The OpenStack cloud infrastructure has always efficiently monitored the utilization of its compute services and schedule workloads according to the available resources on the compute hosts. That was on day one when the virtual machine (VM) workload was initially scheduled. But what about day two? How can we manage workload rebalancing in the event of host downtime, planned and unplanned? How can we avoid the occasionally pesky “noisy neighbor?" Fortunately, there is a way: Introducing the Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift workload optimization operator in Feature Release 4.
What to expect
Users can expect optimized workload distribution and reduced infrastructure hotspots caused by running an imbalanced workload after creation.
Users can also expect reduced operational costs by balancing the workload. We can enable better infrastructure resource usage, which can result in:
- Lower hardware needs.
- Reduced utilities (power, cooling, etc.).
- Fewer hotspots and congestions means fewer service outages and scrambling engineers.
- Enhanced performance: A balanced infrastructure can facilitate more workloads, more demands, and eventually business growth.
OpenStack Workload Optimization
OpenStack Workload Optimization (OWO) is based on the OpenStack Watcher upstream project, which provides a robust framework to help you achieve a wide range of infrastructure resource utilization goals, ultimately reducing data center operating costs.
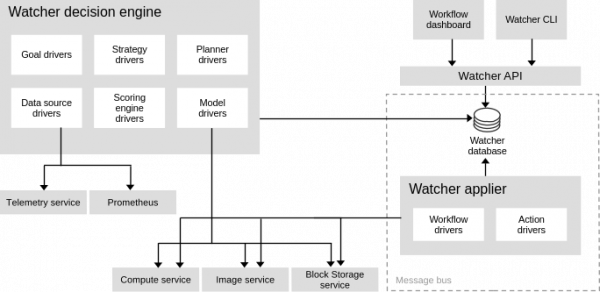
The optimized service framework includes a metrics receiver, a complex event processor and profiler, an optimization processor, and an action plan applier.
Similar to the other control plane services, the OWO runs on top of the OpenStack Services on the OpenShift cluster and interacts with the different services, as depicted in Figure 1.
To install the OWO operator (currently in tech preview), create the following CR in the openstack-operators project and apply it as follows:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: watcher-operator
namespace: openstack-operators
spec:
name: watcher-operator
channel: stable-v1.0
source: redhat-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
oc apply -f watcher-operator.yamlAlternatively, you can just choose it from the operator-catalog in the OpenShift console. Red Hat will merge the OWO-Watcher operator into the openstack-operator at GA time (Figure 2).
Once set up, the OpenStack Services on OpenShift administrator can use the optimization service to create a workflow that results in moving VM workloads within a given environment.
For example, to reduce the number of compute nodes required to save energy, an administrator can create a VM consolidation workflow. At a high level, the workflow resembles Figure 3.
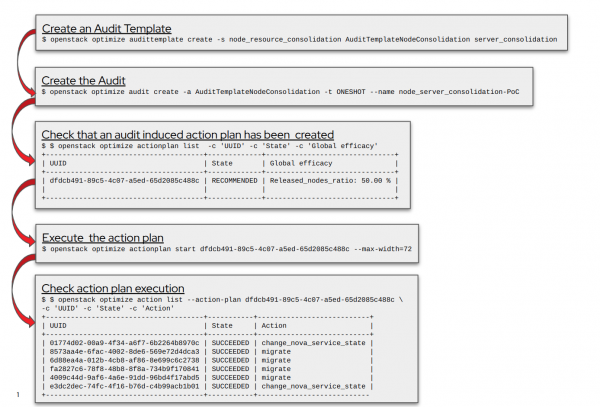
The optimization workflow can go through the OpenStack CLI or the Horizon UI. Here is a quick demo using OWO from the Horizon UI.
OWO workflow creation
In the OWO workflow creation, we need to know a few key concepts:
Goals: Represents the main objective of an optimization. For example, you might have a goal to save energy, consolidate servers, or balance workloads across your cloud. Each goal is associated with one or more strategies that define how to achieve that objective.
Strategies: The "how-to" for achieving a goal. Strategies are the algorithms and logic that OWO (watcher) uses to analyze the current state of your cloud and determine the best course of action. They are pluggable and customizable. You can use the default strategies provided with OWO (watcher) or create your own to meet your specific needs. Examples of strategies include basic offline consolidation, VM workload consolidation, and workload balance migration.
Audit templates: Audit templates are reusable configuration for an audit. Think of it as a preset that defines what you want to do and specifies the goal, strategy, and any other parameters for an optimization task. This allows for consistency and makes it easier to run the same type of audit multiple times.
Audits: This is the process of running an optimization. An audit is a request for OWO (watcher) to analyze your cloud and generate an action plan. It can be triggered manually or automatically. You can launch a one-time audit, schedule them to run continuously, or trigger them based on specific events in your cloud. When an audit runs, the OWO (watcher) decision engine uses the specified strategy to generate a solution.
Action plans: This is the output of a successful audit. An action plan is a series of steps that need to be taken to achieve the desired optimization and presented for review. Before any changes are made, the action plan is in a recommended state, allowing an administrator to approve or deny it. Once approved, the action plan moves to an ongoing state and executes the actions.
Actions: The actions are the individual tasks within an action plan. These are the specific operations that OWO (watcher) will perform on your cloud. Examples of actions include live migrating a virtual machine, changing the power state of a host, or even evacuating of a complete set of hosts (i.e., a zone) to enable maintenance or other day-2 operations. The OWO (watcher) applier is the component responsible for executing these actions.
Figure 4 is an example of a zone migration at a high level.

Wrap up
Based on OpenStack watcher, OWO is a powerful new tool that helps cloud administrators manage their workloads more efficiently and productively. For more information, visit our official documentation.
