Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform 2.6 is now generally available (GA). This release continues our focus on making automation more accessible, transparent, and intelligent for technical teams.
Ansible Automation Platform 2.6 introduces powerful new features designed to streamline content creation, provide deeper insights into your automation's impact, and empower other teams to consume your work through self-service.
Key updates for automation developers include the now generally available self-service automation portal, Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant, and the on-premise automation dashboard for tracking key metrics. Ansible Automation Platform 2.6 also comes with a technology preview of Ansible development workspaces, offering a more consistent development environment for creating automation content.
Ansible self-service automation portal
A significant challenge in scaling automation is safely delegating its execution. While developers can write Ansible Playbooks to handle complex tasks like provisioning a development environment or deploying an application, running that automation has often required direct access to the Ansible Automation Platform controller or assistance from a dedicated automation team.
The self-service automation portal, now generally available, solves this problem by providing a simplified web interface for business users to launch pre-approved automation jobs. As an automation creator, you can now build a job template and, using role-based access control (RBAC), make it available to other teams. The portal includes step-by-step forms to guide users through automation requests—letting them input necessary parameters without needing to understand the underlying playbook logic.
This allows developers to empower teams like QA and support to run automation on demand. You write and control the automation, while they get a simple interface to execute it.
Ansible automation dashboard
As automation adoption grows, understanding its impact becomes critical. The Ansible automation dashboard is a new, on-premise component that lets you track and visualize key metrics like time savings, return on investment (ROI), and job success.
For developers, the dashboard offers a direct feedback loop on the automation you create. You can see which of your job templates are being used most frequently, monitor their performance over time, and identify patterns in job failures that may indicate a need for playbook improvements. This data can help you prioritize your work, demonstrate the value of your automation efforts to stakeholders, and make informed decisions about where to focus future development.
The Ansible automation dashboard is an on-premise utility deployed via containerized installation only.
Check out the following interactive demo.
Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant
The Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant is a new service integrated directly into the Ansible Automation Platform UI to help platform administrators install, configure, and maintain their automation environment. While automation developers focus on writing playbooks, this tool supports the operators who manage the platform itself.
Trained on trusted Red Hat data sources, the assistant provides guidance on common administrative tasks and helps troubleshoot issues. Platform operators use natural language prompts to ask questions, such as “How do I configure Event-Driven Ansible?” or “What is an execution environment?”, and the Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant uses large language models (LLMs) to generate a quick, accurate, and personalized response. (See Figure 1.) This service is installed using the Ansible Automation Platform operator on Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform, and requires a connected LLM hosted on Red Hat AI platforms.
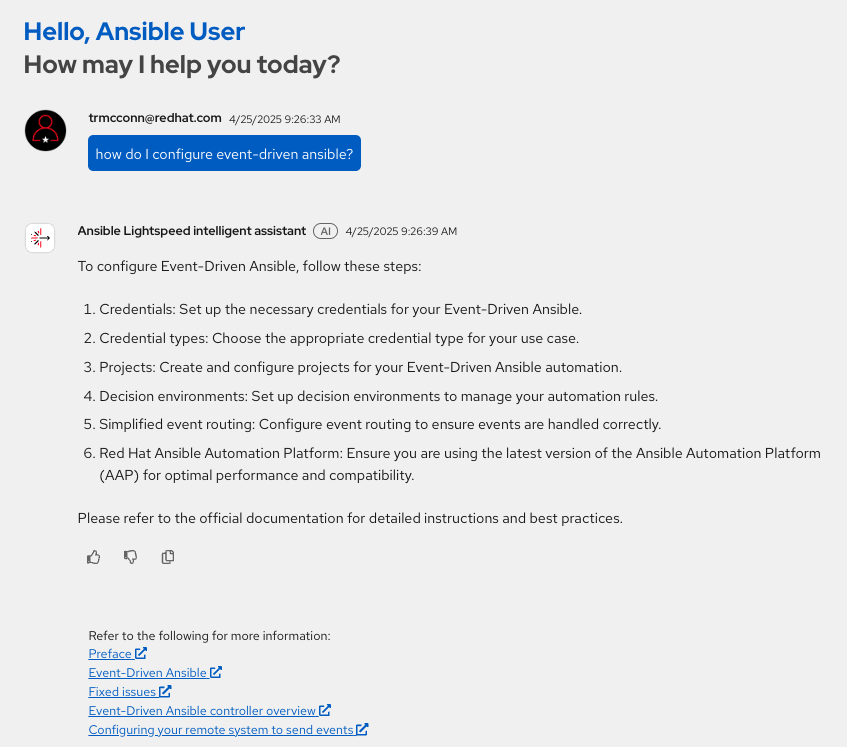
Test drive the Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant in the following demo.
Ansible development workspaces (Tech Preview)
The Ansible Automation Platform 2.6 release introduces a technology preview of Ansible development workspaces, a feature designed to solve the common challenge of inconsistent development environments. Built on Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces, Ansible development workspaces provide a standardized, browser-based development environment that can be provisioned with a single click.
For developers, this means you get an enterprise-ready environment that comes preloaded with everything you need to create, test, and deploy Ansible content. This includes a browser-based instance of Microsoft Visual Studio Code, Ansible development tools, Ansible Content Collections, Ansible Lightspeed, and other necessary dependencies. See Figure 2.
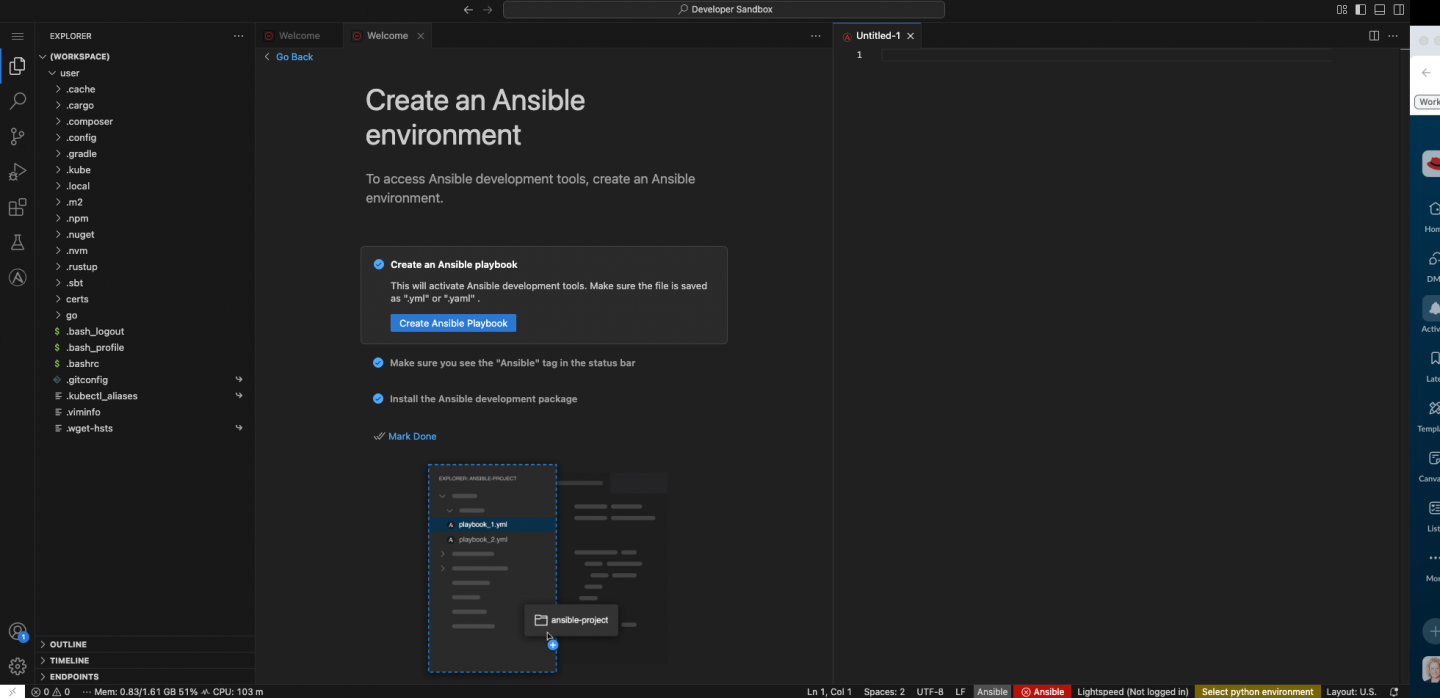
This approach ensures that all developers are working from the same baseline, which simplifies onboarding and provides centralized management and policy enforcement.
Get started today
Ansible Automation Platform 2.6 delivers powerful new tools to help developers and automation creators build, scale, and measure their automation more effectively. From empowering end-users with self-service to providing clear insights into your automation's performance, these features are designed to enhance your daily workflow.
You can download the latest version of the Ansible Automation Platform at no cost. Get started with the Ansible Automation Platform by exploring interactive labs.
To learn more about the full scope of this release, including bug fixes and other updates, see the official release notes.
For more information about Ansible Automation Platform, check out the product page.
