In previous articles, we set up a fully functional Red Hat Developer Hub installation in Red Hat OpenShift integrated with a GitHub organization for users through the use of dynamic plug-ins. In this article, we will explore another set of dynamic plug-ins allowing deep integration with Red Hat OpenShift GitOps (based on ArgoCD).
Setting up ArgoCD
The OpenShift GitOps operator provides a quick, easy setup for ArgoCD with an instance defaulted to “cluster” scope. Use the following manifests to create the default instance of ArgoCD. ArgoCD is a tool that allows automated deployments and enforcement of your declarative manifests, allowing Git to be the source of truth for your cluster and application configurations.
Prerequisites:
- Red Hat Developer Hub
- OpenShift 4.x cluster
Note: If your cluster uses self-signed certs, the backend plug-in will reject the ArgoCD endpoint. You can set up Developer Hub to ignore insecure TLS, but this is only recommended in a PoC environment.
Create the required namespaces.
---
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
---
kind: Namespace
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: openshift-gitopsCreate the required OperatorGroup and subscription.
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
namespace: openshift-gitops-operator
spec:
upgradeStrategy: Default
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-operator
namespace: openshift-gitops-operator
spec:
channel: latest
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: openshift-gitops-operator
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplaceThis will create an “ArgoCD” custom resource in the namespace “openshift-gitops” called “openshift-gitops.” For integration with Developer Hub, we require an account with apiKey access.
Amend the default RBAC configuration and add extraConfig for the “openshift-gitops” Argo CD resource with the following:
rbac:
defaultPolicy: ''
policy: |
g, system:cluster-admins, role:admin
g, cluster-admins, role:admin
g, rhdh, role:admin
scopes: '[groups]'
extraConfig:
accounts.rhdh: apiKeyThis will create an account in ArgoCD called “rhdh” with the full admin role. For real workloads, the account should have a role with appropriate access.
Next, create a token for the “rhdh” ArgoCD account. From the CLI, this involves a few simple calls.
ARGOCD_SERVER=$(oc get route openshift-gitops-server -n openshift-gitops -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')
ADMIN_PASS=$(oc get secret openshift-gitops-cluster -ojsonpath='{.data.admin\.password}' -n openshift-gitops | base64 -d)
# NOTE:If your cluster uses self signed certs use -k in curl
ARGO_TOKEN=$(curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://$ARGOCD_SERVER/api/v1/session -d '{"username":"admin","password":"'$ADMIN_PASS'"}' | jq -r '.token')
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $ARGO_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"expiresIn": 0,"id": "rhdh","name": "RHDH top level token"}' https://$ARGOCD_SERVER/api/v1/account/rhdh/token
{"token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9…………"}Use this token to create a secret for Developer Hub to use within the rhdh-operator namespace.
kind: Secret
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: argo-secrets
namespace: rhdh-operator
stringData:
ARGOCD_TOKEN: <argo token previously generated>
ARGOCD_URL: <argo route in OCP>
type: OpaqueLast, add appropriate permissions to ArgoCD to create namespaces and resources. In a normal case, we would set up a separate “namespaced” instance of ArgoCD to deploy application resources to specific namespaces in the cluster.
In this demo, we are giving Argo’s controller full access for simplicity. This is not recommended for production environments.
Create a ClusterRoleBinding to give ArgoCD’s application controller cluster-admin permissions. Again, this is dangerous for anything but an isolated proof-of-concept cluster.
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: openshift-gitops-argocd-application-controller-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: openshift-gitops-argocd-application-controller
namespace: openshift-gitops
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-adminOptional: If you’re using self-signed certs, you can use the environment variable NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED to prevent Developer Hub from checking insecure connections. Update the Backstage CR with the extra variable. This may cause issues with various plug-ins. You should only use it for a PoC environment.
apiVersion: rhdh.redhat.com/v1alpha4
kind: Backstage
...
spec:
application:
...
extraEnvs:
envs:
- name: NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED
value: '0'Integrating ArgoCD with Developer Hub
First, we need to enable the dynamic plug-ins for the backend and scaffolding. Add the three entries to the dynamic-plugins ConfigMap.
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: dynamic-plugins-rhdh
namespace: rhdh-operator
data:
dynamic-plugins.yaml: |
includes:
- dynamic-plugins.default.yaml
plugins:
...
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/roadiehq-backstage-plugin-argo-cd-backend-dynamic
disabled: false
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/backstage-community-plugin-redhat-argocd
disabled: false
- package: ./dynamic-plugins/dist/roadiehq-scaffolder-backend-argocd-dynamic
disabled: falseAdd an ArgoCD section to the Developer Hub app config ConfigMap to allow connections with our service account.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: app-config-rhdh
namespace: rhdh-operator
data:
app-config-rhdh.yaml: |
app:
title: My Red Hat Developer Hub Instance
...
argocd:
appLocatorMethods:
- type: 'config'
instances:
- name: clusterargo
url: "${ARGOCD_URL}"
token: "${ARGOCD_TOKEN}"
projectSettings:
clusterResourceWhitelist:
- group: ''
kind: 'Namespace'
# Only the listed resources will be allowed
namespaceResourceWhitelist:
- group: 'apps'
kind: 'Deployment'
- group: ''
kind: 'Service'
- group: 'route.openshift.io'
kind: 'Route'Update the Backstage CR to use the additional secret we created for ArgoCD.
apiVersion: rhdh.redhat.com/v1alpha3
kind: Backstage
metadata:
name: developer-hub
namespace: rhdh-operator
spec:
application:
...
extraEnvs:
secrets:
- name: github-secrets
- name: argo-secretsViewing Argo applications in Developer Hub
Create a new component in Developer Hub either through a template or manually.
apiVersion: backstage.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
namespace: default
annotations:
...
argocd/app-name: quarkus-app-openshift-blog-rhdh
name: quarkus-app-openshift-blog
title: quarkus-app-openshift-blog
tags:
- quarkus
- java
- maven
...Notice the “argocd/app-name” annotation. This tells the Developer Hub plug-in which name to look for in ArgoCD to tie to the component. When an application with that name is created, the plug-in will look for it in ArgoCD and display its current status on a component’s page (Figure 1).
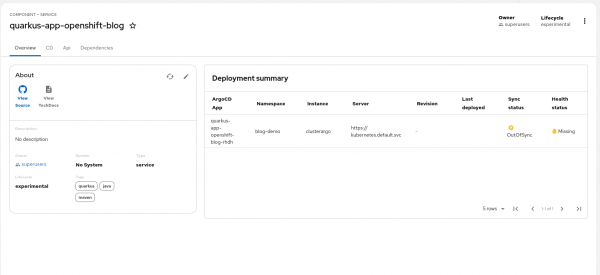
If multiple ArgoCD applications apply to a component, you can use “argocd/app-selector” to group them based on labels. Refer to the RoadieHQ ArgoCD Plugin for Backstage documentation for more details. If no applications with the selector are present in ArgoCD, the user will receive a 403 error.
Wrap up
This article demonstrated how to integrate ArgoCD with Red Hat Developer Hub. This integration gives powerful insight into your application status, which is a great start to your Developer Portal journey. Be sure to explore all of the dynamic plug-ins to get the most out of Developer Hub.
