Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift introduces a modern, cloud-native framework designed to revolutionize how you deploy, manage, monitor, and update your cloud infrastructure.
In the context of OpenStack Services on OpenShift, there are three types of releases that could be applicable for an update:
- Async release: Any release that needs to be shipped ASAP without a full cycle or planned cadence.
- Bug-fix updates: Periodic updates to resolve bugs or CVEs in the OpenStack Services on OpenShift codebases. These will generally also pick up fixes in the underlying products (i.e., Red Hat Enterprise Linux) and will often resolve container grades as well.
- Feature updates/packages: Periodic releases that incorporate fixes from all types of releases (i.e., CVEs, bugs, grades), allowing feature backports and RFEs.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the OpenStack Services on OpenShift update workflow that ensures a reliable process for updating the control plane and data plane components to the latest release.
Prerequisites for a successful update
Before starting, ensure the following prerequisites are in place to optimize the update workflow and prevent interruptions:
Access to the oc command-line tool on your workstation, and a backup of the current environment.
These enabled repositories for Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift compute nodes:
- RHEL 9.2 if you decide to delay the update of Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift on Compute nodes during the Red Hat OpenStack Platform 17.1 to Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift upgrade using the adoption mechanism.
- RHEL 9.4 on compute nodes, if it's a fresh deployment of Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift, or you have already updated the Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift on compute nodes after the Red Hat OpenStack Platform 17.1 to Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift upgrade.
Initial steps
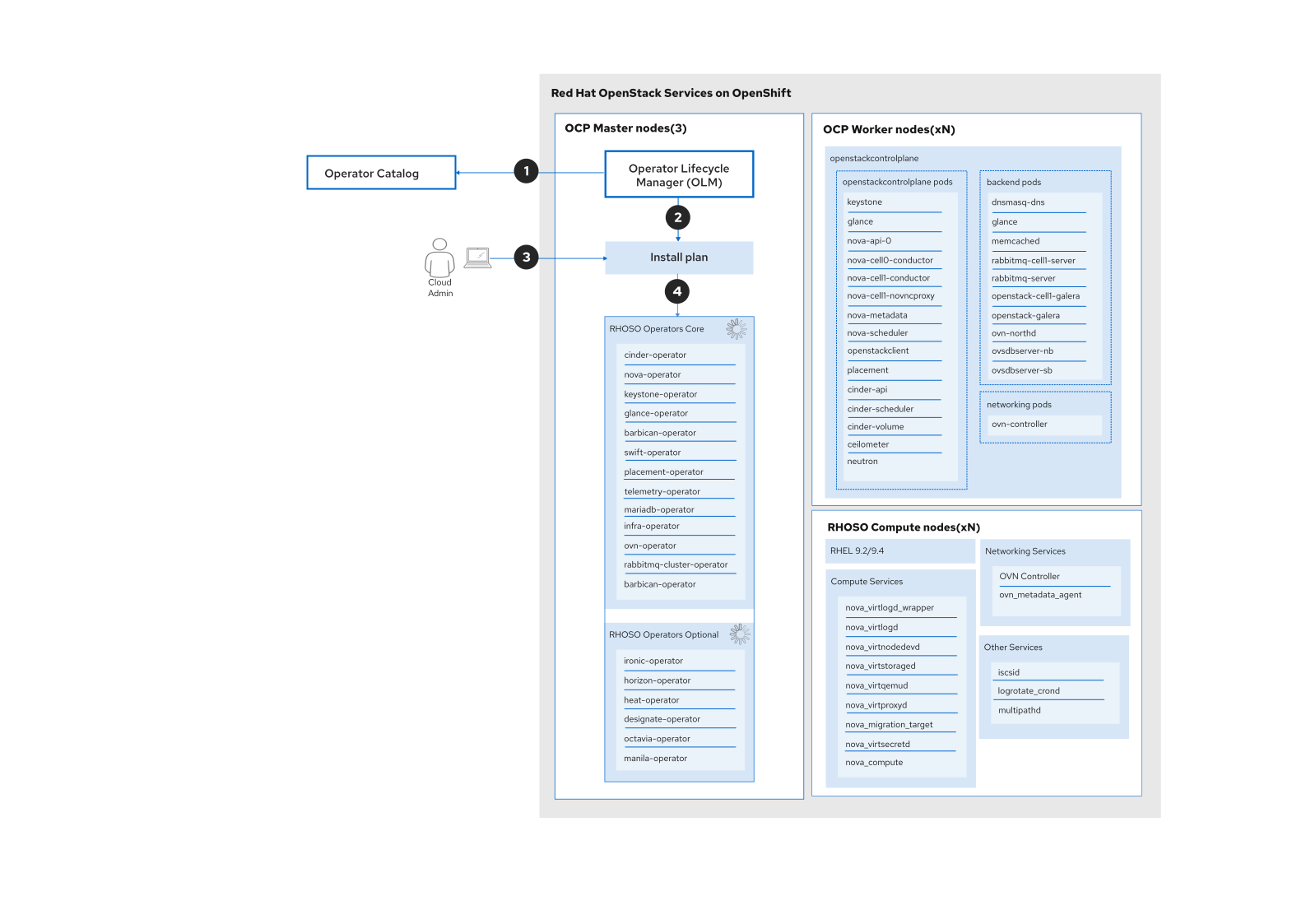
You will need authorization to the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RHOCP) cluster and an updated set of OpenStack Services on OpenShift operators using the Operator Lifecycle Manager.
In the initial state, the cloud operator would be updating the OpenStack operators to the latest version.
- A new version of OpenStack Operator catalog is available and downloaded to the cluster (OpenShift checks every 5 minutes for a new version of catalog).
- A new InstallPlan is created if there are newer operators available and it is possible to download from one version of operators to another version.
- The InstallPlan is either started automatically or needs to be approved.
- Once the InstallPlan runs the following will happen:
- The service operators are updated if they were are part of InstallPlan update. During this phase, the OpenStack operators evaluate the current state of the deployments they manage. If any changes are detected, the OpenStack operators automatically apply the necessary adjustments to align the deployments with the desired state. As part of this process, some pods might need to be restarted to ensure that the changes take effect.
- When a new set of operators is updated via OLM the OpenStackVersion resources will be reconciled and a new AvailableVersion will be set on each custom resource (CR).
When installing OpenStack Services on OpenShift greenfield, it’s encouraged to use installPlanApproval: Manual.
When applying the subscription CR, operators have more control over their deployments and manually approve the operators updates. The following graph shows the steps previously described (Figure 1).
The update procedure
To update your OpenStack Services on OpenShift environment to the latest maintenance release, perform the following steps:
- Update OVN services on the control plane.
- Update OVN services on the data plane.
- Wait for the OpenStack Operator to complete the automatic update of the remaining control plane packages, services, and container images.
- Update the remaining services on the data plane.
Set the desired version state
Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift services are deployed using a container image for a specific release and version.
The container images used by the installer are controlled through the OpenStackVersion CR. An OpenStackVersion CR is automatically created by the OpenStack operator during the deployment of services.
The OpenStackVersion version CR contains 3 key fields for managing updates:
- Target version: The version that we want to install.
- Available version: The version available to be updated.
- Deployed version: The version that is currently deployed.
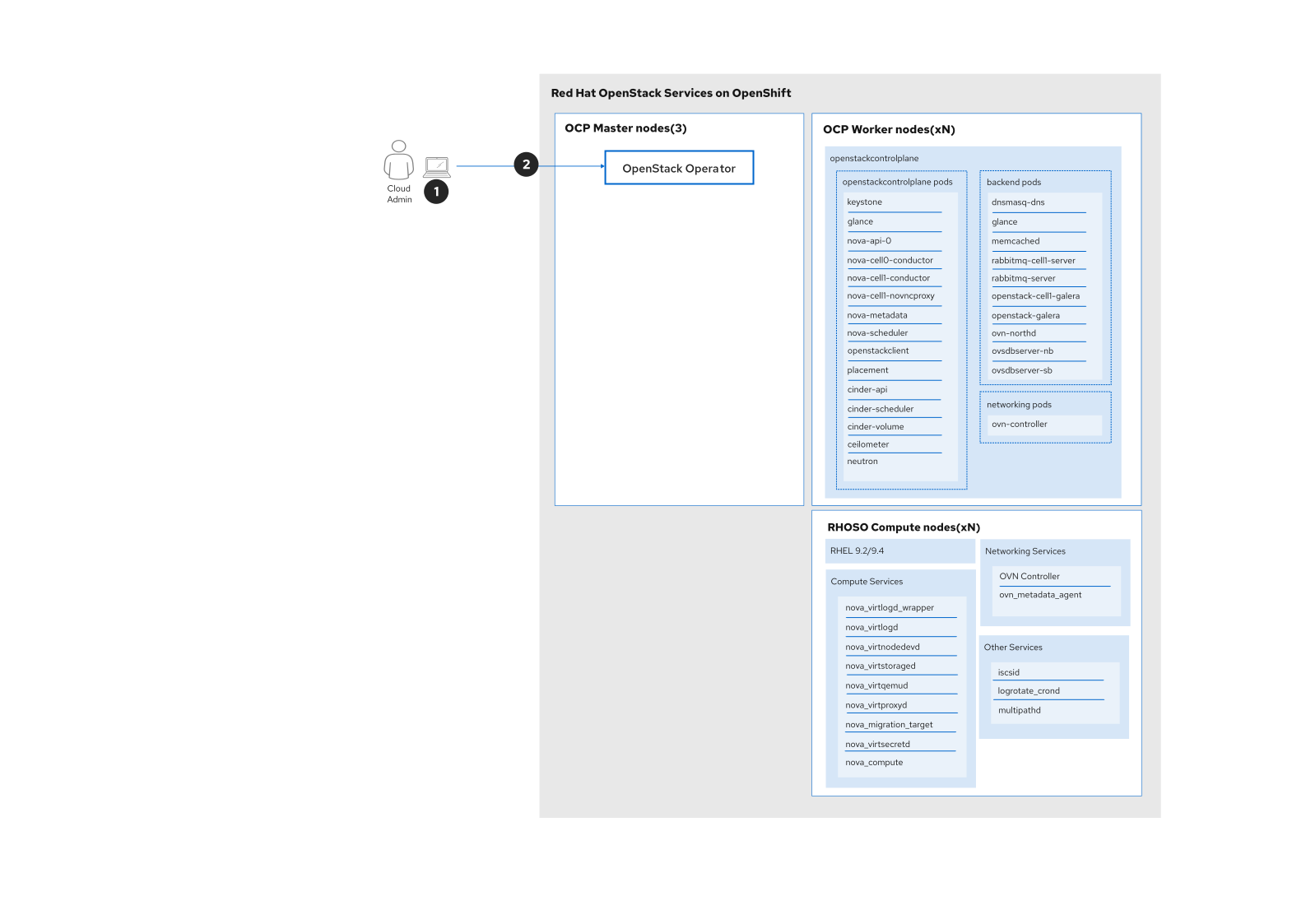
First, the cloud operator retrieves the OpenStackVersion CR to check the version available for updating (step 1).
$ oc get openstackversion -n openstackThe following output shows the available version.
NAME TARGET VERSION AVAILABLE VERSION DEPLOYED VERSION
openstack-control-plane 18.0.2-20240923.2 18.0.3-20241126.2 18.0.2-20240923.2Then, the cloud operator patches the targetVersion on the OpenStackVersion CR to trigger the start of the minor update (step 2).
cat <<EOF >openstackversionpatch.yaml
"spec": {
"targetVersion": 18.0.3-20241126.2
}
EOF
oc patch openstackversion openstack-control-plane --type=merge --patch-file openstackversionpatch.yamlThe graph in Figure 2 shows step 1 and step 2 initiating the OpenStack Services on OpenShift update process.
Update OVN services on the control plane
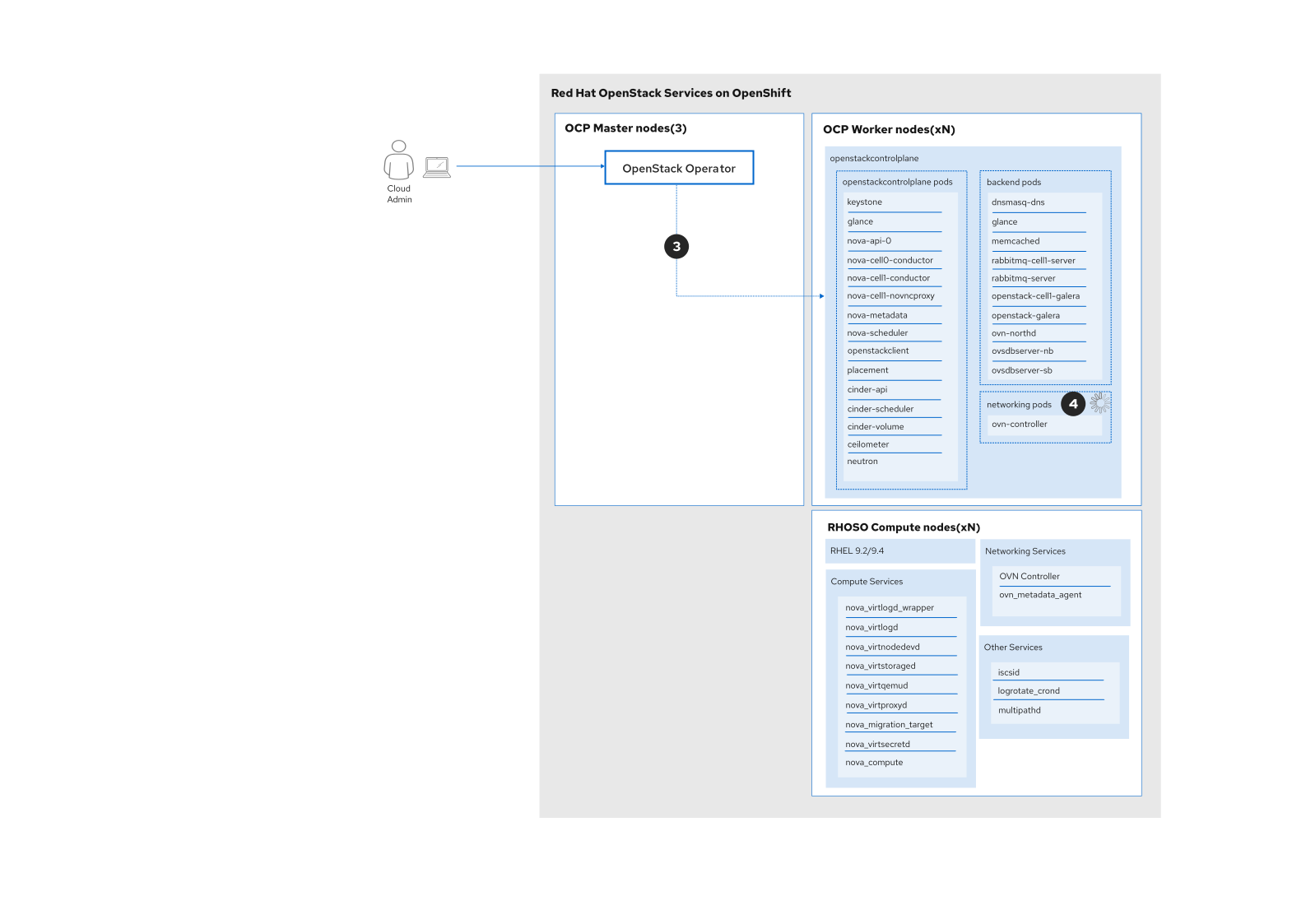
The graph in Figure 3 shows the patch operation from the previous section. The OpenStack operator initiates the update of the OVN services on the control plane: the OVN Controller (steps 3 and 4).
Update OVN services on the data plane
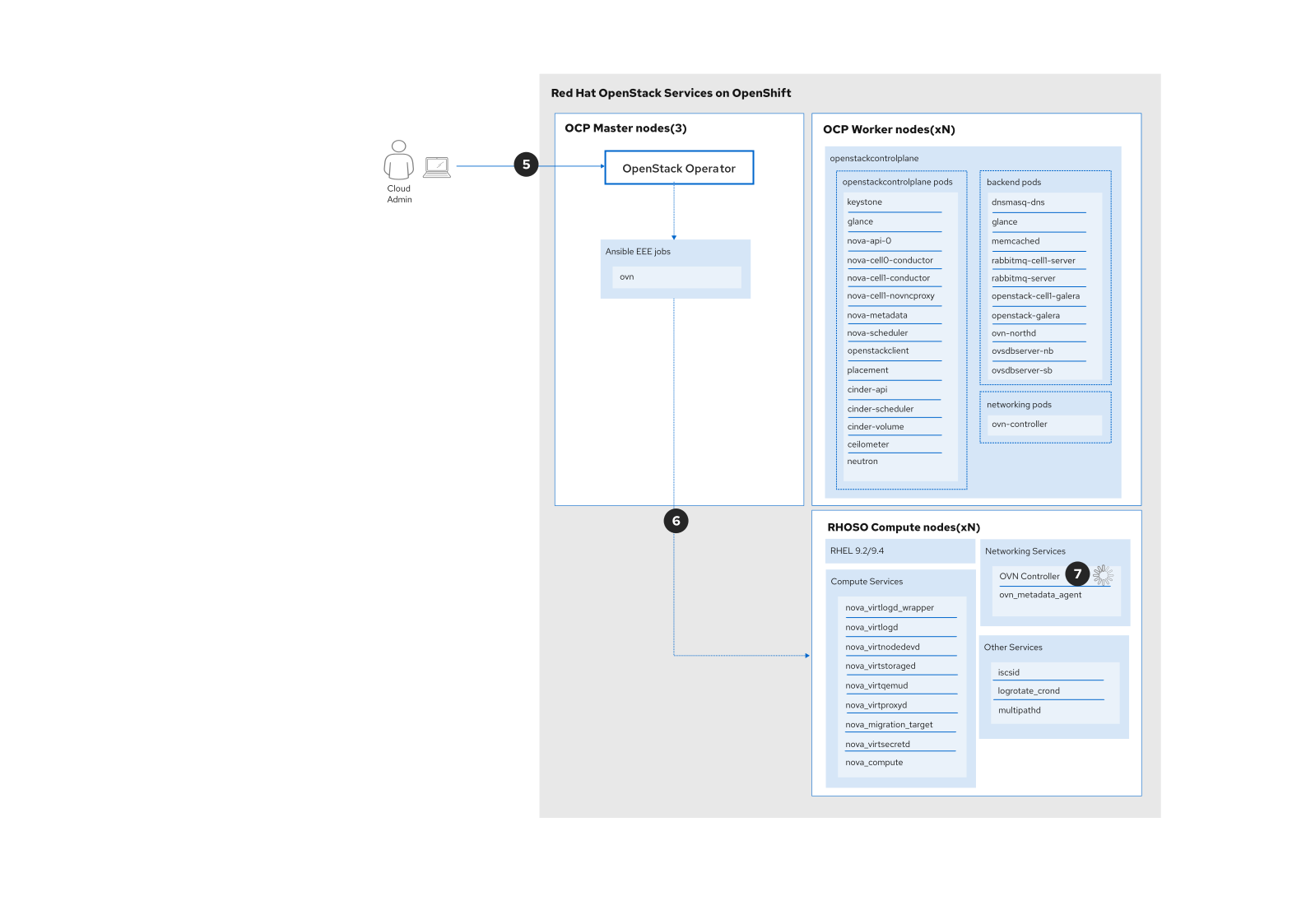
To update OVN services on the data plane, the cloud operator creates an OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment custom resource (CR) that will trigger the execution of the OVN OpenStackDataplaneService.
cat << EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: dataplane.openstack.org/v1beta1
kind: OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment
metadata:
name: edpm-deployment-ipam-ovn-update
spec:
nodeSets:
- openstack-edpm-ipam
servicesOverride:
- ovn
EOFThis process in depicted in Figure 4.
The cloud operator can check if the control plane has been successfully updated by using this command:
oc wait openstackversion openstack-control-plane --for=condition=MinorUpdateControlplane --timeout=20mThe graph in Figure 5 describes the process following the execution of the OVN OpenStackDataplaneService. The OpenStack control plane will automatically be updated. Pods will be rebooted and point to the new images that are stored in the OpenStackVersion CR.
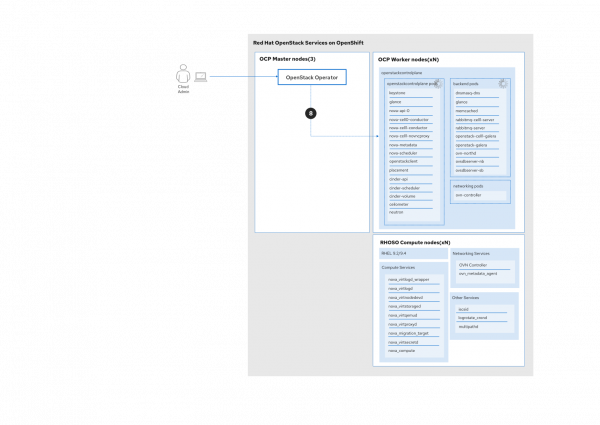
Update the remaining services on the data plane
The graph in Figure 6 shows the update of the remaining services on the data plane.
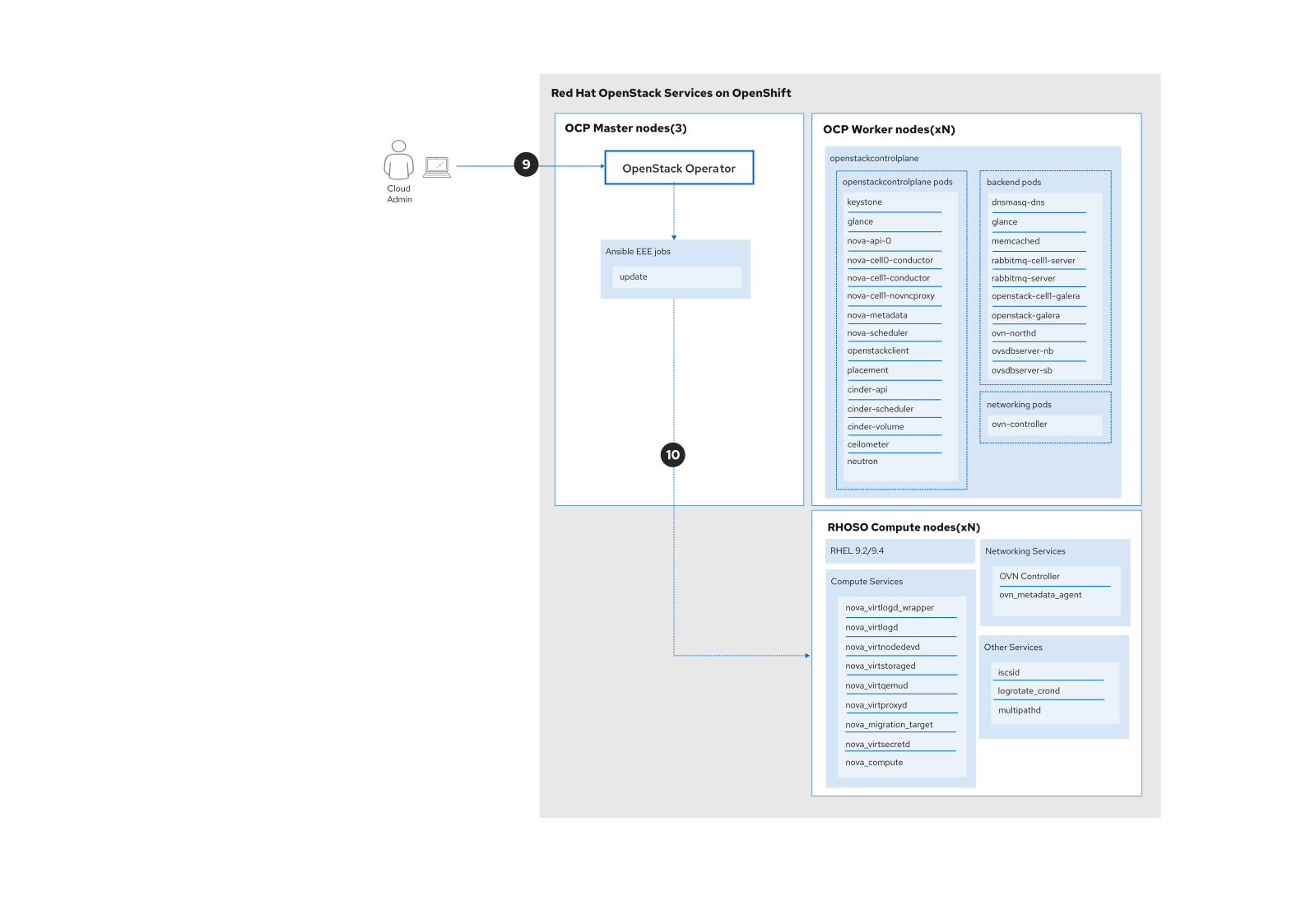
The cloud operator creates an OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment custom resource (CR) that will trigger the execution of the update OpenStackDataplaneService:
cat << EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: dataplane.openstack.org/v1beta1
kind: OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment
metadata:
name: edpm-deployment-ipam-update-dataplane-services
spec:
nodeSets:
- openstack-edpm-ipam
servicesOverride:
- update
EOFThe cloud operator can check if the data plane services have been successfully updated by executing the following command:
oc wait openstackversion openstack-galera-network-isolation --for=condition=MinorUpdateDataplane --timeout=20mAt this stage, all Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift content in the cluster has been updated to the latest version.
Once updates are completed, a controlled reboot of the compute nodes ensures that your environment fully transitions to the new configurations, including kernel and networking components. Before rebooting, migrate workloads as needed to avoid downtime.
To initiate the reboot, create an OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment CR with specific nodes or entire sets targeted for reboot. Monitoring the process helps to verify that each node completes the reboot successfully. You can find more information in the documentation.
Update OpenStack Services on OpenShift
Updating to the latest release of Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift equips your infrastructure with optimal performance, security, and flexibility. By carefully managing the control plane and data plane updates and coordinating compute node reboots, administrators can enhance the reliability of their environment, providing a strong foundation for future innovation.
