Virtualization lets you define a desired number of VM replicas, ensuring your specified number of VM instances are always running and ready. You can even configure the system to automatically scale your VMs up or down based on their CPU utilization, bringing container-like elasticity to your virtualized workloads.
Unifying observability, resilience, and security
After bringing VMs under OpenShift management, integrating them into the OpenShift Service Mesh (via Istio and tools like Kiali) is a natural progression. This integration allows VMs to function as fully integrated elements, similar to those in a microservices-based design.
This integration brings a significant transformation as follows:
- Unified observability: Gain a unified view of all your services, whether they are running in VMs or containers. You can see their communication patterns and traffic flow in real time, providing deep insights into your application's behavior that might not be available with traditional VM tools. For example, Figure 1 depicts virtual machines in Kiali.
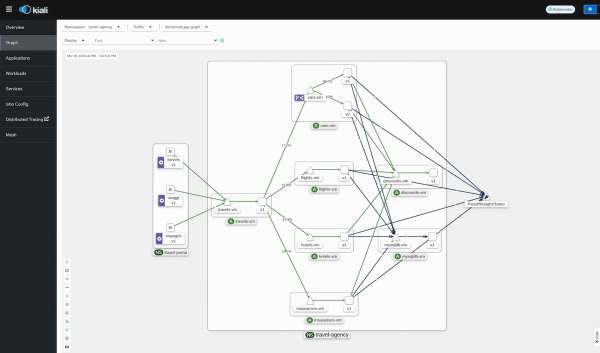
- Traffic management: Implement advanced strategies to manage network traffic effectively. For example, when deploying new versions of a VM-based application, you can perform "canary releases," smoothly transitioning a small percentage of traffic to the new version before a full rollout. This enables low-risk updates and A/B testing for your VM services.
- Enhanced resilience with circuit breakers: Protect your applications from cascading failures. You can define policies that automatically detect unresponsive VM instances and temporarily remove them from the active service pool. This ensures that end-user requests continue to be served by healthy instances, maintaining service availability.
- Granular security with authorization policies: Apply fine-grained access control to your VM interactions. You can start with a secure "deny-all" approach and then selectively allow only necessary communication paths between services (e.g., allowing a web portal to access a backend database VM). This provides strong, identity-based security for your virtualized environment.
VM management via OpenShift GitOps
Another key step in the modernization journey is adopting OpenShift GitOps built on Argo CD (Figure 2). GitOps establishes Git as the single source of truth for all configurations, enabling fully automated, declarative deployments, and continuous synchronization.
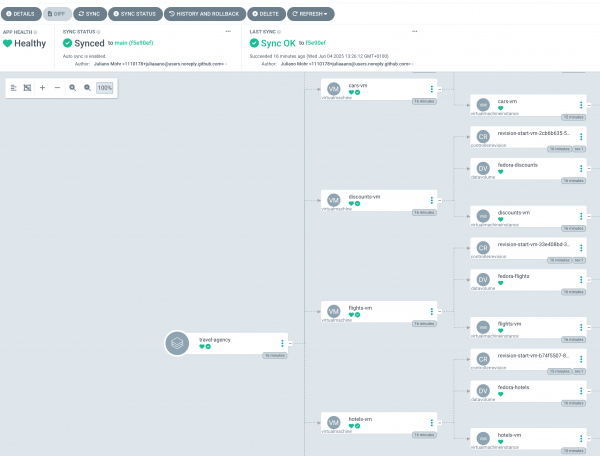
GitOps offers several powerful aspects for VMs such as:
- Configuration as Code (CaC): You can manage your VM definitions and configurations, like any other platform setting, as code in a version-controlled system. This provides a clear audit trail and simplifies collaboration.
- Automated deployment and rollbacks: Changes made in your configuration repository are automatically applied to your environment, ensuring consistency and reducing manual errors. If an issue arises, you can easily roll back to a previous, stable configuration.
- Self-healing: GitOps provides robust self-healing capabilities. If a managed VM or its configuration is accidentally altered or deleted, the system immediately detects the drift. It then automatically restores the correct state from your central configuration, maintaining your desired environment with minimal human intervention. This automated recovery significantly boosts operational efficiency.
The future is hybrid
Your existing VM investments don't have to be an obstacle to cloud-native adoption. By leveraging Red Hat OpenShift with its integrated Virtualization, Service Mesh, and GitOps capabilities, organizations can seamlessly bring traditional VMs into a modern, declarative management paradigm. This approach streamlines VM management, enhances security, improves observability, and brings the agility of cloud-native development to your entire infrastructure.
Ready to explore these capabilities for your own environment? Dive into the Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization, Service Mesh, and GitOps documentation to discover how you can uplift your VM operations in a hybrid cloud environment. You can also connect with a Red Hat representative or watch a live demo. The future is hybrid, managed declaratively.
