Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 is now available. For the improvements in this release, we focused on performance and configuration, plus updating CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 to use newer versions of the most popular runtimes and stacks. We also added the ability to allocate only the CPU that you need for IDE plugins, and we introduced a new diagnostic feature that lets you start up a workspace in debug mode.
CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 is available on OpenShift 3.11 and OpenShift 4.3 and higher, including tech-preview support for OpenShift 4.5.
Note: Based on Eclipse Che, CodeReady Workspaces is a Red Hat OpenShift-native developer environment that supports cloud-native development.
Faster workspace loading
Every time you start a workspace, the underlying cluster fetches and deploys all of the remote images that comprise that workspace. This activity can result in a longer wait time before the workspace is available.
In CodeReady Workspaces 2.2, we've added a new, optional Operator that reduces the time required to start your workspace. The Image Puller Operator pre-pulls the remote images designated for your workspace, which results in shorter wait times. All you need to do is install the Image Puller Operator on the same cluster where you are running CodeReady Workspaces. Figure 1 shows the new Operator in the OperatorHub.

Figure 2 shows the installation page with instructions for installing the Image Puller Operator.

Support for multiple devfile registries
It is now possible to configure CodeReady Workspaces with multiple devfile registries. Using this feature, organizations can provide multiple sources of their curated devfiles for developer workspaces. Figure 3 shows a devfile registry configured in the CodeReady Workspaces cluster.

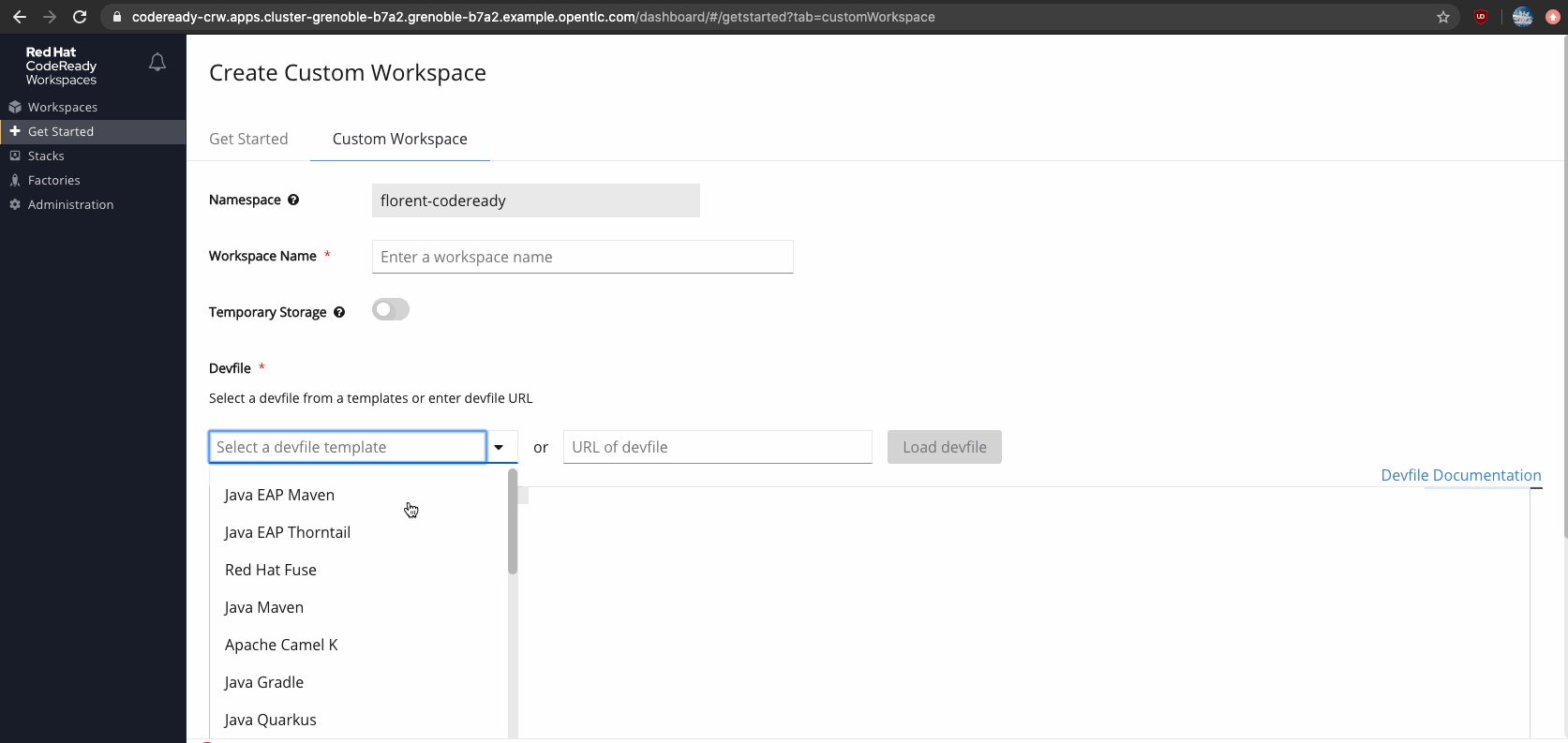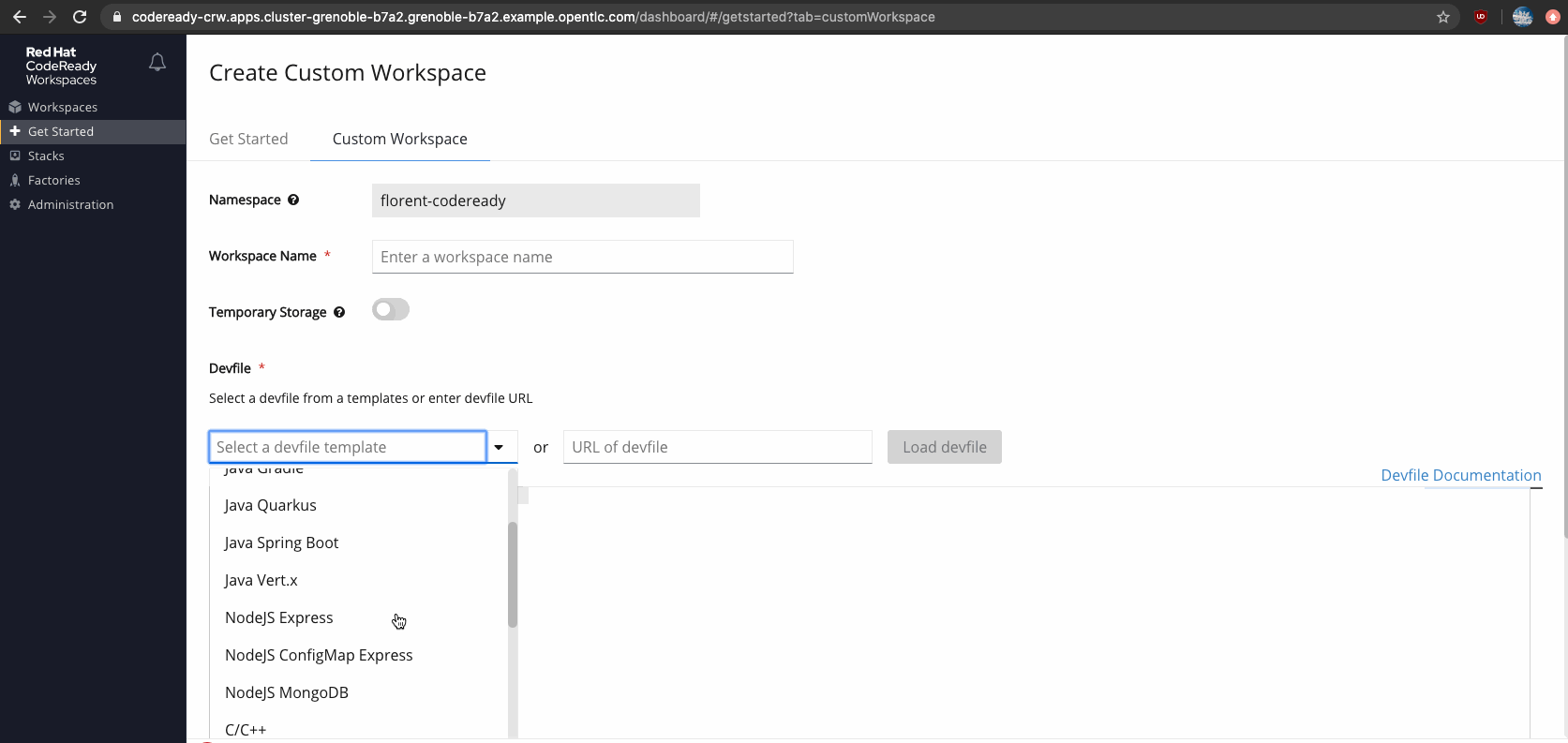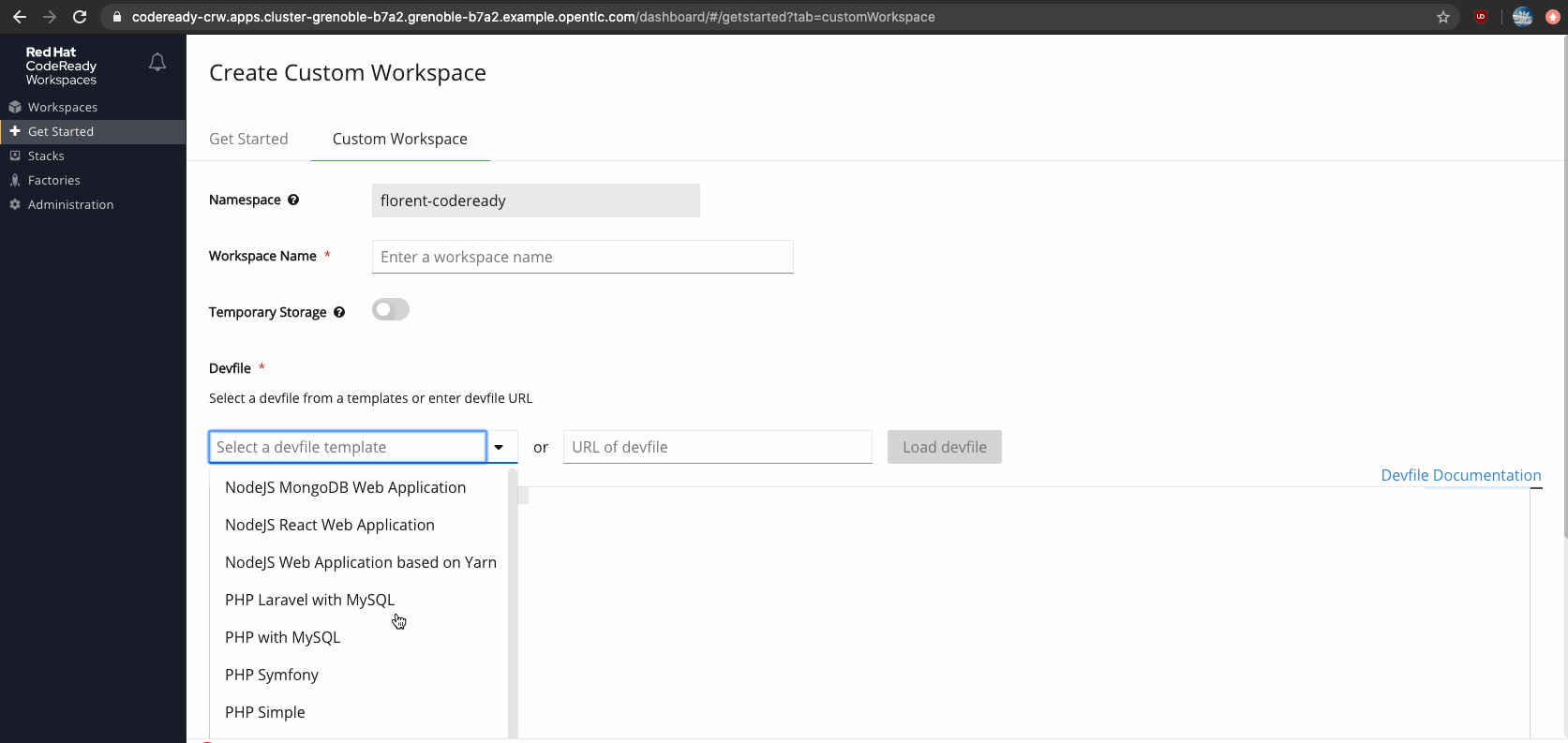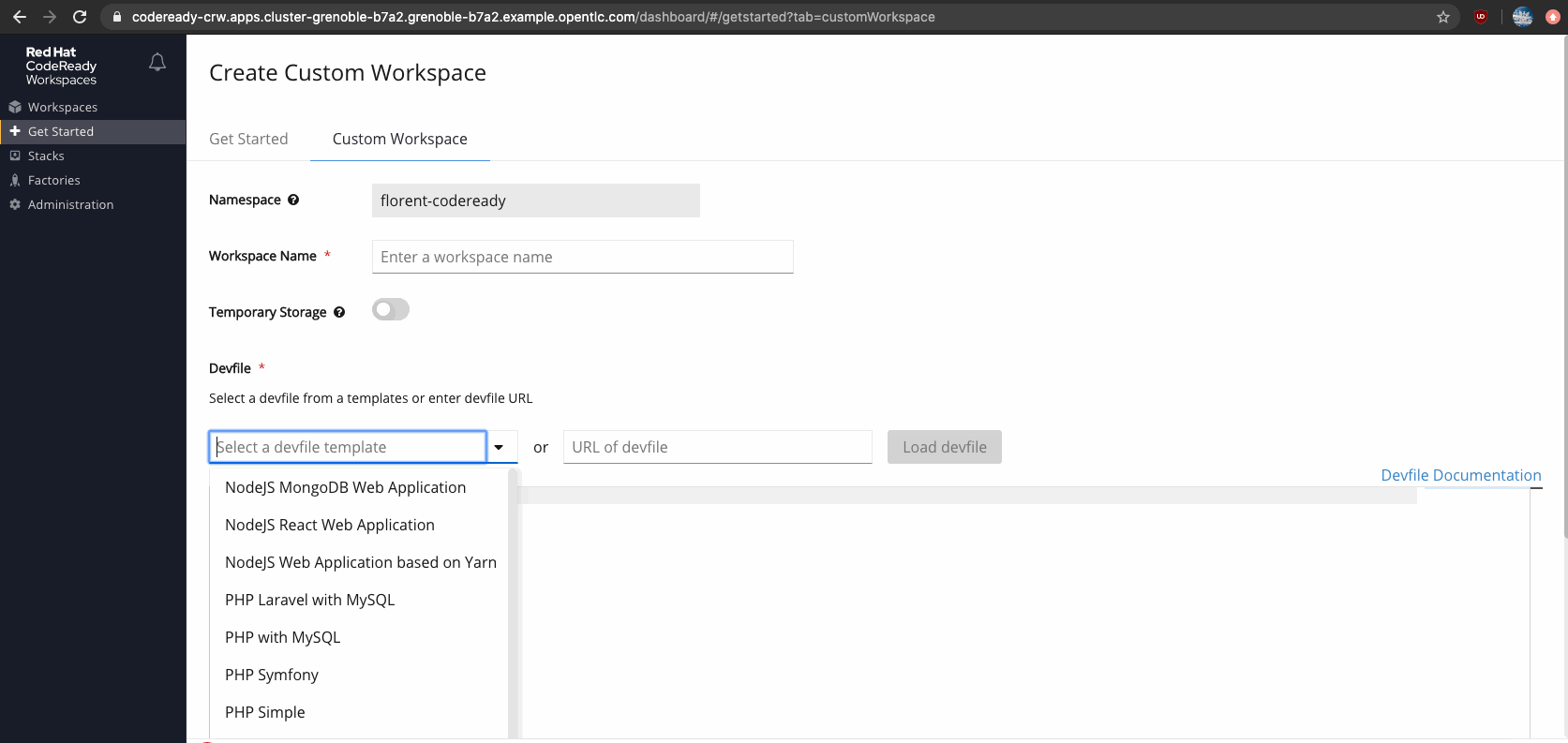
Figure 4 shows a listing of devfiles available for creating a custom workspace in CodeReady Workspaces.
Deprecated selfSignedCert setting in CR definition
CodeReady Workspaces now automatically detects if the router certificate is self-signed or not. If the certificate is found to be self-signed, it is propagated to the CodeReady Workspaces server and its components. As a result, the selfSignedCert setting in the CR for CodeReady Workspaces instance is now ignored and does not need to be specified.
Updates to core runtimes and stacks
We also updated the set of devfiles that are provided with CodeReady Workspaces to more recent versions. CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 features updates to the following runtime images and stacks:
- Maven 3.6: This update includes improvements to memory and CPU consumption.
- MongoDB 3.6: This update includes enhancements related to security and stability.
- Code samples: We updated various code samples to fix issues related to usage.
Set CPU limits on IDE plugins
CodeReady Workspaces now lets you assign CPU limits to your IDE plugins with cpuLimit and cpuRequest. Similar to the existing capability that allows developers to allocate memory limits, this feature lets you declare system limits for plugins. Setting CPU limits can prevent the workspace pod from getting overloaded. Figure 5 shows a devfile with the new option to set CPU limits for IDE plugins.

Run your workspace in debug mode
CodeReady Workspaces now allows you to run your workspace in debug mode, which means that you can view the logs while the workspace is starting up. Having access to the logs helps with troubleshooting issues encountered during startup. Figure 6 shows the new option to start a workspace in debug mode.
Get CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 today!
CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 is available now on OpenShift 3.11 and OpenShift 4.3 and higher:
- If you are using OpenShift 3.11, follow the OpenShift 3.11 installation instructions to install CodeReady Workspaces 2.2.
- If you are using OpenShift 4.3 or higher, you can install CodeReady Workspaces 2.2 directly from the OpenShift OperatorHub. Follow the OpenShift 4.3 documentation for this procedure.
Additional resources
For developers new to CodeReady Workspaces, we recommend these additional resources:
- Download the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces command-line interface (CLI)
- Visit the Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces product page.
- Visit the Getting Started with Red Hat CodeReady Workspaces page.
