In a telecommunications network environment, it's crucial to have access to low-latency synchronization events, such as those used in Precision Time Protocol (PTP). It is essential for applications requiring precise timing, such as financial transactions, telecommunications, and real-time data processing, where even small timing discrepancies can lead to significant errors. To facilitate this, Red Hat has re-architected the REST API to provide direct and efficient access to event notifications, while fully adhering to the latest O-RAN standards.
Synchronization event notifications
Open RAN stands for Open Radio Access Network and is a new way of building cellular networks. It divides or disaggregates a network's hardware and software into separate components, with open and standardized interfaces freeing service providers from dependency on proprietary systems from a single vendor.
O-Cloud is the cloud infrastructure layer in O-RAN Alliance architecture. It hosts virtualized network functions like the RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC), O-RAN Radio Units (O-RU), Centralized Unit (CU), and O-RAN Distributed Units (O-DU). See Figure 1.
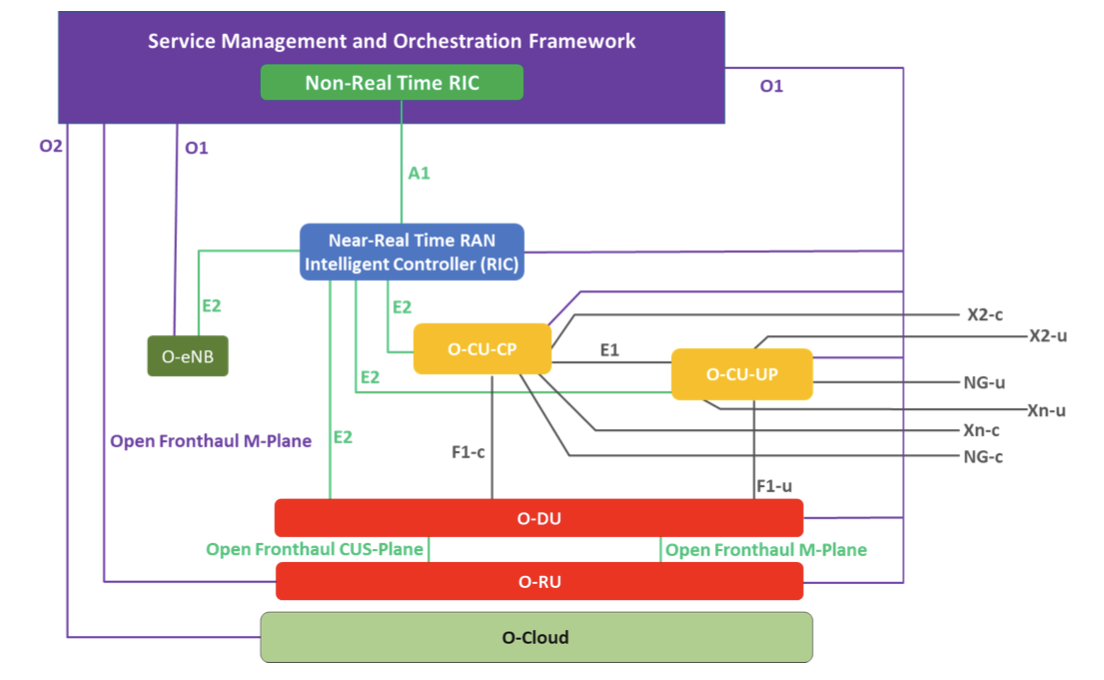
Synchronization event notifications allow Open RAN components to communicate changes, alerts, or status updates within the O-Cloud environment. These notifications are crucial for maintaining observability, automation, and interoperability across multi-vendor deployments. These notifications include:
- PTP state updates
- Synchronous Ethernet (SyncE) state updates
- Resource state changes
- Alarm triggers
Compliance with O-RAN API
Defined in the O-RAN Working Group 6 (WG6) specifications, the O-Cloud Notification API specification for Event Consumers standardizes synchronization event notifications between O-Cloud event producers and consumers.
Compliance with the O-RAN specification is important because it creates a more competitive and innovative market, lowers costs, and allows for more flexible networks and multiple vendors. As of Red Hat OpenShift 4.16, the V2 fast event notification framework is fully compliant with the O-Cloud Notification API specification.
A simplified and flexible architecture
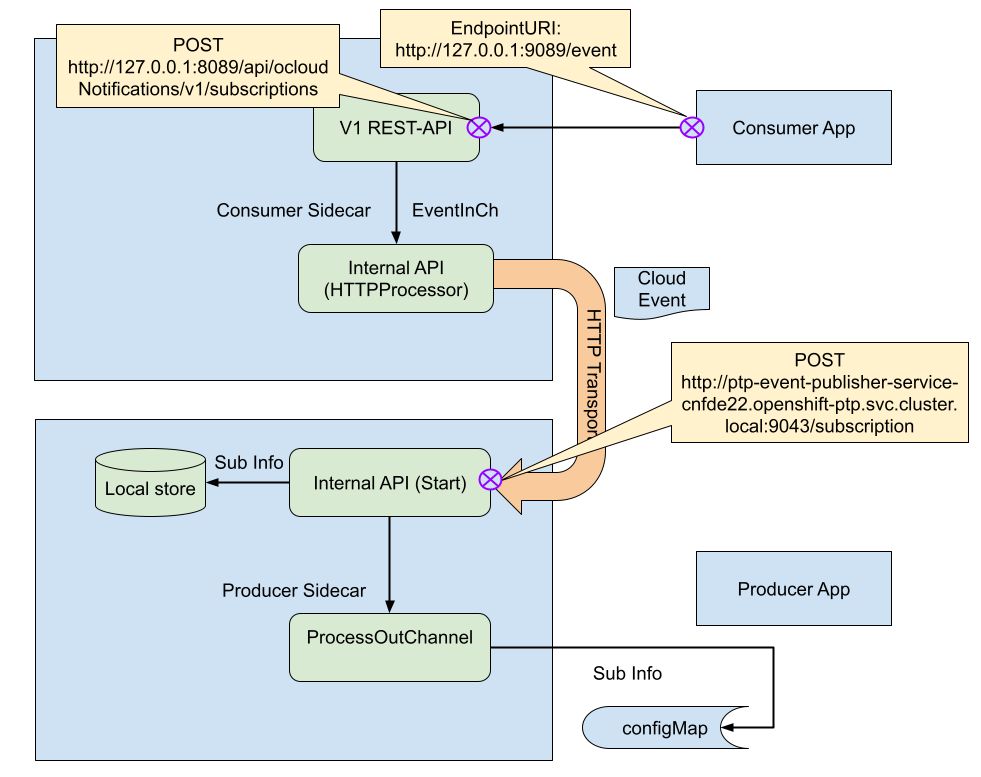
Traditionally, event consumers interacted with the event producer through a cloud-event-proxy sidecar. While effective, this approach added an extra layer (the consumer sidecar), which complicated deployments especially when consumers resided in separate pods.
Figure 2 shows the legacy design.
In the V2 fast event notifications framework, the new architecture design now exposes the REST API with a cluster-wide service endpoint. This allows customers to directly subscribe to and consume events without needing a sidecar in the consumer pod. This significant simplification of the architecture has not only reduced complexity but also lowered latency and increased scalability.
The new design is illustrated in Figure 3.

Seamless upgrade path
For OpenShift 4.16 through 4.18, Red Hat provides support for both the legacy V1 and the new V2 fast event notification frameworks. During these releases, existing deployments that utilize the consumer sidecar architecture will continue to function without any modifications.
Upgrading from V1 to V2 is straightforward, requiring only an update to the value of ptpEventConfig.apiVersion within PtpOperatorConfig.
Embrace open standards
CloudEvents is a specification for describing event data in a common and consistent way. O-Cloud Notification API specification mandates the use of the CloudEvents format for all its notifications. Red Hat has updated our event message schema to CloudEvents V1 to meet this requirement. For the V2 fast event notifications framework, Red Hat has leveraged open standards by using CloudEvents for message schemas.
Red Hat is also using OpenAPI to document our REST API. OpenAPI provides a standard, machine-readable contract for a REST API that enables the automatic generation of interactive documentation, client code, and server stubs. This drastically accelerates development, simplifies testing, and improves collaboration between teams by creating a single source of truth.
This commitment to open standards facilitates easier adoption of our implementation and encourages open source contributions.
Enhancing O-RAN specifications
The current O-RAN specification document assumes that the event consumer and the event producer are located within the same pod, and it mandates the Endpoint URI to use localhost.
In a real-world scenario, service providers might prefer to have the event producer (or multiple producers) and event consumers located in different pods. For example, service providers might want multiple consumers across several pods to receive events from the same linuxptp-daemon pod. In such cases, EndpointUri cannot use localhost. To enable communication across different pods, Red Hat utilizes a service name as the EndpointUri, structured as follows:
http://{servicename}.{namespace}.svc.cluster.local:{port}Similarly, UriLocation can use service names to facilitate inter-pod communication.
In summary, the Red Hat implementation has successfully demonstrated a solution for enabling events to be consumed across multi-pod deployments, which is a scenario currently not fully specified within the O-RAN architecture. We're actively engaging with the relevant O-RAN workgroup to propose an official update to the specification. Our goal is to standardize inter-pod communication, including robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, to formally close this identified gap.
Learn more about Ret Hat telecommunications solutions
Ready to learn more about how Red Hat is helping to shape the future of telecommunications? Visit our Red Hat telecommunications solutions page to explore more resources, including e-books, case studies, and webinars. If you're ready to start a conversation, contact a Red Hatter today to discuss how our open source solutions can help you achieve your business goals.
