This article provides a step-by-step guide to implement multicluster authentication between Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management. This integration, illustrated in Figure 1, enables Ansible Automation Platform to securely authenticate with multiple managed clusters through the centralized authentication capabilities of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management.
The goal is to eliminate credential proliferation in Ansible Automation Platform by leveraging the ManagedServiceAccount and ClusterProxy features of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for secure, token-based authentication across multiple clusters.
Value proposition
This integration addresses the critical security and operational challenge of credential proliferation. Instead of managing separate credentials for each managed cluster in Ansible Automation Platform, this solution provides:
- Centralized authentication: All authentication flows go through the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub cluster
- Network security: API access to managed clusters is routed through Cluster Proxy
- Dynamic token management: ManagedServiceAccount provides on-demand tokens without storing long-lived credentials
- Reduced attack surface: Eliminates the need to store cluster credentials in Ansible Automation Platform
Prerequisites
You must have these components installed and configured:
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.9 or greater
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- ManagedServiceAccount and Cluster Proxy features enabled (default as of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.9)
Verify components
In Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.13, both ManagedServiceAccount and Cluster Proxy features are enabled by default. Verify their status:
oc get multiclusterengine multiclusterengine -o yamlLook for the following components in the spec.overrides.components section:
managedserviceaccountmust be enabledcluster-proxy-addonmust be enabled
Get cluster proxy URL
Get the cluster proxy URL that Ansible Automation Platform will use for authentication:
oc get route -n multicluster-engine cluster-proxy-addon-user
NAME HOST/PORT
cluster-proxy-addon-user cluster-proxy-user.apps.ocp4.example.com cluster-proxy-addon-user user-portCreate a hub ServiceAccount for multicluster authentication
Create a ServiceAccount on the cluster hub that Ansible Automation Platform can use to create ManagedServiceAccounts and retrieve authentication tokens:
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount-role
rules:
- verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- secrets
- verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- create
- update
- patch
- delete
apiGroups:
- authentication.open-cluster-management.io
- work.open-cluster-management.io
- addon.open-cluster-management.io
resources:
- managedserviceaccounts
- manifestworks
- managedclusteraddons
- managedserviceaccounts/finalizers
- manifestworks/finalizers
- managedclusteraddons/finalizers
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount-rb
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: aap
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount-role
---
kind: ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: aapGenerate authentication token
For OpenShift 4.11 and above, create the authentication token manually:
oc create token aap-integration-serviceaccount -n aapFor long-lived tokens (1 year):
oc create token aap-integration-serviceaccount -n aap --duration=8760hConfigure authentication credentials
Store the authentication credentials for Ansible Automation Platform to authenticate with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management. This example uses Ansible Vault, but you can also use Ansible Automation Platform credentials or any other method that provides access to the required values.
Using Ansible Vault
Store the authentication credentials securely in an Ansible vault. First, create a directory called vault:
$ mkdir vault
In the directory, create a file called vault.yaml with the authentication credentials in it:
$ cat vault/vault.yaml
hub_url: https://cluster-proxy-user.apps.ocp4.example.com
token_acm: yJhbGciOiJSUzI1NXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXUse the ansible-vault command to encrypt the file:
$ ansible-vault encrypt vault/vault.yamlUsing custom credential types
Create a custom credential type in Ansible Automation Platform to securely store and manage Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management authentication credentials. This approach provides a structured way to handle multicluster authentication credentials with proper validation and help text.
The custom credential type interface allows you to define specific fields for cluster proxy URL and the hub token, providing an easy way to manage authentication credentials within Ansible Automation Platform.
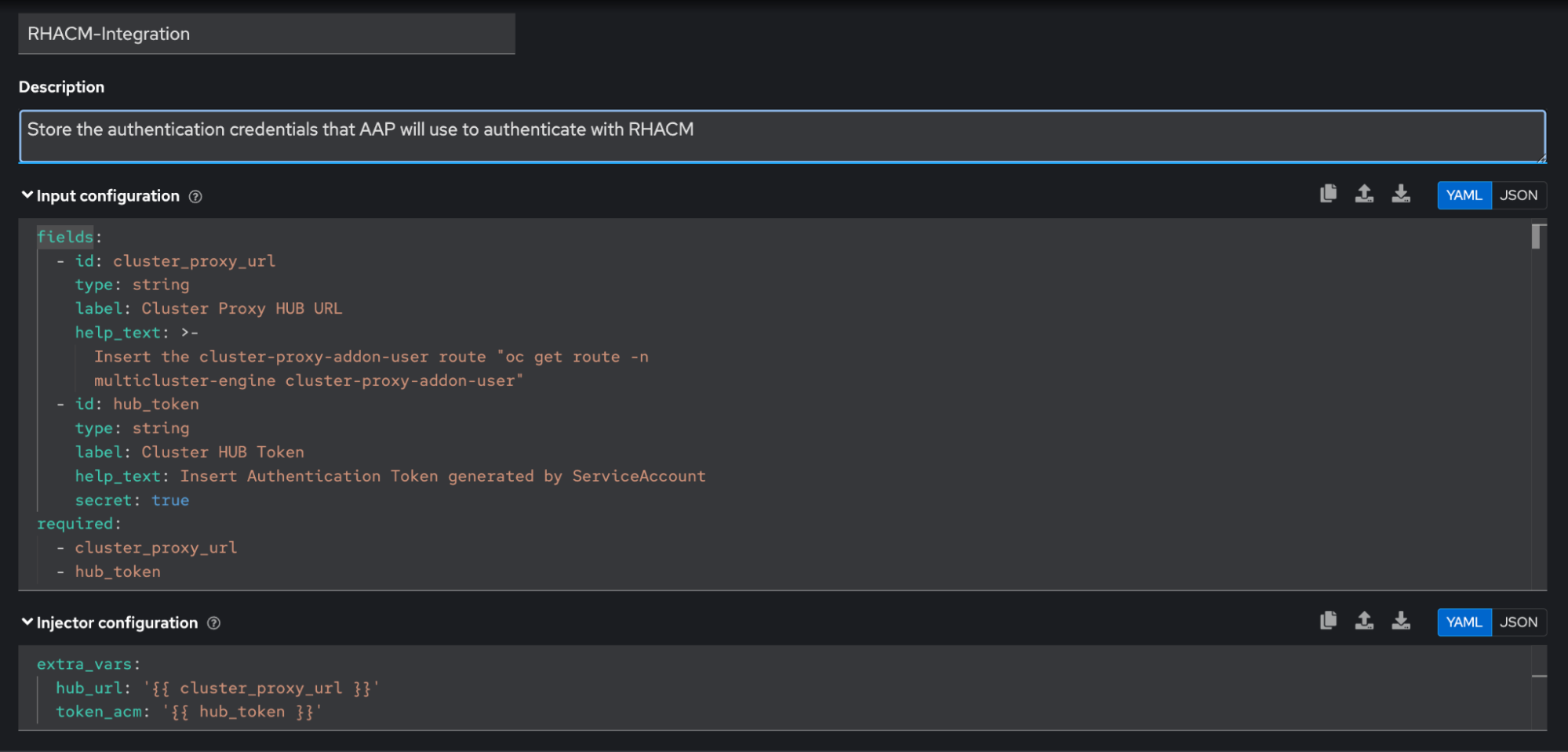
For this example, the input configuration field contains:
fields:
- id: cluster_proxy_url
type: string
label: Cluster Proxy HUB URL
help_text: >-
Insert the cluster-proxy-addon-user route "oc get route -n
multicluster-engine cluster-proxy-addon-user"
- id: hub_token
type: string
label: Cluster HUB Token
help_text: Insert Authentication Token generated by ServiceAccount
secret: true
required:
- cluster_proxy_url
- hub_tokenThe injector configuration:
extra_vars:
hub_url: '{{ cluster_proxy_url }}'
token_acm: '{{ hub_token }}'Authentication flow
The multicluster authentication process follows a secure, step-by-step flow that ensures proper authentication and authorization across all managed clusters. Figure 3 illustrates how Ansible Automation Platform interacts with RHACM to securely access managed clusters through a centralized authentication mechanism that eliminates credential proliferation.
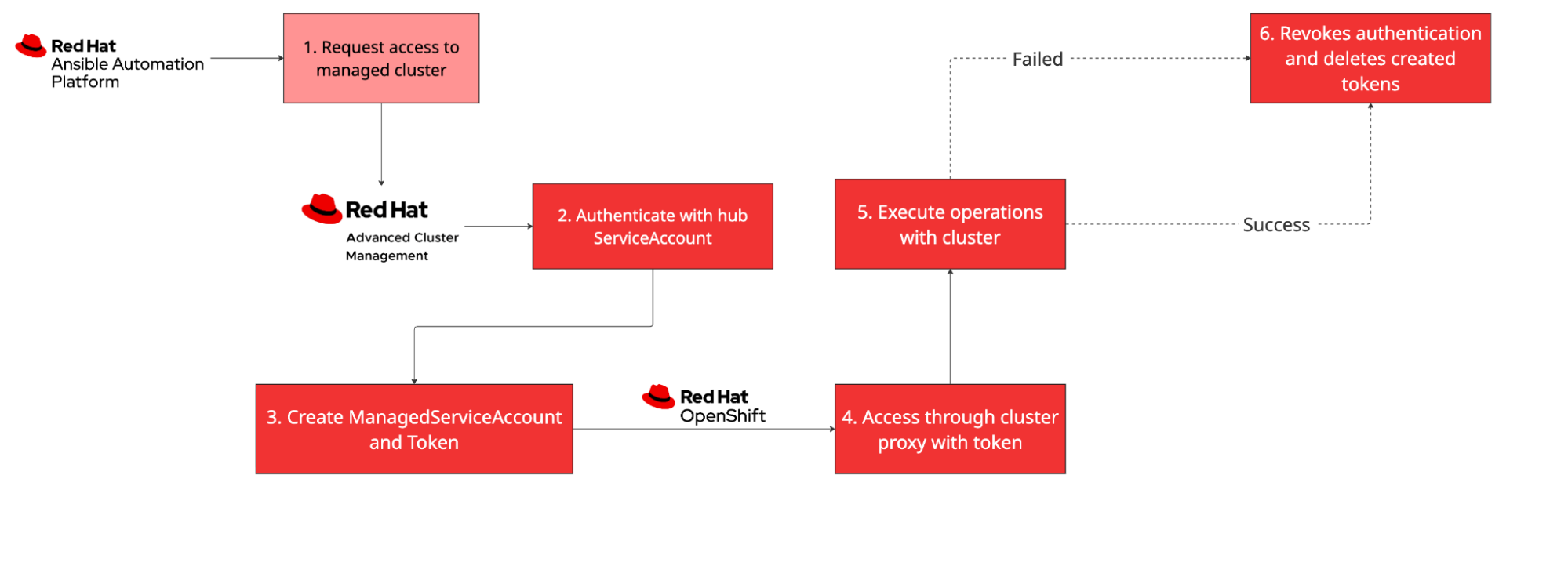
In detail:
- Ansible Automation Platform request: Playbook requests access to a managed cluster.
- HUB authentication: Ansible Automation Platform authenticates with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub using the configured ServiceAccount.
- Token generation: Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management creates a ManagedServiceAccount on the target cluster and generates a token.
- Cluster proxy: Ansible Automation Platform accesses the managed cluster through the cluster proxy using the generated token.
- Secure communication: All communication is routed through the hub cluster.
- Cleanup: ManagedServiceAccount is deleted up after operations complete and token is revoked.
Using multicluster authentication in Ansible Automation Platform playbooks
Here's an example of how to use the multicluster authentication in your Ansible Automation Platform playbooks:
---
- name: Multi-Cluster Operations with RHACM Authentication
hosts: localhost
vars_files:
- ../vault/vault.yaml # Contains hub_url and token_acm
vars:
target_clusters: ["cluster1", "cluster2", "cluster3"] # Name of ManagedCluster
tasks:
- block:
- name: Create ManagedClusterAddOn
kubernetes.core.k8s:
definition: |
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterAddOn
metadata:
name: managed-serviceaccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
spec:
installNamespace: open-cluster-management-agent-addon
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
- name: Create ManagedServiceAccount
kubernetes.core.k8s:
definition: |
apiVersion: authentication.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: ManagedServiceAccount
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
spec:
rotation:
enabled: true
validity: 8640h0m0s
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
- name: Get UID of ManagedServiceAccount
kubernetes.core.k8s_info:
api_version: authentication.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: ManagedServiceAccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
register: msa_info
- name: Create ManifestWork
kubernetes.core.k8s:
definition: |
apiVersion: work.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ManifestWork
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
spec:
workload:
manifests:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-admin-app
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: open-cluster-management-agent-addon
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
- name: Check if token is created
kubernetes.core.k8s_info:
kind: Secret
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
register: secret_info
until: secret_info is not failed
retries: 10
delay: 15
- name: Create empty array
set_fact:
clusters_tokens: []
- name: Fetch secret aap-integration-serviceaccount
kubernetes.core.k8s_info:
api_version: v1
kind: Secret
namespace: "{{ item }}"
name: "aap-integration-serviceaccount"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
validate_certs: false
register: secret_result
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
- name: Extract and decode token
set_fact:
clusters_tokens: "{{ clusters_tokens + [clusters] }}"
vars:
clusters:
cluster_name: "{{ item }}"
token: "{{ secret_result.results[0].resources[0].data.token | b64decode }}"
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
# Include your specific tasks here
- name: Your custom operations
include_tasks: "tasks/your-custom-task.yaml"
vars:
cluster_name: "{{ item }}"
loop: "{{ target_clusters }}"
always:
- name: Delete ManagedServiceAccount
kubernetes.core.k8s:
state: absent
definition: |
apiVersion: authentication.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: ManagedServiceAccount
metadata:
name: aap-integration-serviceaccount
namespace: "{{ item }}"
host: "{{ hub_url }}/local-cluster"
api_key: "{{ token_acm }}"
validate_certs: false
with_items: "{{ target_clusters }}"
Important notes about this example:
- Uses
host: "{{ hub_url }}/{{ cluster_name }}"to access the specific managed cluster - Uses
api_key: "{{ clusters_tokens | selectattr('cluster_name', '==', cluster_name) | map(attribute='token') | first }}"to get the correct token for the cluster - Performs operations directly on the managed cluster using the generated token
Here's an example of a task that can be executed on managed clusters using the multicluster authentication:
---
- name: Get jobs completed in "Failed" status {{ cluster_name }}
kubernetes.core.k8s_info:
api_version: batch/v1
kind: Job
namespace: "{{ namespace }}"
host: "{{ hub_url }}/{{ cluster_name }}"
api_key: "{{ clusters_tokens | selectattr('cluster_name', '==', cluster_name) | map(attribute='token') | first }}"
validate_certs: false
register: failed_jobs
- name: debug jobs Failed {{ cluster_name }}
debug:
msg: "{{ item.metadata.name }}"
with_items: "{{ failed_jobs.resources }}"
when: item.status.conditions | selectattr('type', 'equalto', 'Failed') | selectattr('status', 'equalto', 'True')Summary for Ansible Automation Platform playbooks
Here are the key points you need to remember:
- Vault integration: Use
vars_filesto include your encrypted vault with credentials - Cluster login: Authenticate with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub using the stored credentials
- Dynamic token generation: Create ManagedServiceAccount for each target cluster
- Token retrieval: Extract the generated token for each cluster
- Cluster operations: Use the cluster-specific token to perform operations
- Cleanup: Always clean up ManagedServiceAccount resources after use
Workflow integration
With the automation controller, you can create a job template that references vault credentials, executes your playbook against multiple clusters, and handles authentication automatically through Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management integration.
Troubleshooting multicluster authentication
As you set up multicluster authentication, you might need to test and diagnose parts of the process as you go. Here are some of the common components to watch:
- Verify that ManagedServiceAccount and Cluster Proxy are enabled
- Check token validity and permissions
- Ensure that the Cluster Proxy URL is accessible
- Review Ansible Automation Platform and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management logs for authentication errors
Security best practices
Keep your clusters safe. Before your configuration goes live, make sure to:
- Use short-lived tokens when possible
- Regularly rotate authentication tokens
- Monitor authentication logs
- Follow the principle of least privilege for ServiceAccount permissions
Conclusion
This multicluster authentication setup provides a robust and scalable solution for managing authentication across multiple Kubernetes clusters. By leveraging the ManagedServiceAccount and ClusterProxy features of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management, you can:
- Eliminate credential proliferation by centralizing authentication through the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub
- Enhance security by using dynamic, short-lived tokens instead of long-lived credentials
- Simplify operations by managing authentication from a single point of control
- Scale efficiently as new clusters are added without requiring additional credential management
- Reduce attack surface by eliminating the need to store cluster credentials in Ansible Automation Platform
The integration between Ansible Automation Platform and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management creates a powerful automation platform that can manage and operate across multiple clusters while maintaining strict security controls and audit trails.
