As Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform expands its footprint with a growing customer base, security continues to be an important aspect of organizations' overall strategy. Red Hat regularly reviews and enhances the foundational codebase to follow better security practices. As part of this effort, we introduce the libssh connection plug-in that uses the libssh library. Red Hat Ansible Network Automation users can now achieve industrial scale performance while maintaining strict adherence to FIPS 140 readiness standards and fulfilling critical requirements for federal security compliance as outlined in DISA STIG ID: 1057.
Network SSH connection basics
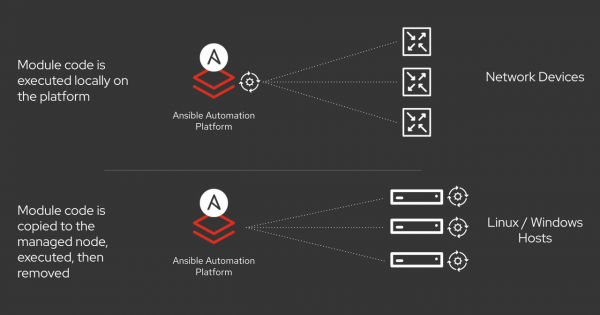
Since most network appliances don't support or have limited capability for the local execution of a third-party software, the network modules are not copied to the remote host unlike Linux hosts. Instead, they run on the control node. Hence, the network can't use the typical Ansible SSH connection plug-in used with a Linux host. Due to this behavior, performance of the underlying SSH subsystem is critical (Figure 1). Not only does the new LibSSH connection plug-in enable FIPS readiness, but it is more performant than the existing Paramiko SSH subsystem.
The top level network_cli connection plug-in, provided by the ansible.netcommon collection, specifically the ansible.netcommon.network_cli, provides an SSH based connection to the network appliance. Then it calls the ansible.builtin.paramiko_ssh connection plug-in that depends on the Paramiko Python library to initialize the session between the control node and the remote host. After that, it creates a pseudo terminal (PTY) to send commands from the control node to the network appliance and receive the responses.
Why replace Paramiko?
The primary reason to replace the Paramiko library is that it doesn't guarantee FIPS readiness, and thus limits the Ansible Automation Platform network capability to run in environments that mandate FIPS mode enablement. Paramiko also isn't the speediest of connection plug-ins, so that can be enhanced. Therefore, you can now swap the new ansible.netcommon.libssh connection plug-in for Paramiko. The ansible.netcommon collection now contains this by default, and you can use it for testing purposes until the codebase becomes more stable (currently in Technology Preview).
Comparing the connection flow to the previous flow, the top level network_cli connection plug-in that is provided by the ansible.netcommon collection, specifically the ansible.netcommon.network_cli still provides an SSH based connection to the network appliance. It in turn calls the ansible.netcommon.libssh connection plug-in that depends on the ansible-pylibssh Python library to initialize the session between control node and the remote host. This python library is essentially a Python wrapper on top of the libssh C library. It then creates pseudo terminals (PTY) over SSH using Python.
Switching Ansible Playbooks to use LibSSH
With the ansible.netcommon collection version 1.0.0, a new configuration parameter within ansible.netcommon.network_cli connection plug-in was added, which allows for you to set the ssh_type to either libssh or paramiko.
If the value of the configuration parameter is set to libssh, it will use the ansible.netcommon.libssh connection plug-in, which in turn uses the ansible-pylibssh Python library that supports FIPS readiness. If the value is set to paramiko, it will continue to use the default ansible.builtin.paramiko connection plug-in that relies on the paramiko Python library.
Again, the default value is set to paramiko, but in the future plans are to change the default to libssh.
Installing and configuring LibSSH
To utilize the LibSSH plug-in, you must first install the ansible-pylibssh Python library from PyPI using the following command:
pip install ansible-pylibsshThe current PyPI installation method bundles the correct version of libssh library and its dependencies as platform-specific wheels that don't rely on any OS-level libraries in runtime.
Future plans include creation, publishing, and maintenance of stand-alone RPM and DEB packages for the ansible-pylibssh library that you can install with well-known Linux package managers. These will install the required system libssh version and its dependencies on the control node. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.1 and later contains the proper libssh package version and its dependencies.
The current primary use case for using LibSSH with Ansible Automation Platform is for connecting to network devices. Connecting to other types of endpoints such as Linux will be officially enabled at a later date.
How to use LibSSH in Ansible Playbooks
There are two methods to using LibSSH in Ansible Playbooks.
Method 1: You can set the ssh_type configuration parameter to use libssh in the active ansible.cfg file of your project as follows.
[persistent_connection]
ssh_type = libsshMethod 2: Set the ANSIBLE_NETWORK_CLI_SSH_TYPE environment variable as follows.
$export ANSIBLE_NETWORK_CLI_SSH_TYPE=libsshMethod 3: Set the ansible_network_cli_ssh_type parameter to libssh within your playbook at the play level.
Note: This setting can be made at the individual task level, but only if the connection to the remote network device is not already established. That is, if the first task uses paramiko, then all subsequent tasks in the play must use paramiko even if libssh is specified in any subsequent tasks.
Troubleshooting LibSSH connections
To quickly verify the libssh transport is set correctly, you can run the following playbook using the ansible-playbook command line with the verbose flag -vvvv. Before running, ensure the inventory file is set correctly.
This example playbook uses the cisco.ios collection and must first be installed from Ansible Galaxy or Ansible Automation Platform on your control node.
- hosts: "changeme"
gather_facts: no
connection: ansible.netcommon.network_cli
vars:
ansible_network_os: cisco.ios.ios
ansible_user: "changeme"
ansible_password: "changeme"
ansible_network_cli_ssh_type: libssh
tasks:
- name: run show version command
ansible.netcommon.cli_command:
command: show version
- name: run show interface command
ansible.netcommon.cli_command:
command: show interfaceshttps://gist.github.com/ganeshrn/78149adca85c809b69ed1b5f5262844c
In the output verbose logs, you should see the line "ssh type is set to libssh" displayed on the console, which confirms the configuration is set correctly.
Next steps
Start testing your Ansible Playbooks by setting the configuration to use the ansible-pylibssh library. Help with performance profiling of your existing playbook of ansible-pylibssh library with respect to paramiko library. Get involved with the ansible-pylibssh project.
