The release of OpenAI's gpt-oss models is a significant milestone for developers and enterprises looking to control their own AI journey. These open-weight models, available in 20B and 120B parameter variants, bring ChatGPT-level reasoning capabilities to your local machine under the Apache 2.0 license. But here’s the catch: How do you run these models securely, without compromising your system or spending hours configuring GPU drivers?
Enter RamaLama, a command-line tool that makes running AI models as simple as running containers. By leveraging OCI containers and intelligent GPU detection, RamaLama eliminates the complexity of AI infrastructure while providing strong isolation via containerization.
This post guides you through the steps to get gpt-oss running on your machine in minutes so you can quickly integrate it into your chat interface, RAG application, agentic workflow, and more.
Why use RamaLama for the gpt-oss models?
Before diving into the setup, let's address the elephant in the room: Why not just use Ollama or run the models directly?
The answer lies in RamaLama's unique approach to AI model management:
- Zero trust security: Models run in rootless containers with no network access by default
- Automatic GPU optimization: RamaLama detects your hardware and pulls the right container image
- Familiar container workflows: Use the same tools and patterns you already know
- Production-ready path: Easily transition from local development to Kubernetes deployment
Understanding the gpt-oss models
OpenAI's gpt-oss models come in two flavors, gpt-oss-20b and gpt-oss-120b.
| Model | Parameters | Active per token | Memory required | Use case |
| gpt-oss-20b | ~21 B | ~3.6 B | ~16 GB | General chat, coding assistance |
| gpt-oss-120b | ~117 B | ~5.1 B | ~80 GB (ex. NVIDIA H100) | Complex reasoning, advanced tasks |
Both models support a 128,000k token context length (although reduced context lengths between 8k–32k are recommended unless you have ≥ 80GB of VRAM or substantial unified memory on Apple silicon).
They use MXFP4 quantization, which enables memory-efficient deployment on consumer GPUs. Read Optimizing generative AI models with quantization to learn more about how quantization works.
Benchmarks show 20B ≈ o3-mini, and 120B ≈ o4-mini on tasks like reasoning, coding, and MMLU (learn more on the OpenAI blog).
Getting started with RamaLama
Let's get gpt-oss running on your machine with RamaLama.
Step 1: Install RamaLama
On macOS/Linux via the install script:
curl -fsSL https://ramalama.ai/install.sh | bashOr via PyPI:
pip install ramalamaOne line, and that's it. You can now use ramalama in the terminal to pull, run, and serve models from your system. Behind the scenes, RamaLama will automatically detect your container runtime, like Podman or Docker, when running and serving models.
Step 2: Pull and run gpt-oss-20b
Here's where RamaLama shines. With a single command, it will:
- Detect your GPU configuration.
- Pull the appropriate container image (CUDA, ROCm, or CPU).
- Download the model.
- Launch it in an isolated container.
Enter:
ramalama run gpt-oss:20bWith that single command, we’ve pulled and started an inference server for gpt-oss, right from our command line using RamaLama.
While you still need the appropriate GPU drivers installed, RamaLama removes the need to install CUDA, CUDA deep neural network (cuDNN), or other GPU dependencies in your environment—the container image includes those.
Note
RamaLama isn't limited to Ollama's registry; it's transport-agnostic. It supports Hugging Face (huggingface://), OCI (oci://), ModelScope, and Ollama (ollama://).
Security by default
When RamaLama runs your model, several security measures kick in automatically:
- Container runs with
--network=none(no internet access) - Model mounted read-only
- All Linux capabilities dropped (no attack access)
- Temporary data wiped on exit with
--rm
Why does this matter? Many models today are shared peer-to-peer or through community hubs, and their provenance isn’t always clear. Running such models directly on your host could expose you to data leaks or system tampering. By default, RamaLama’s container isolation ensures that—even if a model is malicious—it cannot exfiltrate data or modify your system outside its sandbox.
Maximizing your performance with RamaLama
RamaLama automatically detects your hardware and pulls the appropriate container image, but you can fine-tune performance based on your system's capabilities.
High-end systems (16 GB+ VRAM or 64 GB+ unified memory)
For NVIDIA RTX 4060 Ti or better, or Apple silicon with substantial memory:
ramalama serve gpt-oss:20bThis runs with full GPU acceleration and launches a REST API server with web UI at http://localhost:8080. RamaLama automatically uses all available GPU layers (--ngl 999) and the model's default context size.
Figure 1 shows the process of locally serving the gpt-oss model with RamaLama and interacting with it via a local web interface.
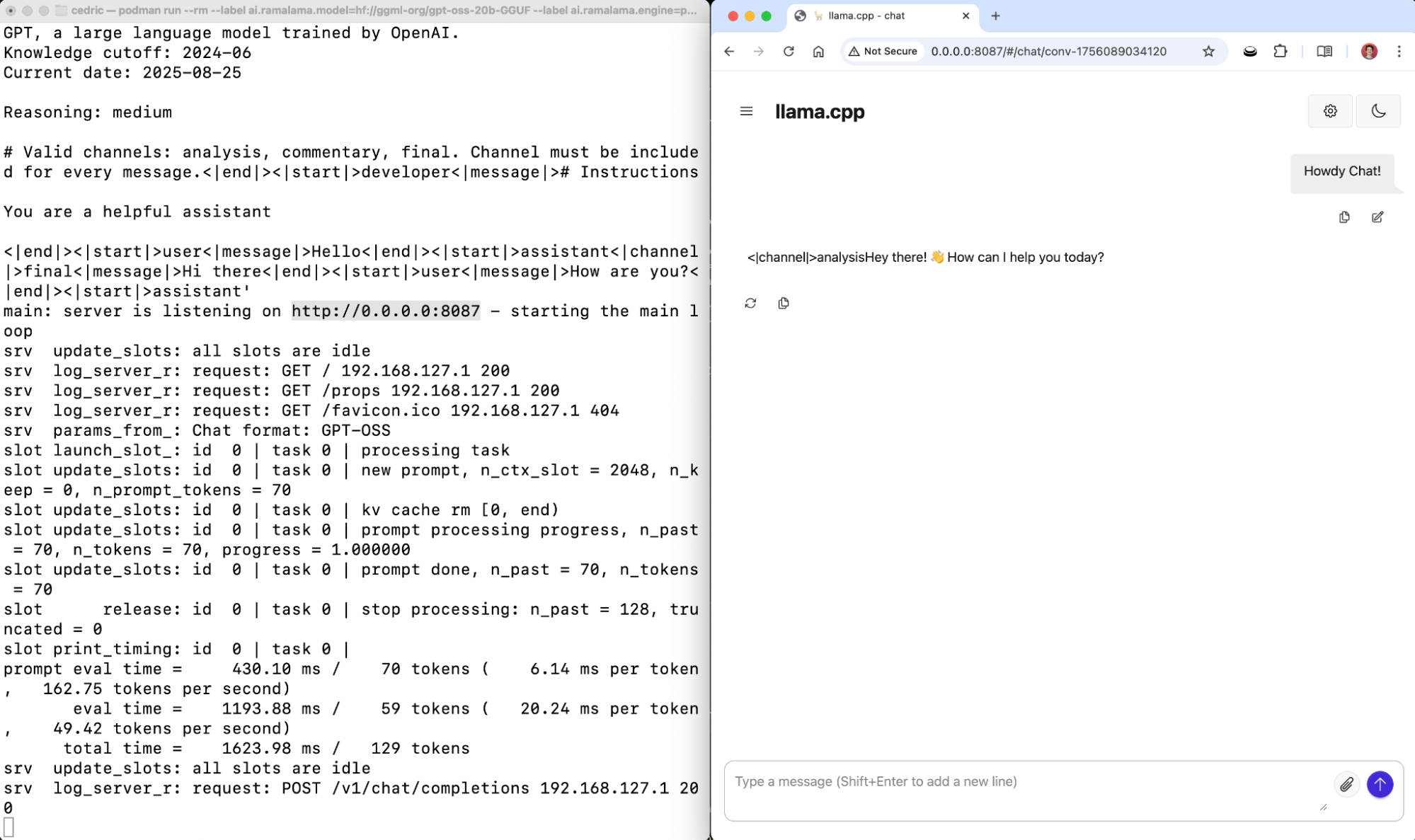
Memory-constrained systems (8-16GB VRAM)
For mid‑range GPUs or systems with limited memory, you can offload 10 layers to the GPU with --ngl 10 (leaving the rest on the CPU to save VRAM) while limiting the context to ~16k tokens with --ctx-size 16384 to reduce overall memory usage.
ramalama serve --ngl 10 --ctx-size 16384 gpt-oss:20bCPU-only systems
On systems without a compatible GPU, use --ngl 0 to force CPU-only inference and --threads 8 (adjust as needed) to set the CPU thread count.
ramalama serve --ngl 0 --threads 8 --ctx-size 4096 gpt-oss:20bMonitoring resource usage
Running AI models can be heavy on your system. RamaLama containers make it easy to keep an eye on performance so you know whether you’re maxing out CPU, GPU, or memory. Let’s check container details and resource consumption:
ramalama containersLet’s say we’re using Podman. Here we can use podman stats to stream container resource usage:
podman stats <container_name>Alternatively, we can use nvtop, the task monitor for NVIDIA GPU’s and other accelerators to monitor load and memory usage (shown in Figure 2):
nvtop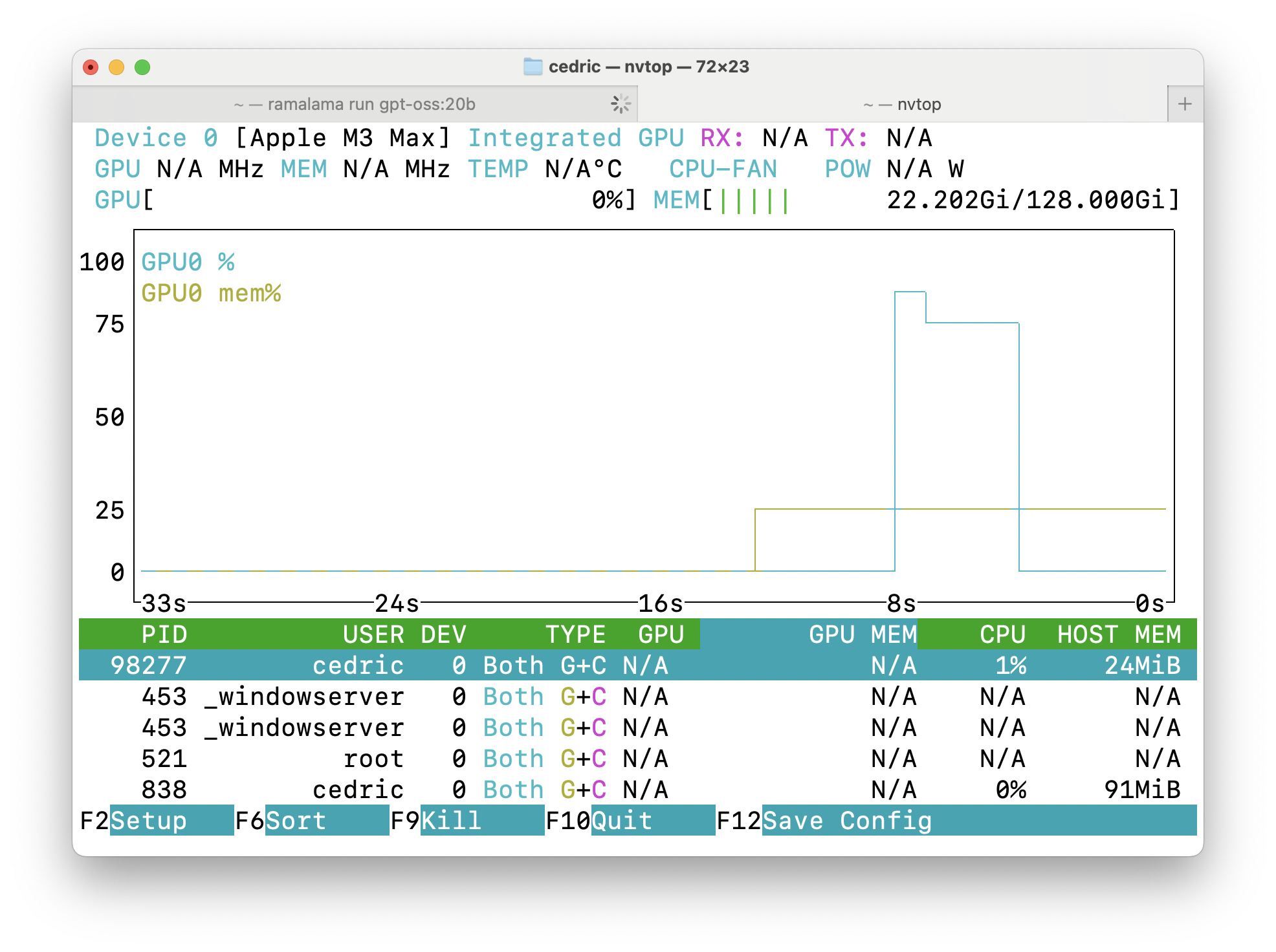
Community and next steps
RamaLama is a collaborative effort to make AI as simple as possible by using containers to run and serve models. With support for a wide variety of registries including Hugging Face and Ollama (even OCI registries), as well as multiple inference runtimes (namely llama.cpp and vLLM), you run and build apps using countless different types of models, including gpt-oss. What will you try?
In the meantime, here are some helpful links:
- Check out the RamaLama repository.
- Join the Matrix chat.
- Try the quick start examples.
- Read the blog post How RamaLama runs AI models in isolation by default.
The future of AI is local, secure, and containerized, and with tools like RamaLama, that future is already here.
