This article is about my experience installing Red Hat Data Grid (RHDG) on Red Hat CodeReady Containers (CRC) so that I could set up a local environment to develop and test a Quarkus Infinispan client. I started by installing CodeReady Containers and then installed Red Hat Data Grid. I am also on a learning path for Quarkus, so my last step was to integrate the Quarkus Infinispan client into my new development environment.
Initially, I tried connecting the Quarkus client to my locally running instance of Data Grid. Later, I decided I wanted to create an environment where I could test and debug Data Grid on Red Hat OpenShift 4. I tried installing Data Grid on OpenShift 4 in a shared environment, but maintaining that environment was challenging. Through trial-and-error, I found that it was better to install Red Hat Data Grid on CodeReady Containers and use that for my local development and testing environment.
In this quick tutorial, I guide you through setting up a local environment to develop and test a Quarkus client—in this case, Quarkus Infinispan. The process consists of three steps:
- Install and run CodeReady Containers.
- Install Data Grid on CodeReady Containers.
- Integrate the Quarkus Infinispan client into the new development environment.
Step 1: Install and run CodeReady Containers
To start, download the current version of CodeReady Containers. If you need installation instructions, see this guide from the CodeReady Containers development team.
After I installed CodeReady Containers, I ran the following command to set it up and start it in the same sequence:
# crc setup # crc start
Starting your CRC installation automatically starts OpenShift. You can check the logs at https://api.crc.testing:6443 to confirm that OpenShift is running. In the logs, you will also see the following login details:
[INFO]"To access the cluster, first set up your environment by following 'crc oc-env' instructions" [INFO]"Then you can access it by running 'oc login -u developer -p developer https://api.crc.testing:6443'" [INFO]"To login as an admin, run 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p 8rynV-SeYLc-h8Ij7-YPYcz https://api.crc.testing:6443'"
That's it for the first step.
Step 2: Install Red Hat Data Grid on CodeReady Containers
Next, you want to install the Data Grid Operator on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (OCP). You can use either the command-line interface (CLI) or the OCP user interface (UI). I chose to use the UI for my installation. Here are the installation steps:
- Log in to the OCP console, as shown in Figure 1.
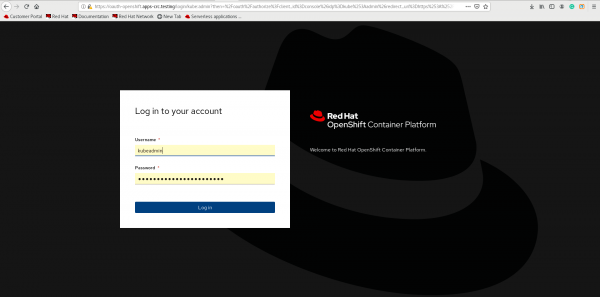
Figure 1. Log in to the OpenShift Container Platform console. - Create a project to install the Data Grid Operator, as shown in Figure 2.
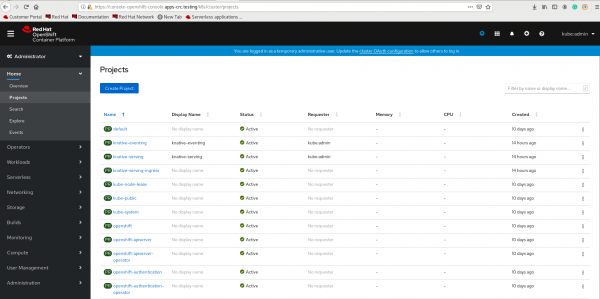
Figure 2. Create a project to install the Data Grid Operator. - Create an instance of the Data Grid Operator. Doing this also creates the Data Grid pod, as shown in Figure 3.
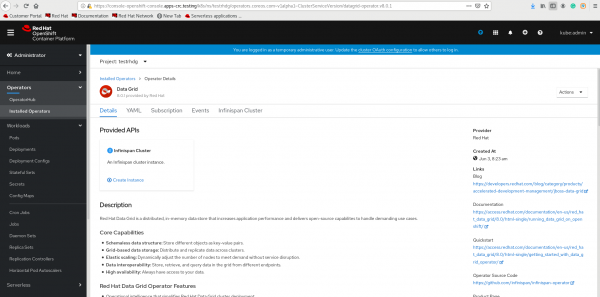
Figure 3. Create an instance of the Data Grid Operator - Check the running pods on OCP:
$ oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE example-infinispan-0 1/1 Running 0 6d4h infinispan-operator-77cd666d7d-xjqcj 1/1 Running 0 6d4h
Gather information for your next installation
After you confirm that Data Grid is installed, take note of the service IP for the Data Grid service. You will need this information when you install the Quarkus Infinispan client.
$ oc get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE example-infinispan ClusterIP 172.30.51.239 <none> 11222/TCP 6d4h
Next, check the user ID for Data Grid and the clustered-openshift.xml:
$ oc rsh example-infinispan-0 sh-4.4$ cat /opt/infinispan/server/conf/users.properties #$REALM_NAME=default$ #Tue Jun 09 03:58:58 GMT 2020 developer=RSRKP8snxVdCbQP3 operator=brw2JVxLQw1gsF4M
Finally, check the configuration files details for your sasl-mechanism:
$ oc rsh example-infinispan-0 sh-4.4$ cat /opt/infinispan/server/conf/infinispan.xml
Figure 4 shows the correct output:

Install and run the Quarkus Infinispan client
Finally, you can install and run the Quarkus Infinispan client.
- Download the client from Quarkus.io, as shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. Download the Quarkus Infinispan client from Quarkus.io. - Once you have Quarkus Infinispan, extract the client code. Test the code against your local Data Grid instance to ensure that it is working.
- Assuming the code works, add the following values to the Infinispan client's
application.propertiesfile (see thepod/servicedirectory for these values):
# The IP should be CLUSTER-IP shown by oc get svc for RHDG deployment Quarkus.infinispan-client.server-list=172.30.51.239:11222 #The following would be the authentication details for the RHDG installed Quarkus.infinispan-client.auth-username=developer Quarkus.infinispan-client.auth-password=RSRKP8snxVdCbQP3 Quarkus.infinispan-client.use-auth=true Quarkus.infinispan-client.sasl-mechanism=DIGEST-MD5 #you can choose the sasl machenism and set it here Quarkus.kubernetes-client.trust-certs=true Quarkus.infinispan-client.client-intelligence=BASIC #The following properties are required to push the build to OCP Quarkus.openshift.expose=true Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment-target=openshift Quarkus.s2i.base-jvm-image=registry.access.redhat.com/openjdk/openjdk-11-rhel7
- After you have updated the
application.propertiesfile, run this command at the project's base directory:
./mvnw clean package -DQuarkus.kubernetes.deploy=true
The application will be deployed to CodeReady Containers, and you should see the following logs:
[INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Deploying to openshift server: https://api.crc.testing:6443/ in namespace: testrhdg. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: ServiceAccount infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: Service infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: ImageStream infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: ImageStream openjdk-11-rhel7. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: BuildConfig infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: DeploymentConfig infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.kubernetes.deployment.KubernetesDeployer] Applied: Route infinispan-client-quickstart. [INFO] [io.Quarkus.deployment.QuarkusAugmentor] Quarkus augmentation completed in 120321ms [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 02:06 min [INFO] Finished at: 2020-06-10T07:04:53+05:30 [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Check your installation
You can run additional checks to ensure that the Infinispan client is running in your development environment. First, check the new pods that were created with the Quarkus Infinispan build:
$ oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE example-infinispan-0 1/1 Running 0 6d22h infinispan-client-quickstart-1-build 0/1 Completed 0 2m50s infinispan-client-quickstart-1-deploy 0/1 Completed 0 72s infinispan-client-quickstart-1-hlwg6 1/1 Running 0 66s infinispan-operator-77cd666d7d-xjqcj 1/1 Running 0 6d22h
Second, check the route for the newly deployed service and access it:
$ oc get routes NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD infinispan-client-quickstart infinispan-client-quickstart-testrhdg.apps-crc.testing / infinispan-client-quickstart 8081 None
Now you can access the client in any web browser at http://infinispan-client-quickstart-testrhdg.apps-crc.testing/infinispan, or on the command line, and play with it. As an example, you could add more interfaces to the client code, which would allow you to perform different operations with Red Hat Data Grid.
Conclusion
In this article, I showed you what I did to create a client for Infinispan with the help of Quarkus. I also showed you how to run the client on OpenShift 4.x for an installed Red Hat Data Grid 8.0 instance. There might be a more sophisticated way to implement the same solution or find values from the OpenShift cluster. I hope sharing my experience will be helpful to others.
Download the source code for these examples from my Infinispan Client Quickstart on GitHub.
Last updated: June 25, 2020