This article explains two methods that I use frequently to troubleshoot both Red Hat OpenShift and middleware problems. These two methods apply to different scenarios rather than the same problem:
- Fault tree analysis (FTA) helps you find the root cause of a problem by eliminating components.
- The PIOSEE framework (Problem, Information, Options, Select, Execute, Evaluate) is for critical production environments where you must take action immediately.
Finally, this article explores how AI tools, such as gen AI, can help you use these methods to speed up root cause analysis and decide on the best course of action. While this moves beyond our typical technical discussions, it provides frameworks for fault scenarios that can help you from now on—even with gen AI or agent-based AI tools.
Fault tree analysis (FTA)
Fault tree analysis, illustrated in Figure 1, is a top-down method for tracking system failures. You can use it to find application deployment issues in environments like OpenShift 4.
The aviation industry commonly uses this method, and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) relies on it. Because it is not specific to aviation, other industries apply it to troubleshoot tasks in the IT field.
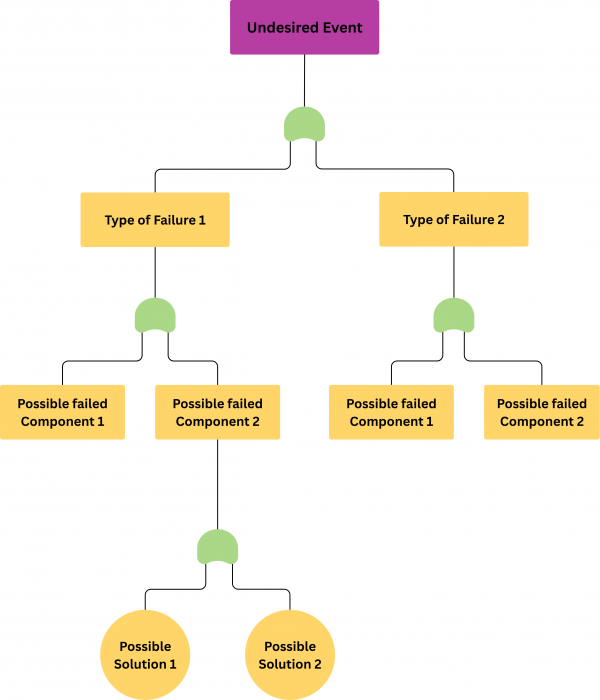
Problematic scenarios
These scenarios illustrate common challenges where applying a structured troubleshooting method can prevent small issues from becoming major outages.
Ineffective diagrams for container image troubleshooting
After identifying a container image change that caused a problem, the deployment and development teams discussed the root cause. They listed the events that contributed to the issue and realized their current diagrams did not help them analyze the problem.
Memory fluctuations and cluster instability
A new server deployment caused memory use to fluctuate, which affected the entire OpenShift cluster. In this complex scenario, the node is failing and might crash. This small problem could lead to a significant outage for other applications in the cluster.
OOMKilled errors during OpenShift migration
A Spring Boot application that uses the Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI) for the Red Hat build of OpenJDK was moved from OpenShift 3 to OpenShift 4.14+. The application is now failing due to a cgroups OOMKilled error, even though the deployment has not changed since OpenShift 3.11. For example:
Jun 08 21:58:58 dev-example kernel: Memory cgroup out of memory: Killed process 2826157 (vector) total-vm:1570664kB, anon-rss:1039172kB, file-rss:45312kB, shmem-rss:0kB, UID:0 pgtables:3116kB oom_score_adj:-997When to use fault tree analysis
While this method was not created for IT troubleshooting, it provides high-level guidance for investigations. This method is simple if:
- The team understands the system overview.
- The team includes experts to help.
- The team will have more success knowing the problematic components of the deployment
Fault tree analysis helps you solve problems using a structured approach. These three use cases show how this method can reduce recovery time and help you find the specific root cause faster.
PIOSEE framework introduction
The PIOSEE method, originally from the aviation industry, helps you troubleshoot problems in production environments. PIOSEE stands for Problem, Information, Options, Select, Execute, and Evaluate, as described in the following table and illustrated in Figure 2. You can move through these steps quickly, moving to the next stage as soon as the current one is complete in a mandatory sequence of events.
| Step | Name | Action |
|---|---|---|
| P | Problem | Diagnose the problem. |
| I | Information | Gather as much information as possible. |
| O | Options | Verify which options apply and consider the trade-offs. |
| S | Select | Select an option based on time and trade-offs. |
| E | Execute | Execute the option as closely as possible to the defined procedure. |
| E | Evaluate | Evaluate the option based on the output. |
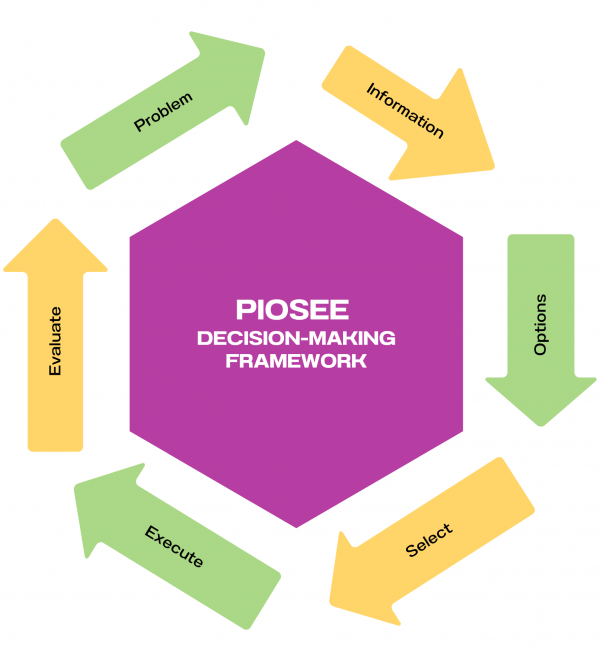
Each step requires a specific action. For example, during the first step (Problem), you should verify the specific issue in the most rational and direct way possible.
Problematic scenarios
These scenarios show how the PIOSEE framework helps manage complex global handovers and technical ambiguity, improving performance by helping you solve problems faster. The following scenarios describe this.
Global handovers during regional outages
Problem: After a new feature deployment, a Spring Boot application in OpenShift is failing in a crash back loop.
Root cause: The team later identified a cgroups OOMKilled error.
How to use this method: Because the crash occurred across several regions, teams collaborated globally to find the cgroups root cause. Explaining the problem status and next steps between teams can be difficult, which slows down handovers. The PIOSEE framework helps the next shift understand the investigation's current stage and the required steps using clear language.
Ambiguous next steps for production fixes
Problem: After identifying the root cause of a production problem, the deployment team received clearance for the next update. However, during the review, the team lacked a clear next step. This ambiguity delayed the deployment even though the handover was complete.
How to use this method: In this case, the PIOSEE framework clarifies the next step. If the current process is unclear, the team knows how to fall back (in objective terms of deployment).
Best practices for using PIOSEE
Using the PIOSEE framework is an effective way to debug live problems and improve efficiency. However, there are a few points to discuss:
- Train the team on how to use the framework correctly
- The framework discussion should not take more time than the solving the actual problem. This includes the time spent on communication and tools.
- Discuss the implementation openly rather than imposing it. Open communication and transparency allow teams to suggest other methods.
The PIOSEE framework is an effective way to debug live problems and transition investigations between teams. Finally, it can be used for discussions after the post-mortem and later due diligence. It also provides a structure for post-mortem discussions and later reviews.
Containment and contingency plans
Having a containment plan and a contingency plan are helpful strategies, though they are not heuristics or methodologies. You can use them with the PIOSEE phases to speed up the recovery process.
A containment plan is a set of steps to isolate a problem and limit its impact.
A contingency plan might include having a load balancer or a reliable version of your application ready to deploy immediately.
AI as a tool for troubleshooting
AI tools, such as gen AI, can help you speed up the following processes and complement the methods described earlier:
- Provide high level ideas and causes
- Explain low-level details and next steps
- Documentation
However, consider the following for both processes:
- Generic ideas from AI can distract from the investigation and delay finding the root cause.
- Low-level details might be outdated or incorrect depending on the AI's sources.
- AI might not cite sources, making it harder to verify information.
These tools produce great results, but you must review the output carefully to stay on track.
To keep this article concise, I will not go into detail here. I may cover this in a future article. AI tools can help with many tasks, such as scraping data, generating statistics and code, or reviewing documentation. Here, I wanted to highlight tips for combining AI with FTA and PIOSEE.
Conclusion
In summary, this article covers two troubleshooting methods: FTA and PIOSEE. Both help speed up your work and guide your next steps. FTA focuses on root cause analysis, while PIOSEE helps you take immediate action and find your way through a live problem.
Finally, we looked at how AI tools can complement these methods. Due to the article's scope, we focused on specific uses within these frameworks.
Additional resources
For specific inquiries, open a case with Red Hat support. Our global team of experts can help you with any issues.
Special thanks to Joshua Brandenburg for his leadership on these issues over the years.
