Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed is the generative AI service for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform that helps your automation team build content more efficiently.
The Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant lets you bring your own AI service to power the inference engine that helps generate answers. These answers use enhanced context from retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) requests. This blog post shows you how to integrate a custom AI service to drive the inference process and get the most out of Ansible Lightspeed.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you must install Red Hat OpenShift AI and deploy the inference service.
Also ensure you have a valid Ansible Automation Platform license or subscription.
Create a secret chatbot configuration
- From the OpenShift homepage, go to Workloads→ Secrets.
- Select Create→ Key/Value secret and add 3 key/value pairs:
chatbot_model: The LLM model name that is configured on your LLM setup.chatbot_token: The API token or the API key (see Figure 1). This token is sent along with the authorization header when an inference API is called.chatbot_url: The inference API base URL on your LLM setup (for example,https://your_inference_api:8080/v1).
Note
Be sure to include the correct port number and /v1 at the end of your URL. To find the port number, go to Networking → Services and find the service with the same name as your chatbot_model. Look for the Service port mapping tab and add the TCP port to the end of your URL.
Install and set up the Ansible Automation Platform Operator
Follow these steps to install and configure the Ansible Automation Platform Operator:
From the OpenShift homepage, go to Operators → OperatorHub and search for Ansible Automation Platform (Figure 2).

Figure 2: The Ansible Automation Platform Operator. Click Install (Figure 3).
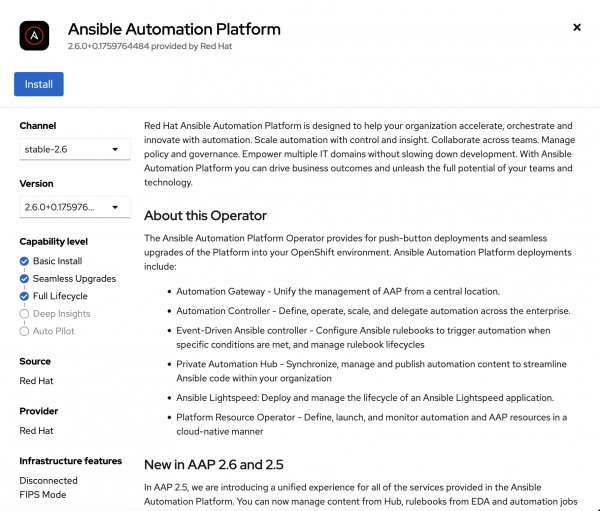
Figure 3: Install the Ansible Automation Platform Operator. Confirm that the Operator is installed. The status should be Succeeded (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Installed Operator. - Go to the installed Ansible Automation Platform Operator.
- Select the Ansible Automation Platform tab.
- Click Create AnsibleAutomationPlatform.
Select the YAML view option. Add the following YAML content with your application name, namespace, and secret chatbot configuration file name, then click Create.
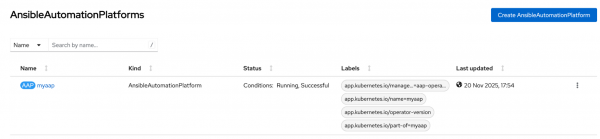
apiVersion: aap.ansible.com/v1alpha1 kind: AnsibleAutomationPlatform metadata: name: <Insert your name here> namespace: <Insert your namespace here> spec: controller: disabled: false eda: disabled: true hub: disabled: true lightspeed: chatbot_config_secret_name: <Insert your secret chatbot configuration file name> disabled: false no_log: false redis_mode: standalone route_tls_termination_mechanism: Edge- Scroll to the Ansible Automation Platform tab and then select the Ansible Automation Platform Operator you just created. Wait for the status to show Running, Successful (Figure 5).
Access the Ansible chatbot
Now that you have configured the chatbot for the Ansible Automation Platform instance, you can access the Ansible Automation Platform dashboard and start using it.
- From the OpenShift homepage, go to Workloads→ Secrets and click myaap-admin-password under your namespace.
- In the Data section, select Reveal values to get the admin password. Save this password.
- From the OpenShift homepage, go to Networking→ Routes.
Click the location for
myaap(https://myaap-chatbot-test.apps-crc.testing/), as shown in Figure 6.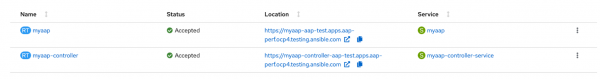
Figure 6: Getting the chatbot URL. Log in using the admin as the username and use the saved text as the password (Figure 7).

Figure 7: Ansible Automation Platform login page. Welcome to the Ansible Automation Platform dashboard. Click the chat icon in the top right corner. The chatbot will appear on the right side (Figure 8).
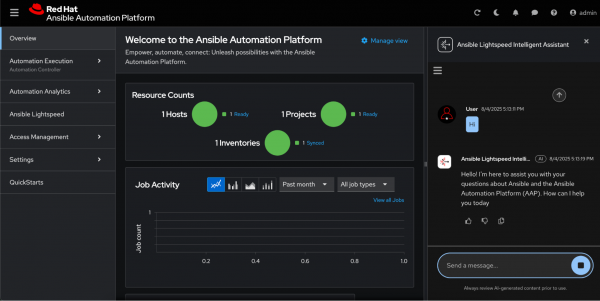
Figure 8: Initiating the Ansible Lightspeed chatbot. - Enter queries about Ansible to resolve your issues.
Summary
In this final article of the series, we deployed the Ansible Lightspeed chatbot with a custom inference service.
Review the previous blogs in this series:
- How to enable Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant
- Deploy an LLM inference service on OpenShift AI
Further resources:
