Agentic AI is best understood as a distributed system, and many of the same patterns that made microservices successful apply. This article explains how to design agentic workflows with composable components, explicit contracts and guardrails, resilience practices like timeouts and idempotency, and end-to-end observability. We will also discuss how the Red Hat AI portfolio supports production-ready agentic systems across the hybrid cloud, from efficient inference to consistent execution and lifecycle management at scale.
Agentic AI through a microservices lens
Microservices changed software engineering by forcing us to treat systems as distributed by default with small components, explicit contracts, independent scaling, and a serious focus on reliability and observability. Agentic AI is driving a similar shift. Instead of HTTP services calling other services, we now have agents coordinating models, tools, and enterprise data to complete multi-step tasks.
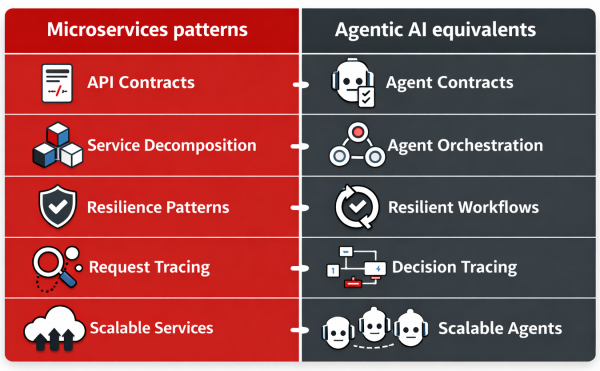
If you build cloud-native applications, this analogy is useful because it replaces hand-wavy intuition with a familiar engineering frame. Agentic AI is a distributed system. The same realities apply: latency, partial failure, versioning, security boundaries, and operational visibility. Once you accept that, building agentic systems becomes far more practical. Figure 1 illustrates a comparison of microservices patterns and Agentic AI equivalents.
From one big agent to composable workflows
Early agent implementations often become a single, do-everything agent. It retrieves context, decides what to do, calls tools, handles errors, and writes the final answer. That looks convenient, but it is the AI equivalent of a monolith. When something goes wrong, it is difficult to isolate the cause. When you want to improve one part (i.e., retrieval), you risk breaking everything.
A more scalable pattern is the same one microservices pushed us toward, decomposition. Break the workflow into smaller, purpose-built agents and orchestrate them as a pipeline. For example, you might have an agent that retrieves and ranks information, another that validates policy and safety constraints, and another that executes tool calls and formats results. You can test, update, and scale each component independently, so that failures become easier to contain.
Contracts are more important with agents
Microservices succeed when interfaces are explicit. Agents need that discipline even more, because ambiguity is where unpredictable behavior lives. Define what the agent accepts and produces, ideally with structured outputs you can validate (e.g., JSON schema). You must be equally explicit about tool contracts and allowlists. For instance, define what tools can be called, with what parameters, and what data can be accessed. This is how you prevent prompt drift from turning into system drift, and it is how you make agentic workflows governable across teams.
A strong contract mindset also improves portability. When your tools and agent steps have stable interfaces, you can swap models, change retrieval methods, or add new workflow steps without rewriting the whole system.
Reliability patterns carry over
Microservices taught us to assume failure. Networks drop, dependencies degrade, and tail latency ruins user experience. Agentic systems have the same issues plus a few new ones, such as tool calls failing, retrieval returning irrelevant context, and inference latency spikes. The lesson from microservices still holds. It is the same operational playbook: timeouts, retries with backoff, circuit breakers to avoid cascading failures, and fallback behaviors that let a workflow degrade gracefully. For tool calls, it also helps to design for idempotency so retries do not create duplicate actions.
This is where agentic design becomes an engineering discipline. You define failure semantics, set performance expectations, and decide what the system should do under degradation. In other words, you are making explicit tradeoffs about latency, cost, and correctness when a dependency is slow or unavailable.
Observability: Tracing decisions
In microservices, we trace requests through services. In agentic systems, we also need to trace decisions through workflow steps. When a result is wrong, you want to know whether the failure came from retrieval, a tool invocation, or the model’s reasoning. That means capturing step-level traces, tool-call inputs and outputs, and inference performance metrics; then correlating them end-to-end through a single trace that spans the workflow.
Without observability, agentic AI remains stuck in the prototype stage. With it, teams can tune quality, reduce cost, and improve reliability with the same confidence they bring to cloud-native operations.
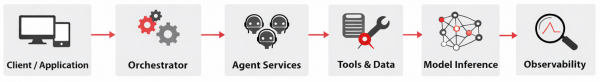
Figure 2 shows a simple reference architecture for an agentic workflow, tracing a request from the client through an orchestrator and agent services, into tools and data, then model inference, and finally end-to-end observability.
How Red Hat AI fits in this microservices-inspired model
Agentic AI becomes real when it is supported by a consistent platform layer across hybrid cloud, one that delivers efficient inference, consistent runtimes, and lifecycle management at scale. Together, the following Red Hat services map cleanly to the microservices mindset, including inference as a service, consistent runtimes where you need them, and a platform to build and operate AI workflows reliably across environments.
- Red Hat AI Inference Server provides the inference layer by turning model execution into a managed, high-throughput service. Powered by vLLM, it helps maximize accelerator utilization and reduce latency so agentic workflows can make frequent model calls without cost or performance surprises. It also provides access to validated, optimized third-party models, helping teams standardize their deployments across environments.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI provides a purpose-built, single-server platform for AI inference workloads, such as LLMs, when tighter control and repeatable operations matter. It combines a bootable Red Hat Enterprise Linux image with popular AI libraries and hardware-optimized inference, and it includes Red Hat AI Inference Server so teams can start serving models quickly with a consistent, supported stack.
- Red Hat OpenShift AI provides an operationally consistent platform to build, train, fine-tune, serve, and monitor predictive and generative AI models at scale across hybrid cloud environments, including private and sovereign deployments. It includes capabilities for model monitoring and drift detection, and it supports distributed serving through an optimized vLLM framework while standardizing access to models and tools for agentic workflows.
This mindset shift unlocks production
Agentic AI is not a replacement for engineering discipline. It demands more of it. Agentic AI is a distributed system with probabilistic components, and that raises the bar for architecture and operations. In practice, you must engineer agents like microservices by breaking workflows into composable components, enforcing clear contracts and guardrails, designing for failure with timeouts and fallbacks, and instrumenting everything so behavior is observable and auditable.
