Observability is more than just reactive monitoring of failing systems; it's a culture of understanding your application and platform environment. It's about making informed, data-driven decisions to build a stable and reliable foundation for your business. In any high-performing organization, observability should be at the core of its operations. The latest Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift release leverages the reliability, security, and velocity of Red Hat OpenShift to address one of the major pain points of OpenStack: day-2 operations. This article introduces the Telemetry Operator, a tool for customizing observability in OpenStack Services on OpenShift.
Unified observability
This new foundation presents an opportunity to rethink our observability offering and build a better experience. As a first step, we are tailoring OpenShift monitoring capabilities through the Telemetry Operator to begin presenting data in unified observability dashboards (Figure 1). Our goal is to continue this effort with other tools and telemetry, providing a single, comprehensive view of your entire environment.
We will explore how to configure these features with a special focus on the metrics you can collect. We will also explore other capabilities like logging and autoscaling in upcoming blogs.
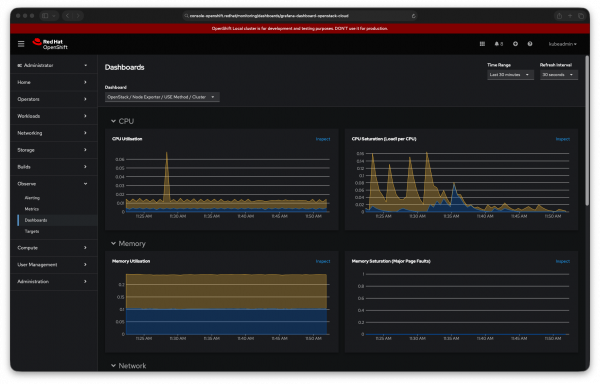
Monitoring OpenStack services with the Telemetry Operator
The OpenStack Operator automatically installs and enables the Telemetry Operator. You configure it when deploying the OpenStack Control Plane (see a sample configuration in Chapter 4. Creating the control plane | Deploying Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift).
While the Telemetry Operator offers features like alerts, logging, autoscaling, and power monitoring, it only enables metrics collection by default. This default configuration gathers three types of metrics:
- OpenStack infrastructure metrics leveraging kube-state-metrics (OpenStack Services on OpenShift services running on OCP metrics).
- OpenStack control plane metrics through OpenStack Ceilometer (OpenStack services metrics), mysqld-exporter (control plane database metrics) and RabbitMQ (control plane shared queue metrics).
- OpenStack data plane metrics with the use of node exporter (individual node system metrics), KEPLER (power monitoring metrics), openstack-network-exporter (OVS networking metrics) and Podman exporter (containers in the dataplane metrics).
Some of these metrics are opt-in. Database metrics via mysqld-exporter are opt-in. Power monitoring via KEPLER is opt-in and currently in Technology Preview.
Telemetry operator metrics
The easiest way to access to the metrics collected by the Telemetry Operator is by leveraging the openstackclient.
$ oc exec openstackclient -- openstack metric list --disable-rbac
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| metric_name |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| ceilometer_cpu |
| ceilometer_disk_device_allocation |
| ceilometer_disk_device_capacity |
| ceilometer_disk_device_read_bytes |
| ceilometer_disk_device_read_latency |
| (...) |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+List all the metrics collected by Telemetry Operator.
The openstackclient is deployed conveniently by default and it can be used to get a quick view of your OpenStack Services on OpenShift services, including of course, Telemetry Operator.
Telemetry operator queries
The openstackclient can also be used to issue PromQL queries and retrieve information from your OpenStack Services on OpenShift deployment.
For example, before your hypervisors start swapping or triggering the OOM killer, this query shows you which nodes have less than 15% of their total memory available:
$ oc exec openstackclient -- openstack metric query '((node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes) * 100) < 15'
+--------------------+-------------------------------+-------------------+
| instance | fqdn | value |
+--------------------+-------------------------------+-------------------+
| 172.20.250.18:9100 | compute2.ctlplane.localdomain | 76.79894520097449 |
+--------------------+-------------------------------+-------------------+Issue PromQL queries through the OpenStack CLI.
Telemetry operator dashboards
The Telemetry Operator includes a set of pre-built dashboards that are disabled by default and can be enabled with just the flick of a switch.
These dashboards can be easily accessed from the Observe > Dashboard panel, right with other dashboards used for OpenShift administration.
Currently, the set of provided dashboards include:
- OpenStack Ceilometer VMs easily observe the resource utilisation of Nova VMs.
- OpenStack Utilization Saturation and Errors (USE) method per cluster and per node. USE panels for the cluster and per each dataplane node.
- OpenStack Network allows quick access to OVS/OVN metrics from your deployment.
- RabbitMQ provides deep insights into the state of RabbitMQ nodes used in the OpenStack Services on OpenShift deployment.
- OpenStack VMs network traffic: Get all the details of inbound and outbound traffic for all your VMs.
The future of OpenStack observability
The Telemetry Operator, with its powerful metrics collection, PromQL querying capabilities, and pre-built dashboards, marks the first step forward on the road to a significantly better OpenStack observability. By integrating seamlessly with OpenShift's robust monitoring ecosystem, OpenStack Services on OpenShift provides a unified and comprehensive view of your entire environment. This is just the beginning. You can expect further enhancements and capabilities in upcoming releases and articles, as we continue to refine and expand the observability offering for OpenStack.
