Open Data Hub is an end-to-end AI/ML platform that runs and installs on Red Hat OpenShift 4.x. It provides components for every phase of the end-to-end AI/ML process, including data ingestion, model development, and production model serving and monitoring.
The Open Data Hub team recently released Open Data Hub 1.1.0. In this new release, the community focused on hardening JupyterHub deployment, providing a new and improved JupyterHub Spawner UI, integrating the Open Data Hub dashboard with OpenShift's OAuth server, and adding a Kubeflow 1.3 OpenShift distribution stack along with new components such as Trino and Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines. Open Data Hub 1.1.0 also comes with an Operator Level 4 verification indicating "Deep Insight" status after enabling more monitoring and logging.
JupyterHub
The Open Data Hub community focused on improving the JupyterHub user experience from many angles. First, the team created a new Spawner user interface as shown in Figure 1. Users can easily select the appropriate notebook image to launch and specify environment variables such as access keys and passwords hidden in created secrets.
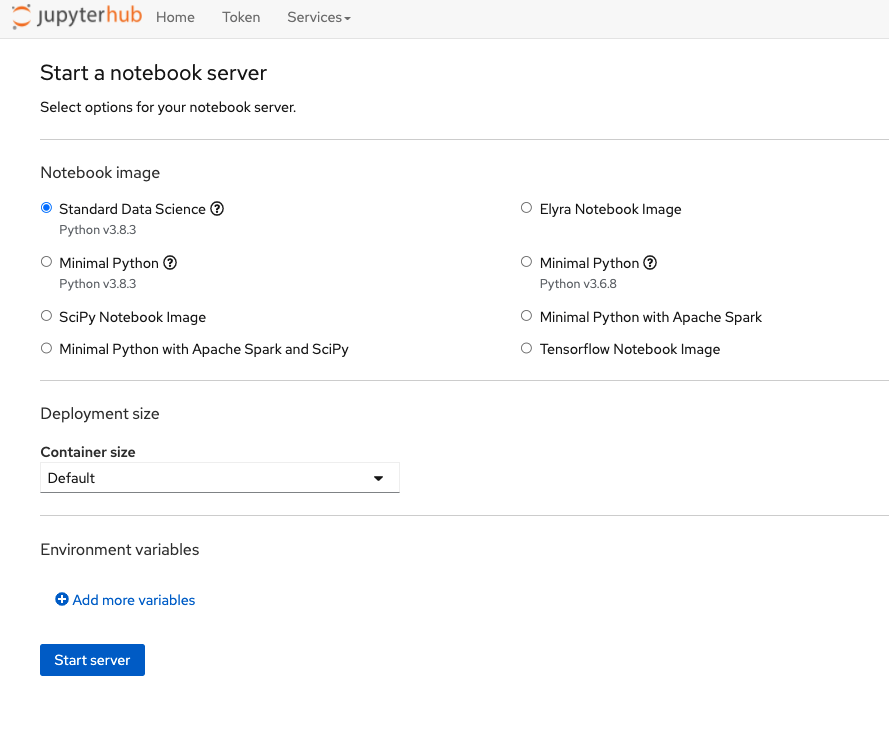
Figure 1: The Open Data Hub JupyterHub Spawner.
The team also added the ability to customize and specify JupyterHub PostgreSQL parameters such as passwords and tokens in a secret, which lets the user secure access to the database. Users also can add groups of users to JupyterHub and specify them as administrators or users for JupyterHub access by creating the following ConfigMap with a comma-separated list of group names:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
labels:
app: jupyterhub
name: jupyterhub-default-groups-config
data:
admin_groups: ""
allowed_groups: ""
The Open Data Hub community also focused on migrating all notebook images to JupyterLab. We provide two Jupyter notebook images in this release: Minimal Python and Standard Data Science. We also added UBI-based CUDA 11.0.3-enabled notebook images with Python 3.8.
Open Data Hub operator
The Open Data Hub operator now supports Operator Level 4: Deep Insights capabilities. This update includes the following enhancements:
- All KfDef objects will report installation status in the
.statusblock of the custom resource. In the block, you will now be able to review the current status of the KfDef deployment to determine whether it is installed correctly or what error is blocking the installation. - Support for Prometheus metrics for the operator, JupyterHub server, and Jupyter user notebooks. In addition, there are now Grafana dashboards that will display relevant information for the JupyterHub server and user notebook pods like CPU, memory, and PVC utilization.
In addition, we added two new Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) channels for stable and rolling releases. So that we can better support users who want the latest updates to the operator and manifests, we are deprecating the current beta channel and adding two new channels:
-
stable: This channel replaces the currentbetachannel and includes the most recent minor stable release. This channel will be for those users that are comfortable with a specific Open Data Hub release and prefer to only upgrade between minor releases. -
rolling: This channel includes the most recent builds of the operator and manifests. Updates to this channel will occur more frequently than thestablerelease and will include the most recent updates available in the operator and odh-manifests repository.
There will be no future releases under the beta channel. If you have deployed the operator under this channel, you will need to manually change to stable or rolling to receive future updates and prevent any errors in the operator deployment when beta is deleted.
Kubeflow 1.3
Open Data Hub 1.1.0 comes with the latest release of Kubeflow, version 1.3. In this version, the team created the OpenShift distribution that includes many Kubeflow components such as Kubeflow Pipelines, KFServing, Katib, PyTorch and TensorFlow distributed training, and Jupyter notebooks. As part of the distribution, Open Data Hub also provides example KfDef resources to install these components on OpenShift using the Open Data Hub operator.
Open Data Hub dashboard
In this release we added an option to enable authentication with Red Hat OpenShift's OAuth server, giving users an option to enable secure authentication to the dashboard. To enable this feature, users will need to add the authentication overlay as shown here:
- kustomizeConfig:
overlays:
- authentication
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: odh-dashboard
name: odh-dashboard
This will prompt users to enter their OpenShift username and password before they access the dashboard (see Figure 2).
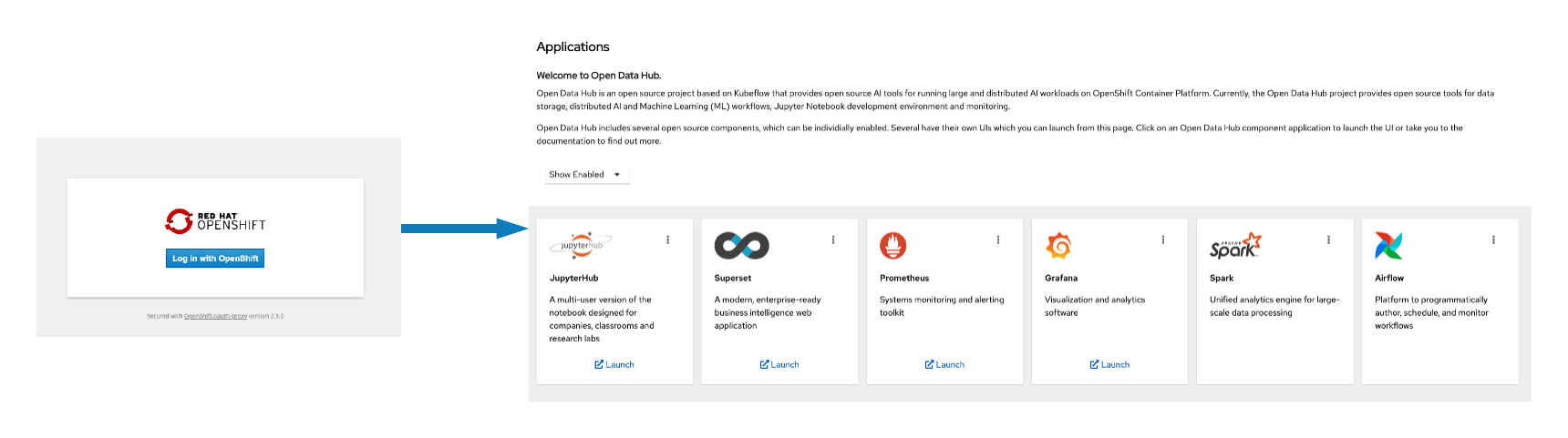
Figure 2: Open Data Hub dashboard authentication.
Trino
Open Data Hub 1.1.0 comes with a new open source component called Trino. Trino is a fast distributed SQL query engine that can integrate with multiple data sources such as S3, SQL databases, and NoSQL databases. To enable the installation of Trino, you can add the following to your KfDef resource:
- kustomizeConfig:
parameters:
- name: s3_endpoint_url
value: s3.odh.com
- name: s3_credentials_secret
value: s3-credentials
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: trino
name: trino
At the moment, the only way to interface with Trino is to use an SQL client such as DBeaver, the Trino command-line interface (CLI), or the Python Client for Trino. In future releases of Open Data Hub we plan to integrate Superset and Hue with Trino so users can use SQL queries for data exploration and visualization.
OpenShift Pipelines
Open Data Hub now supports the installation of Red Hat OpenShift Pipelines along with all of the required custom resources to enable a workflow supported by Tekton pipelines. With OpenShift Pipelines, you can start building a complete end-to-end CI/CD pipeline that can be used to build, push, and deploy your AI/ML workload for production use.
You can enable OpenShift Pipelines as part of your Open Data Hub deployment by adding the following to your KfDef resource:
- kustomizeConfig:
parameters:
- name: namespace
value: openshift-operators
repoRef:
name: manifests
path: openshift-pipelines/cluster
name: openshift-pipelines
To learn more about OpenShift Pipelines, review the documentation on Understanding OpenShift Pipelines.
Upcoming Open Data Hub releases
For the next Open Data Hub minor release, the community is working on many interesting and exciting new functionalities and tools. The team plans to add JupyterHub enhancements such as the ability to create and add custom notebook images. Multitenancy support for Kubeflow and integration with authentication tools are also on the roadmap, along with integrating Kubeflow with Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh and Red Hat OpenShift Serverless. The community is also working on expanding the Open Data Hub community guidelines—for example, adding guidelines for proposing new components and features to the Open Data Hub project.
For the latest information on the Open Data Hub project, please visit opendatahub.io and join our community bi-weekly meetings.
Last updated: June 14, 2023