This article is a continuation of Migrating Java applications to Quarkus: Lessons learned, and here, I’ll make a comparison of performance metrics for building and running a Java app before and after Quarkus. My goal here is to demonstrate how awesome Quarkus is and maybe help you decide to use Quarkus to build your cool microservices.
To make the comparison, I’ll use the same application that was used in the previous article using Thorntail and Quarkus binaries. The comparison will be made based on the following metrics:
- Time to build the whole project
- UberJar size
- Time spent to start the application for the first time
- Average of memory usage
- Average of CPU usage
- Loaded classes and active threads
The application will be tested in three different environments, which are:
- My local dev environment
- Lenovo t460s
- Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6600U
- RAM 20G
- SSD HD
- Lenovo t460s
- Rpi 3 B+, specs
- Red Hat OpenShift v3.11
The set of tests demonstrated here were all done on my local dev environment. To begin, let's build both versions and compare the time spent on the build process:
Quarkus:
spolti@t460s:~$ mvn clean package ... [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 01:01 min
Thorntail:
spolti@t460s:~$ mvn clean package ... [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] BUILD SUCCESS [INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------ [INFO] Total time: 01:20 min
The build times show Quarkus being 19 seconds faster than Thorntail, but the build time itself is not too important. Next, after both versions are built, let’s see its size:
spolti@t460s:~$ du -sh * 201M rebot-telegram-bot-0.4-SNAPSHOT-thorntail.jar 38M rebot-telegram-bot-1.0-SNAPSHOT-runner.jar
Here we have a big difference, Thorntail produces an uber jar five times bigger than Quarkus.
The next comparison shows the time spent to start the app the first time; usually, it takes longer to compare it. The app will be stopped after all plugins are started, tested on my local dev environment and on RPI:
Quarkus:
spolti@t460s:~$ time java -jar <omitted parameters> rebot-telegram-bot-1.0-SNAPSHOT-runner.jar <Startup logs> real 0m10.633s user 0m15.888s sys 0m0.621s pi@raspberrypi:~ $ time java -jar <omitted parameters> rebot-telegram-bot-1.0-SNAPSHOT-runner.jar <Startup logs> real 0m21.309s user 0m24.968s sys 0m1.050s
Thorntail:
spolti@t460s:~$ time java -jar <omitted parameters> rebot-telegram-bot-0.4-SNAPSHOT-thorntail.jar <Startup logs> real 0m38.926s user 1m24.489s sys 0m3.008s pi@raspberrypi:~ $ time java -jar <omitted parameters> rebot-telegram-bot-0.4-SNAPSHOT-thorntail.jar <Startup logs> real 2m38.637s user 2m51.688s sys< 0m6.444s
This, in my opinion, is one of the most important metrics, and one that helped me decide to try Quarkus. It shows an amazing 30 seconds faster than my previous version on my local environment and around 137 seconds faster on RPI. This app particularly takes a few seconds to start, because it has around 10 plugins that do some tasks during startup leading to delays. But, imagine that your microservice is composed with a few Rest endpoints; it could be started in less than 1 second.
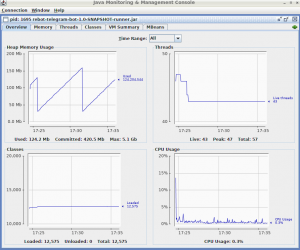
For now, let’s see how the Java memory behaves. The graphics below show information collected for 10 minutes:
Quarkus:
Thorntail:
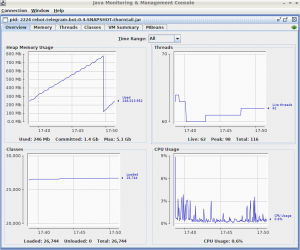
This comparison is very interesting, as we can see, Quarkus has the best numbers except for the threads. The difference is not too big, but the memory usage is a way larger than Thorntail, and the number of the loaded classes is a way bigger, less than the half. With that said, when targeting devices like RPI, Quarkus is a perfect fit because it consumes a very small portion of physical resources.
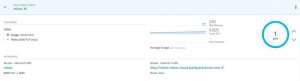
The next metrics were done using the container images created with Thorntail and Quarkus version running on Red Hat OpenShift:
Quarkus:
Thorntail:
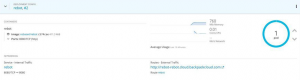
On OpenShift, we can also see a considerable difference in memory usage, but notice that this value can be decreased by fine-tuning the JVM memory configurations. For this example, such fine-tuning was not done.
Conclusion
My experience with migrating an old application running on Thorntail to Quarkus was very good, and so far, I've had only great results with the metrics. In my opinion, migration to Quarkus is a go; of course, there are dozens of different scenarios that I didn’t cover, but I believe that, in most scenarios, the migration can be done and great results can be achieved.
The following table compares all the results I found during my tests:
| Metric | Quarkus | Thorntail |
| build time | 01:01 min | 01:20 min |
| uber jar size | 38M | 201M |
| startup time (local dev env) | 0m10.633s | 0m38.926s |
| startup time (rpi) | 0m21.309s | 2m38.637s |
| Heap Memory | ~45M-~125M | ~240M-~790M |
| Threads | ~43 | ~62 |
| Loaded Classes | ~12.575 | ~26.744 |
| CPU Usage | ~0.3 | ~0.6 |
I hope this article is helpful and encourages you perhaps to try Quarkus in your next project or when migrating an existing one. For the next article, I will share more interesting stuff, which I had to do to make the application run well with a native image. So, stay tuned for the next installment.
Last updated: February 11, 2024