Observability signal correlation for Red Hat OpenShift has exponentially evolved over the past few months. A developer preview was made available to OpenShift users in December 2023 as part of the Logging 5.8 release. But since then, our team has worked to provide you with a series of great new features!
Observability signal correlation for Red Hat OpenShift continues to be powered by Korrel8r—an open source observability project founded within Red Hat—aimed at providing a set of rules for easily correlating metrics, logs, alerts, and additional observability signals across different data stores. Key enhancements include 1) expanded signal support, as you can now correlate netflows, 2) brand new troubleshooting panel in the OpenShift web console that simplifies the overall observability signal navigation, and 3) easier installation and set up process by simply installing the Cluster Observability Operator.
This correlation capability is crucial for organizations to manage and monitor their infrastructure effectively, deal with the increasing data volume, and reduce their overall mean time to detection (MTTD) and mean time to resolution (MTTR). In this article, we will delve into the features, benefits, and setup process for testing the enhanced dev preview features of Korrel8r on OpenShift clusters, namely observability signal correlation for Red Hat OpenShift—a key part of the Observability troubleshooting journey. Learn more about the initiative below.
Enhanced developer preview: Everything you need to know
By installing the Cluster Observability Operator—the Observability umbrella operator—you can deploy a specific set of Observability UI plug-ins in OpenShift. See Figure 1.

That includes the troubleshooting-panel, which is the heart of the observability signal correlation experience. As displayed in Figure 2, click Create UIPlugin in the operator details section of your (now) installed Cluster Observability Operator. Note that creating the plug-in will also automatically install Korrel8r.

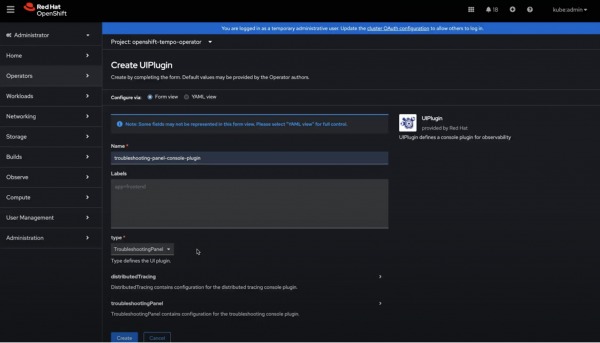
When creating the plug-in, make sure to name it troubleshooting-panel and select TroubleshootingPanel as the type, as shown in Figure 3. Then click Create.
You will then be able to access the troubleshooting panel by clicking Observe → Alerting, as displayed in Figure 4.
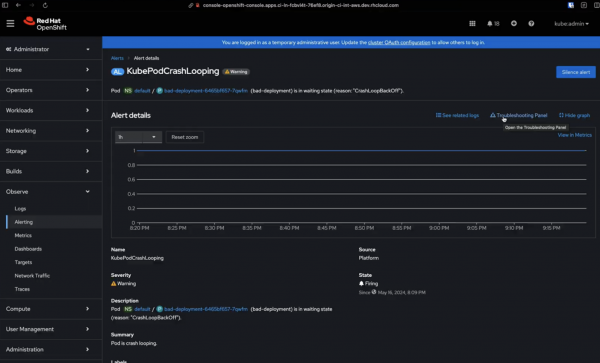
A floating panel will then pop up on the side of the screen, starting with the Korrel8r query related to that specific alert—the starting point of the troubleshooting journey itself. Note that installing the Logging and Network Traffic plug-ins is not necessary for making use of the troubleshooting panel and for the Korrel8r backend to work. However, if not installed, the corresponding relations to logs and netflows will not be rendered in the UI. Based on your use cases, we highly recommend the installation of both. See Figure 5.

The troubleshooting panel is interactive, meaning that users can click each icon/node and be automatically redirected to the web console UI that displays that specific information—in this case, a pod. See Figure 6.

From the starting alert, I can go to the correlated Metric, too (Figure 7).

And also to the corresponding events (Figure 8).

And logs (Figure 9).

There, I can easily take a look at the cause behind that starting alert (Figure 10).

What's next?
Observability signal correlation for Red Hat OpenShift is part of the Observability troubleshooting journey initiative, which is a structured approach designed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of identifying and resolving issues within your cluster(s). The objectives of the initiative include:
- Focusing on the diagnostic data that matters and minimizing the cognitive load required to deal with such increasing data volume and noise.
- Facilitating the root cause analysis and reduce the mean time to detection (MTTD), and thus minimizing the time required to detect incidents.
- Reducing the mean time to resolution (MTTR), and thus minimizing the time required to resolve issues.
More features are planned to be delivered this year, including a Technology Preview of observability signal correlation for Red Hat OpenShift and a Developer Preview of incident detection. We are looking forward to receiving your feedback. You can share your questions and recommendations with us using the Red Hat OpenShift feedback form.
