This article is the latest in my series on middleware deployments, where I cover installation, customization, and the full range of capabilities in the current implementation. In this post, I will cover the Red Hat JBoss Web Server (JWS) container image and the Red Hat JBoss Web Server Operator.
JWS container
To effectively customize your deployment, you first need to understand how the JWS container manages initialization and default settings.
Default container settings
The JWS container starts from the opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/launch.sh script, which is called from the JWS 6 container file.
Here is the call flow:
opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/launch.sh -> opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh
opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/launch/catalincat a.shThis script calls another script, which then calls opt/jboss/container/java/jvm/java-default-options.
Although JWS is not fully supported on Podman, you can use it to display the default environment variables:
podman run --cpus=2 --memory-reservation=1000m --memory=1000m --memory-swap=1000m -e --rm -it registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-6/jws60-openjdk17-openshift-rhel8:6.0.5-3.1739758388
-Xms125m
-Xmx500m
-XX:+UseParallelGC
-XX:MinHeapFreeRatio=10
-XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=20
-XX:GCTimeRatio=4
-XX:AdaptiveSizePolicyWeight=90
-XX:ParallelGCThreads=2
-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism=2
-XX:CICompilerCount=2
-XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError
...
INFO Running jboss-webserver-6/jws60-openjdk17-rhel8-openshift image, version 6.0.5
Using CATALINA_BASE: /opt/jws-6.0/tomcat
Using CATALINA_HOME: /opt/jws-6.0/tomcat
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/temp
Using JRE_HOME: /usr/lib/jvm/java-17
Using CLASSPATH: /opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar:/opt/jws-6.0/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
Using CATALINA_OPTS: -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -javaagent:/usr/share/java/prometheus-jmx-exporter/jmx_prometheus_javaagent.jar=9404:/opt/jboss/container/prometheus/etc/jws-jmx-exporter-config.yaml -Xms125m -Xmx500m -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:MinHeapFreeRatio=10 -XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=20 -XX:GCTimeRatio=4 -XX:AdaptiveSizePolicyWeight=90 -XX:ParallelGCThreads=2 -Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism=2 -XX:CICompilerCount=2 -XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError The default JVM variables come from the opt/jboss/container/java/jvm/java-default-options file. This file includes several default JVM options, which act as the following arguments (Table 1).
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-Xmx500m, -Xms125m | Calculates max and min heap as a percentage of the container:
|
-XX:+UseParallelGC | Sets the garbage collector (GC) to ParallelGC. |
-XX:MinHeapFreeRatio=10 | Sets the minimum heap free ratio (default is 10). |
-XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=20 | Sets the maximum heap free ratio (default is 20). |
-XX:GCTimeRatio=4 | Sets the GC time ratio (default is 4). |
-XX:AdaptiveSizePolicyWeight=90 | Sets the adaptive size policy weight (default is 90). |
-XX:ParallelGCThreads | Sets the number of parallel GC threads (default is 2). Unless directly specified, a formula determines its value. |
java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism | Sets the parallelism of the common ForkJoinPool (default is 2). Increasing this value allows for more concurrent threads to process tasks with higher throughput. |
-XX:CICompilerCount=2 | Sets the number of threads used by the compilation process (default is 2). |
-XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError | Exits on OutOfMemory error. The heap dump generation and the exit are separated. |
To demonstrate that this image is container-aware, notice that a GC task thread is created for each CPU available to the container. For example, a JWS container with 1 CPU shows one thread:
podman run --cpus=1 --memory-reservation=700m --memory=500m --memory-swap=1000m --rm -it registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-5/jws58-openjdk8-openshift-rhel8:5.8.2-TAG:"GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f254c05b000 nid=0x164 runnable <--JWS container with 2 CPUs:
podman run --cpus=2 --memory-reservation=700m --memory=500m --memory-swap=1000m --rm -it registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-5/jws58-openjdk8-openshift-rhel8:5.8.2-TAG:"GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f254c05b000 nid=0x164 runnable <--
"GC task thread#1 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f254c05d000 nid=0x165 runnable <--Custom environment variables
You can use the following environment variables for customization.
CATALINA_OPTS:# CATALINA_OPTS (Optional) Java runtime options used when the "start", # "run" or "debug" command is executed. # Include here and not in JAVA_OPTS all options, that should # only be used by Tomcat itself, not by the stop process, # the version command etc. # Examples are heap size, GC logging, JMX ports etc.CATALINA_OPTS_APPEND: The flag is appended on the deployment.GC_CONTAINER_OPTIONS:podman run --cpus=2 --memory-reservation=1000m --memory=1000m --memory-swap=1000m -e GC_CONTAINER_OPTIONS="-XX:+UseZGC" --rm -it registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-6/jws60-openjdk17-openshift-rhel8:6.0.5-3.1739758388JAVA_OPTS: You can use this variable as well.# JAVA_OPTS (Optional) Java runtime options used when any command # is executed. # Include here and not in CATALINA_OPTS all options, that # should be used by Tomcat and also by the stop process, # the version command etc. # Most options should go into CATALINA_OPTS.Therefore,
JAVA_OPTSdoes not work as a GC replacer:podman run --cpus=2 --memory-reservation=1000m --memory=1000m --memory-swap=1000m -e JAVA_OPTS="-XX:+UseZGC" --rm -it registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-6/jws60-openjdk17-openshift-rhel8:6.0.5-3.1739758388 ... Error occurred during initialization of VM Multiple garbage collectors selectedBased on tests and the scripts, the current JWS images do not use
JAVA_OPTS_APPEND, so this environment variable is ignored.
Customizing garbage collection and ParallelGC
The Parallel Garbage Collector (ParallelGC) is the default, but it is not suitable for all situations, despite generally decent performance:
- Random allocations: G1GC might be more adequate for these scenarios. Although G1GC often has a larger footprint, the difference might not be significant enough to justify using ParallelGC.
- Large heap sizes (5 Gi, 10 Gi+): Shenandoah, Generational Shenandoah (GenShen), or ZGC might be more suitable.
- ParallelGC might consume more memory on OpenJDK 17 and 21.
- ParallelGC might offer less flexibility regarding generation sizing, particularly when using the default configuration in a small container.
To replace the collector, use the GC_CONTAINER_OPTIONS argument in the deployment (for example, GC_CONTAINER_OPTIONS=-XX:+UseG1GC). This article does not discuss specific garbage collectors' behavior or performance, but demonstrates that customization is possible.
JWS Operator
The JWS Operator (also known as the WebServer Operator) allows you to create a WebServer Custom Resource (CR), which enables the deployment of the JWS image. The upstream project is available here and is implemented in Go, not Java.
To install it via OperatorHub, search for "JWS" in the Operator list (Figure 1). Searching for "JBoss" yields three results: JBoss EAP, Kogito Knative, and JWS.
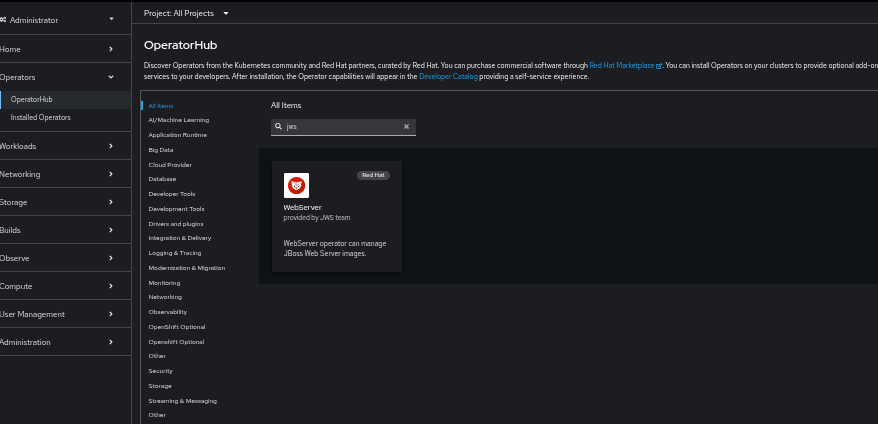
When you install the JWS Operator, three pods run:
### Pod:
$ oc get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jws-operator-controller-manager-f47c9bc58-t7n7b 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
jws-operator-insights-6fbcd7b68f-kdf28 1/1 Running 0 4m30s
insights-proxy-20b02fd04fded82dcd706406391af9ba-5f85f5d5d8pxqsd 1/1 Running 0 4m21s
###
### Subscription
###
$ oc get sub
NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL
jws-operator jws-operator redhat-operators alpha
###
### CSV
###
$ oc get csv
NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
jws-operator.v2.2.0 WebServer 2.2.0 jws-operator.v2.1.3 SucceededThe first pod, jws-operator-controller-manager, is the controller manager that handles the creation of a webserver CR. The controller manager is a Go process, not Java. JWS is the Java process deployed by the JWS Go process:
$ oc get csv
oc NAME DISPLAY VERSION REPLACES PHASE
jws-operator.v2.2.0 WebServer 2.2.0 jws-operator.v2.1.3 Succeeded
$ oc get subscription
NAME PACKAGE SOURCE CHANNEL
jws-operator jws-operator redhat-operators alpha
$ oc get webservers
No resources found in openshift-operators namespace.The new WebServer Custom Resource Definition (CRD) installed inside the cluster is:
$ oc get crd webservers.web.servers.org -o yaml
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
annotations:
controller-gen.kubebuilder.io/version: v0.18.0
operatorframework.io/installed-alongside-9800fd30566b18a1: openshift-operators/jws-operator.v2.2.0
labels:
olm.managed: "true"
operators.coreos.com/jws-operator.openshift-operators: ""
name: webservers.web.servers.org
spec:
conversion:
strategy: None
group: web.servers.org
names:
kind: WebServer
listKind: WebServerList
plural: webservers
singular: webserverUse the plural and singular for handling this feature.
Here is an example WebServer CR created from the CRD above:
apiVersion: web.servers.org/v1alpha1
kind: WebServer
metadata:
name: webserver-example
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
applicationName: webapp
replicas: 1
useInsightsClient: falseAfter you create the WebServer CR, a specific Deployment (named from the CR) is created to start the pod:
### Deployment
$ oc get webservers webserver-example-61 -o yaml
apiVersion: web.servers.org/v1alpha1
kind: WebServer
metadata:
name: webserver-example-61
namespace: openshift-jws-example
spec:
applicationName: webapp
replicas: 1
useInsightsClient: true <------------------- false
webImage:
applicationImage: registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-6/jws61-openjdk21-openshift-rhel8
status:
hosts:
- webapp.openshift-operators.example.openshiftapps.com
pods:
- name: webapp-id
podIP: 10.129.0.36
state: ACTIVE
replicas: 1
scalingdownPods: 0
selector: app.kubernetes.io/name=webserver-example-61
############################# After the webserver custom resource is created:
$ oc get webservers
NAME AGE
webserver-example 2s
############################# Deployment
$ oc get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
insights-proxy-20b02fd04fded82dcd706406391af9ba 1/1 1 1 71m
jws-operator-controller-manager 1/1 1 1 71m
jws-operator-insights 1/1 1 1 71m
webapp 1/1 1 1 50m <---- application
### oc get pod
$ oc get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
webapp-id 1/1 Running 0 45m <--- applicationAccess is simple because the route already exists:
$ oc get route
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
webapp webapp.openshift-operators.apps.example.openshiftapps.com webapp <all> None
$ curl http://webapp.openshift-operators.apps.example.openshiftapps.com/
Hello World!WebServer CR features
Table 2 summarizes each feature.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Replicas | Sets the number of the replicas |
| Enable session clustering in Tomcat | Enables session clustering (not supported in JWS) |
| Enable Red Hat Insights for Red Hat OpenShift | Enables Insights for Red Hat OpenShift data export |
| Web image | Sets the application image (first method) |
| Web image stream | Sets the application image (second method) |
| TLS configuration | Sets the TLS configuration |
| Environment variables | Sets environment variables |
| Persistent logs | Persists the Catalina logs |
| Pod resources | Sets pod resource limits and requests |
| Security context | Sets up Security Context |
| Volume specifications | Configures volume settings |
Red Hat Insights for Red Hat OpenShift
JWS lets you export Insights for Red Hat OpenShift data, which is a feature enabled via a toggle on the WebServer CR. This enables the Insights for Red Hat OpenShift client, but works only with JWS 6.1+ images:
$ oc get webservers webserver-example-61 -o yaml
apiVersion: web.servers.org/v1alpha1
kind: WebServer
metadata:
name: webserver-example-61
namespace: openshift-jws-example
spec:
applicationName: webapp
replicas: 1
useInsightsClient: true <------------------- true
webImage:
applicationImage: registry.redhat.io/jboss-webserver-6/jws61-openjdk21-openshift-rhel8
status:
hosts:
- webapp.openshift-operators.example.openshiftapps.com
pods:
- name: webapp-id
podIP: 10.129.0.36
state: ACTIVE
replicas: 1
scalingdownPods: 0
selector: app.kubernetes.io/name=webserver-example-61This enables the following in the JWS deployment:
INFO Running jboss-webserver-6/jws61-openjdk21-rhel8-openshift image, version 6.1.2
Picked up JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS: -javaagent:/opt/runtimes-agent.jar=name=webapp;is_ocp=true;token=dummy;debug=false;base_url=http://insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local:8080
2025-10-21 17:09:34:551 +0000 [main] INFO com.redhat.insights.agent.AgentMain - Starting Red Hat Insights agentYou must create the insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local service so the information can be accessed.
2025-10-22 01:16:44:223 +0000 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.redhat.insights.agent.shaded.org.apache.http.client.protocol.RequestAddCookies - CookieSpec selected: default
2025-10-22 01:16:44:235 +0000 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.redhat.insights.agent.shaded.org.apache.http.client.protocol.RequestAuthCache - Auth cache not set in the context
2025-10-22 01:16:44:237 +0000 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.redhat.insights.agent.shaded.org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager - Connection request: [route: {}->http://insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local:8080][total available: 0; route allocated: 0 of 2; total allocated: 0 of 20]
2025-10-22 01:16:44:248 +0000 [pool-1-thread-1] DEBUG com.redhat.insights.agent.shaded.org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager - Connection leased: [id: 0][route: {}->http://insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local:8080][total available: 0; route allocated: 1 of 2; total allocated: 1 of 20]Configuring the proxy warrants its own article and is beyond the scope of this one. However, the setting is simple: you must ensure the OpenShift cluster has proxy access to Insight client to connect with the service or JWS application.
When you use this feature, a new insights pod is created. This enables insights analysis.
In case something is wrong - enable debug via the environment variable JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS:
value: ' -javaagent:/opt/runtimes-agent.jar=name=webapp;is_ocp=true;token=dummy;debug=true;base_url=http://insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local:8080'For example, if the service is not created, the result is:
java.net.UnknownHostException: insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local: Name or service not known
at java.base/java.net.Inet6AddressImpl.lookupAllHostAddr(Native Method)
at java.base/java.net.Inet6AddressImpl.lookupAllHostAddr(Inet6AddressImpl.java:52)
at java.base/java.net.InetAddress$PlatformResolver.lookupByName(InetAddress.java:1211)
at java.base/java.net.InetAddress.getAddressesFromNameService(InetAddress.java:1828)
at java.base/java.net.InetAddress$NameServiceAddresses.get(InetAddress.java:1139)
at java.base/java.net.InetAddress.getAllByName0(InetAddress.java:1818)
at java.base/java.net.InetAddress.getAllByName(InetAddress.java:1688)Troubleshooting
The image includes Java Diagnostics (jcmd) for tracking several aspects of the deployment:
$ oc get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
webapp-id 1/1 Running 0 45m
$ oc rsh webapp-id
sh-4.4$ jcmd
1 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start
sh-4.4$ jcmd 1 VM.info
...
...
h-4.4$ jcmd 1 VM.info
1:
#
# JRE version: OpenJDK Runtime Environment (Red_Hat-21.0.8.0.9-1) (21.0.8+9) (build 21.0.8+9-LTS)
# Java VM: OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (Red_Hat-21.0.8.0.9-1) (21.0.8+9-LTS, mixed mode, sharing, tiered, compressed oops, compressed class ptrs, parallel gc, linux-amd64)
--------------- S U M M A R Y ------------
Command Line: -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/jws-6.1/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.ClassLoaderLogManager -Djdk.tls.ephemeralDHKeySize=2048 -Djava.protocol.handler.pkgs=org.apache.catalina.webresources -Dsun.io.useCanonCaches=false -Dorg.apache.catalina.security.SecurityListener.UMASK=0027 --add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.lang.reflect=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.io=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.util=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.util.concurrent=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.rmi/sun.rmi.transport=ALL-UNNAMED -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -javaagent:/usr/share/java/prometheus-jmx-exporter/jmx_prometheus_javaagent.jar=9404:/opt/jboss/container/prometheus/etc/jws-jmx-exporter-config.yaml -XX:+UseParallelGC -XX:MinHeapFreeRatio=10 -XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=20 -XX:GCTimeRatio=4 -XX:AdaptiveSizePolicyWeight=90 -XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError -Dcatalina.base=/opt/jws-6.1/tomcat -Dcatalina.home=/opt/jws-6.1/tomcat -Djava.io.tmpdir=/opt/jws-6.1/tomcat/temp org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap start
///
Host: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8175M CPU @ 2.50GHz, 4 cores, 15G, Red Hat Enterprise Linux release 8.10 (Ootpa)
Time: Tue Oct 21 16:53:18 2025 UTC elapsed time: 2884.677738 seconds (0d 0h 48m 4s)
--------------- P R O C E S S ---------------
Heap address: 0x000000070d400000, size: 3884 MB <-------------------When the Insights for Red Hat OpenShift service is enabled, Java Diagnostics returns the agent details because they come from the JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS environment variable:
sh-4.4$ jcmd
Picked up JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS: -javaagent:/opt/runtimes-agent.jar=name=webapp;is_ocp=true;token=dummy;debug=false;base_url=http://insights-proxy.openshift-operators.svc.cluster.local:8080
2025-10-21 23:12:47:721 +0000 [main] INFO com.redhat.insights.agent.AgentMain - Starting Red Hat Insights agent <----------------------------------------------
2025-10-21 23:12:47:835 +0000 [pool-1-thread-1] WARN com.redhat.insights.agent.AgentMain - No JARs found in AgentSubreport
1 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap startConclusion
This brief article covered the JBoss Web Server (JWS) application deployment, which is supported in Red Hat OpenShift as a container image. (See the JWS Operator documentation for details.) I expanded on the subject with details and discussions that might be useful for other applications running in containers.
One thing I like very much about JWS deployment is its simplicity and the fact that you can enable logs using a single toggle button on the JWS WebServer CR console. This makes JWS versatile and useful, especially for deployments that are typically smaller than JBoss EAP deployments.
JWS supports data externalization through Insights for Red Hat OpenShift, which can then be utilized by services like Red Hat Lightspeed (formerly Red Hat Insights).
Additional resources
To learn more about Java container awareness, read How to use Java container awareness in OpenShift 4
For any other specific inquiries, open a case with Red Hat support. Our global team of experts can help you with any issues.
Special thanks to Leticia Konno and Alexander Barbosa for their outstanding contributions to this article via testing and discussions.
