2017: Time for a new resolution and the most important resolution for this year should be to adopt microservices to spend less effort on development and improve your time to market (TTM). Nowadays, there are plenty of tools and frameworks at the disposal of the discerning developer to rapidly build microservices. A few examples include Spring Boot, Vertx, etc.
Once you build your microservices, the next step is to ensure that these frequent deployments do not impact the availability of the microservice. And this is where the Zero Downtime Deployment (ZDD) comes in, which allows you to deploy a new version of your microservice without interrupting the operation of the service.
How to ensure a "smooth" deployment?
I started working on a Camel microservice based on Spring Boot that exposed a Rest service. One of the goals is how to provide ZDD & Hot reconfiguration feature for the users.
To achieve this goal, I simply have to deploy my microservice on OpenShift, which is based on Kubernetes. What is exciting is that, while successfully handling HTTP requests every second with uninterrupted availability, we have OpenShift perform a zero-downtime rolling upgrade of the service to a new version of the microservice while we're still serving requests per second.
To demonstrate this, we will start from my microservice example here: camel-springboot-rest-ose
It is assumed a running OpenShift platform is already running. If not you can find details how to get started (Personally, the one that I use is MiniShift).
Assuming your current shell is connected to OpenShift, you can type the following command to package your microservice, deploy it on OpenShift, and get the output the logs from the running pods:
mvn clean install fabric8:deploy -Dfabric8.deploy.createExternalUrls=true fabric:log
fabric8:log tails the log of our microservice that's deployed via the fabric8:deploy, and we can check when our microservice is started.
By enabling the following property fabric8.deploy.createExternalUrls, it will create an external URL to reach our Rest Endpoint.
To get this URL, you simply have to run the following command:
$ oc get route
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION
camel-springboot-rest-os camel-springboot-rest-os-springboot.192.168.42.111.xip.io camel-springboot-rest-os <all>
Now, we can invoke our Rest endpoint of our camel microservice every second based on the following watch command:
watch -n1 -c ab -n 10 http://camel-springboot-rest-os-springboot.192.168.42.111.xip.io/api/persons/abouchama
Every 1.0s: curl http://camel-springboot-rest-os-springboot.192.168.42.111.xip.io/api/per... Tue Jan 24 10:38:05 2017
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0 100 85 0 85 0 0 665
0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 669
Hey abouchama --> Enjoy your camel microservices | POD : camel-springboot-rest-os-10-4cxix
In the reply of the Rest service, we mention the Pod that handles the request inside OpenShift.
To hot configure our Camel route, we will use Environment variables. All the endpoints of the route Camel are defined as environment variable properties:
https://gist.github.com/abouchama/63d1cf619e88fed21643d1748ee97a50
All these environment variables are declared in fabric8/deployment.yml:
https://gist.github.com/abouchama/5459b6f6690487b9188b49deb2c15f9f
Now, to update your Camel route, you only have to update the environment variable in the DeploymentConfig, like the following:
$ oc env dc/camel-springboot-rest-os CAMEL_LOG_MSG="LOG UPDATED - This request is handled by this POD: {{env:HOSTNAME}}"
deploymentconfig "camel-springboot-rest-os" updated
By running this command, a new deployment will be triggered:
oc get pods -w | grep Running
[aboucham@aboucham camel-springboot-rest-ose]$ oc get pods -w | grep Running
camel-springboot-rest-os-10-4cxix 1/1 Running 0 7m
camel-springboot-rest-os-11-deploy 1/1 Running 0 3s
camel-springboot-rest-os-11-y00ny 0/1 Running 0 3s
camel-springboot-rest-os-11-y00ny 1/1 Running 0 31s
From the OpenShift web console, we will see the following:
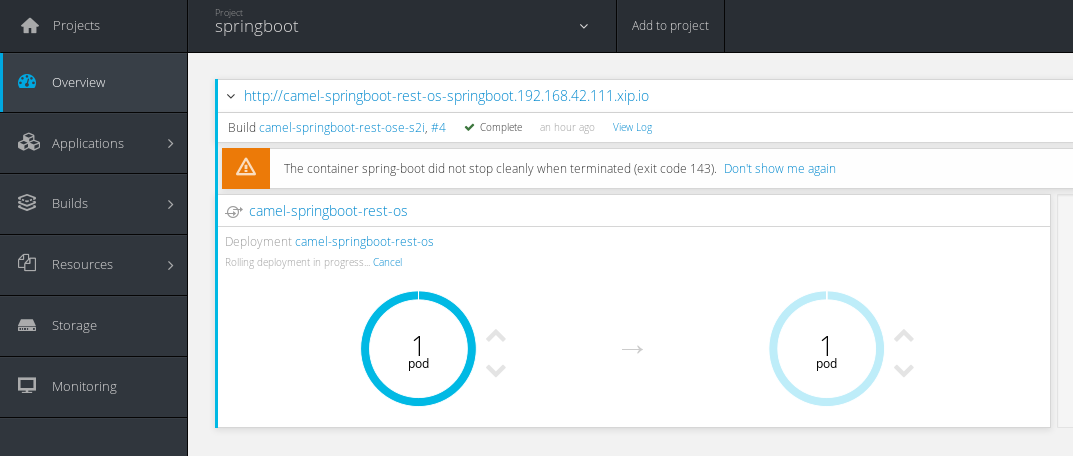
Once the new pod is deployed and running, you will see the output of our REST service updated in the watch command with the new pod running without any interruption or impact for our service:
Hey abouchama --> Enjoy your camel microservices | POD : camel-springboot-rest-os-11-y00ny
Scaling
In addition to ZDD, one of the promises of the microservices is to allow to scale easily in order to get better performance from our service, You've got two 2 ways to do that.
Using deployment configuration:
$ oc scale dc/camel-springboot-rest-os --replicas=10
deploymentconfig "camel-springboot-rest-os" scaled
or using fabric8 start:
mvn fabric8:start -Dfabric8.replicas=10
Conclusion:
It all depends on the frequency of your deployments and your production infrastructure. But if you already use multiple microservices, you have everything to gain from Zero Downtime Deployment, even if you only deploy a new version once a month!
You can learn more on the fundamentals of microservices using Red Hat open-source software.
Last updated: August 30, 2023