Due to the day-to-day activities of developers, system administrators need to automate the management of users and groups. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform simplifies this process with the help of Ansible Playbooks. In this article, we will demonstrate user and group management on managed node instances using Ansible Automation Platform.
How to automate user/group management
We will create a playbook to run the automation task. First, we will create three different groups that identify three kinds of users with access to our Linux system:
- Admins
- Developers
- Quality Assurance
We will add groups to our system. Let's define our groups in our playbook file. Create an playbook.yml and include the following:
---
- hosts: localhost
become: true
tasks:
- name: Create admin group
group:
name: admin
state: present
- name: Create developers group
group:
name: developers
state: present
- name: Create quality assurance group
group:
name: quality_assurance
state: present
Next, we will add a few users to these groups. Add users ad1 and ad2 to the admin group, users dev1 and dev2 to the developer group, and users qa1 and qa2 to the quality assurance group. Add the following content to the previously created YAML file:
- name: Add ad1 and ad2 to admin group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: admin
password: "{{ 'admin' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- ad1
- ad2
- name: Add dev1 and dev2 to developers group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: developers
password: "{{ 'dev' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- dev1
- dev2
- name: Add qa1 and qa2 to quality assurance group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: quality_assurance
password: "{{ 'test' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- qa1
- qa2
Finally, we will grant certain privileges to these groups which will enable the users of these groups with those same privileges:
- name: Grant admin group sudo privileges
lineinfile:
path: /etc/sudoers
line: "%admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL"
state: present
- name: Grant developers group access to /opt/myapp
file:
path: /opt/myapp
owner: root
group: developers
mode: "0755"
state: directory
- name: Grant quality assurance group access to /var/log/myapp
file:
path: /var/log/myapp
owner: root
group: quality_assurance
mode: "0740"
state: directory
The final YAML will look like this:
---
####### creating groups ######
- hosts: localhost
become: true
tasks:
- name: Create admin group
group:
name: admin
state: present
- name: Create developers group
group:
name: developers
state: present
- name: Create quality assurance group
group:
name: quality_assurance
state: present
####### Adding Users in Group ######
- name: Add ad1 and ad2 to admin group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: admin
password: "{{ 'admin' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- ad1
- ad2
- name: Add dev1 and dev2 to developers group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: developers
password: "{{ 'dev' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- dev1
- dev2
- name: Add qa1 and qa2 to quality assurance group
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
groups: quality_assurance
password: "{{ 'test' | password_hash('sha512') }}"
with_items:
- qa1
- qa2
####### Setting up permissions to Groups ######
- name: Grant admin group sudo privileges
lineinfile:
path: /etc/sudoers
line: "%admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL"
state: present
- name: Grant developers group access to /opt/myapp
file:
path: /opt/myapp
owner: root
group: developers
mode: "0755"
state: directory
- name: Grant quality assurance group access to /var/log/myapp
file:
path: /var/log/myapp
owner: root
group: quality_assurance
mode: "0740"
state: directory
Run Ansible Playbooks
Run the playbook using the following command:
ansible-playbook playbook.yml
Now head over to your managed node and log into the dev user from the terminal using the following command:
su - dev1
On the prompt, enter the password: dev. Check the permissions on the /opt/myapp folder as follows: drwxr-xr-x (read and execute for developers and others, write permission reserved for user). Change the permissions to your needs accordingly in the playbook file.
Now, we will use Ansible Automation Platform to run these playbooks. Install the latest version of Ansible Automation Platform. You can also refer to the Ansible Automation Platform 2.3 installation guide for a RHEL 9 system. After the installation is complete, navigate to the dashboard on https://localhost.
Create new project
A project is a collection of Ansible Playbooks which perform a certain set of automated tasks. Here, our project will contain our single playbook.
Steps to create a new project:
- Head over to the Projects tab (Figure 1).
- Click on the Add option and select a name for the project and select the default organization.
- Add the GitHub URL to the Source Control URL field: https://github.com/4molybdenum2/ansible-automation-demos/tree/main/user_mgmt.
- Save the project.
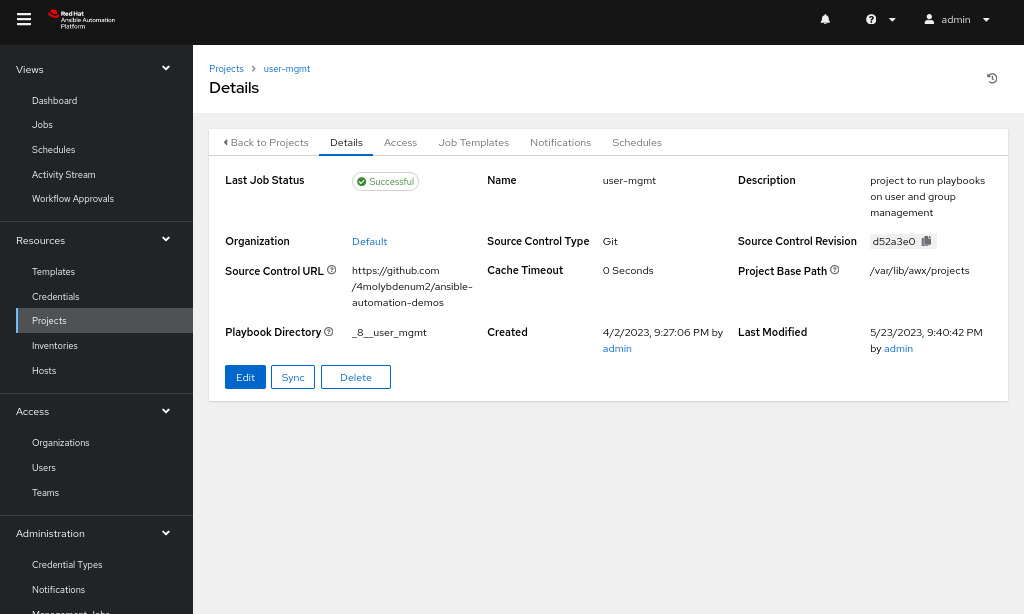
Steps to create an inventory
- Create an inventory from the Inventories tab and add a group named webstack (Figure 2).
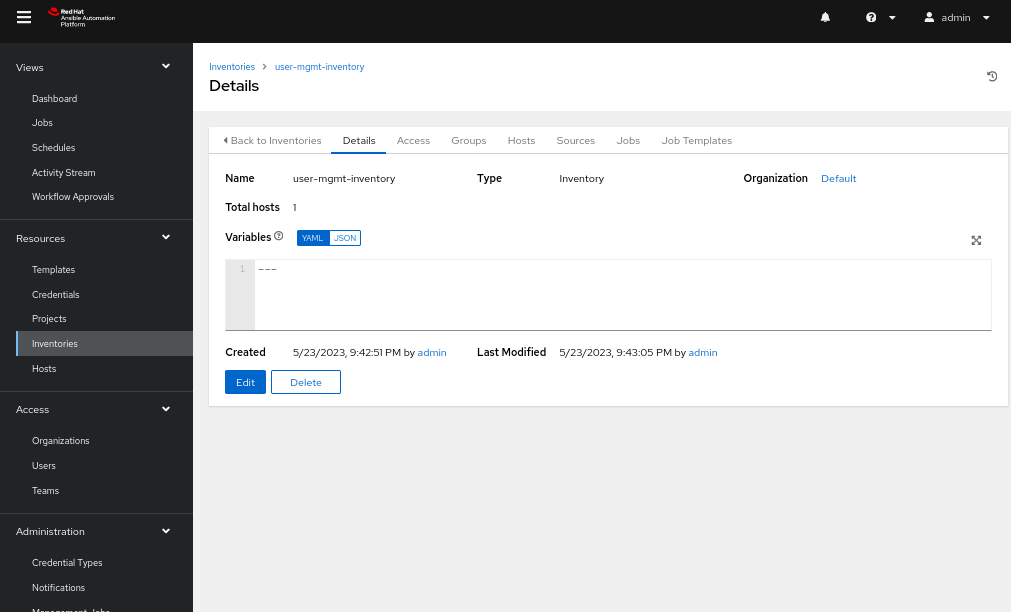
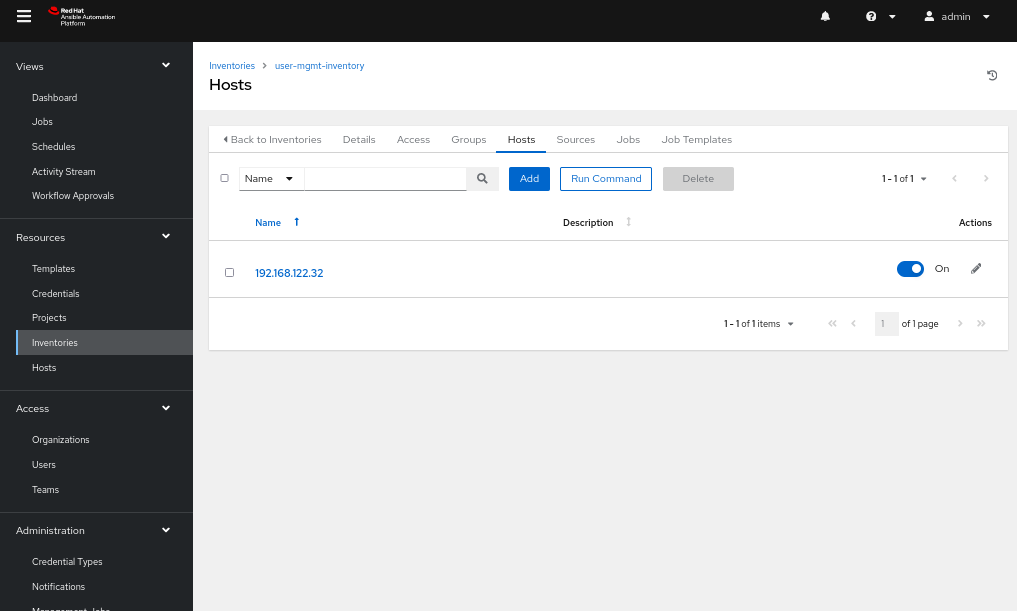
- Head back to the inventory edit page and navigate to the Hosts tab.
- Add a host with the name as the IP address of the node on which the playbook will run (Figure 3).
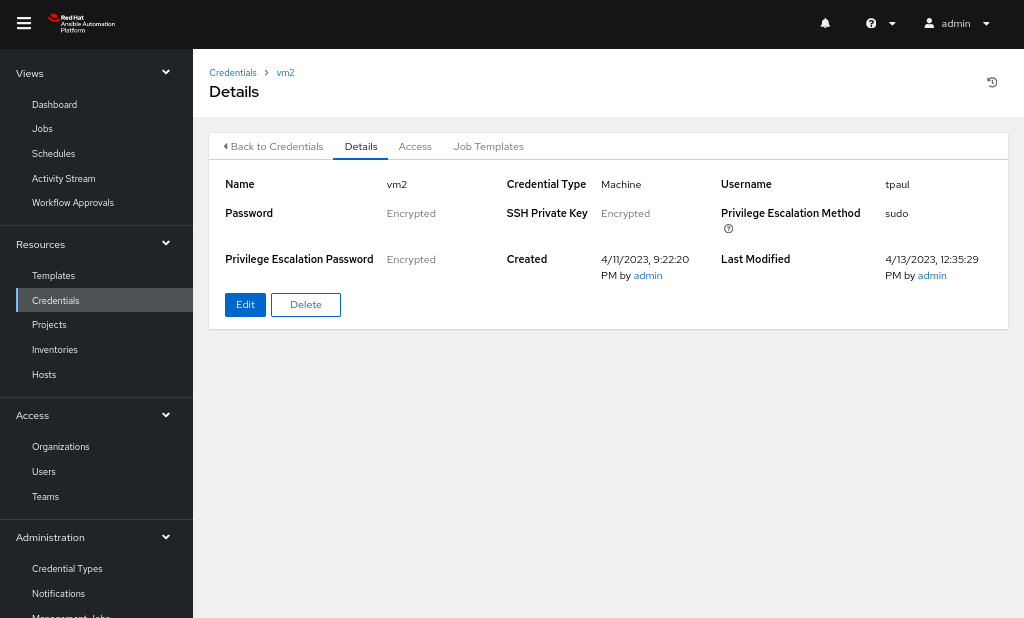
Steps to add a credential
- Navigate to the Credential tab and add a credential with type Machine, username and password as that of our managed node, and private key as copied over from control node file: ~/.ssh/id_rsa (Figure 4).
- Fill the Privilege Escalation password with the password for our managed node which will run the commands as a sudo user.
Steps to create a template
- Head over to the Templates tab and create a new template.
- Add the project that we created and select the playbook from our GitHub or any other source control repository where we uploaded the playbook.
- Add the Inventory, Credentials, and the Execution Environment as Default execution environment (Figure 5).
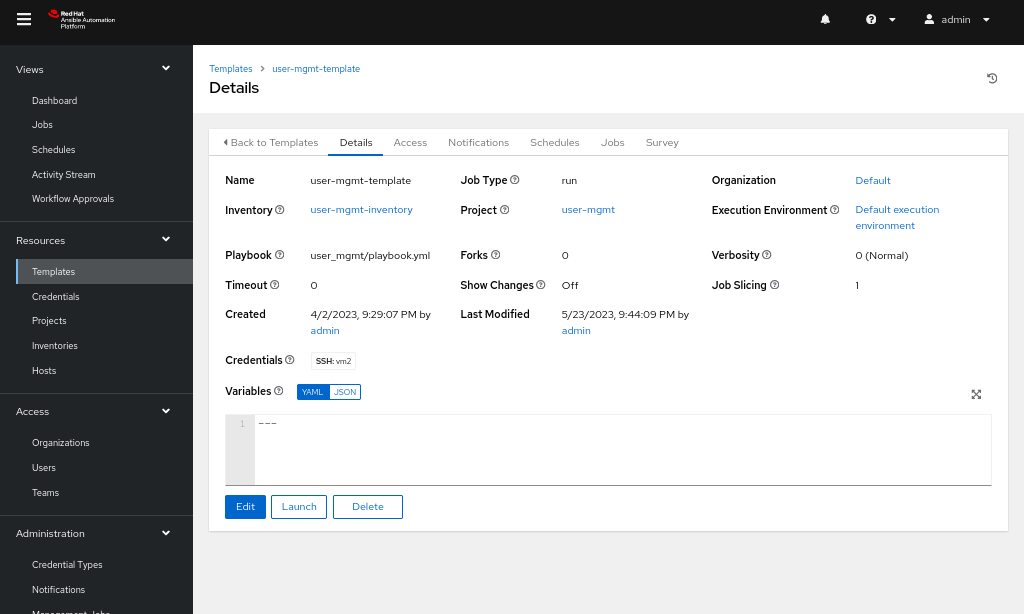
-
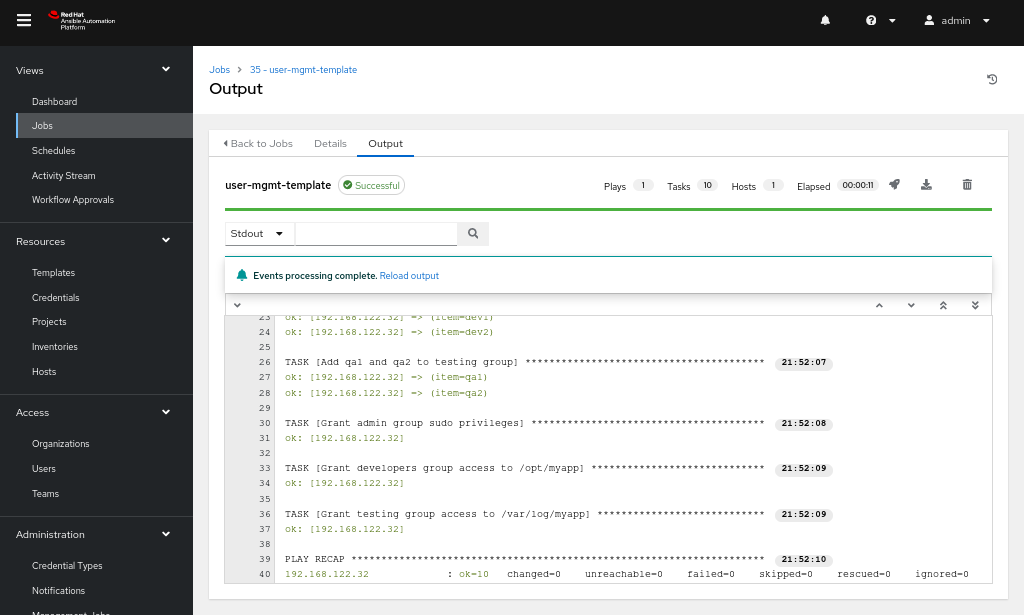
After the template has been created, you can launch it, and the job will be visible under the Jobs tab, as shown in Figure 6.
Continue your automation journey with Ansible Automation Platform
You can get started with the Ansible Automation Platform by downloading at no cost and exploring interactive labs at Red Hat Developer.
