Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.14 is a lightweight, enterprise-grade integration toolkit designed to connect applications and services across hybrid environments. This release expands integration capabilities with newly supported OpenSearch, Azure Data Lake Storage, and Mail Microsoft OAuth (via Microsoft Exchange) components. Developers gain productivity enhancements in the Kaoto integration designer, now supporting visual data mapping for both JSON and XML, along with improved usability and automation features. For operations, the new Camel dashboard (Developer Preview) provides real-time visibility into integration health on Red Hat OpenShift, while the fully supported Artemis Plugin for HawtIO enables direct management of AMQ brokers.
Apache Camel enhancements
The Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.14 introduces several enhancements and updates to the framework.
Red Hat refined and added support for the following components:
- Mail Microsoft OAuth provides OAuth2 support for the Mail component, enabling connections to Microsoft Exchange Online via Azure Active Directory.
- OpenSearch (jvm-only on Quarkus) allows you to interface with an OpenSearch 2.8.x API.
- Crypto PGP encrypts and decrypts messages using Bouncy Castle OpenPGP API.
- Azure Data Lake Storage for storing and retrieving files from Azure Storage Data Lake Service
- XML JAXP type converters and parsers
For the complete list of supported components, check the reference guides in the product documentation.
Other notable changes include: YAML DSL enforces camelCase syntax (e.g., setBody), removed support for kebab-case (e.g., set-body) in the YAML DSL, and camel.main.xxx replaces the deprecated camel.springboot.xxx properties. Automatic upgrade recipes handle this change.
Several improvements to already supported components, such as:
- camel-http added
multipartUpload=truefor native multipart file uploads, OAuth Bearer token authentication, andskipcontrolheadersto automatically ignoreCamelHttpcontrol headers between multiple HTTP calls. - camel-kafka added
topicMustExiststo verify topic presence at startup,breakOnFirstError=truewithbatching=truefor high-throughput reliability, and transacted/transactionalId options to configure producer transactions directly on the endpoint. - camel-sql allows unnamed SQL queries to use a Map body (with ordered parameters) and delivers significant performance gains for batch inserts and updates.
- camel-aws-s3 added the
moveAfterReadoption to automatically relocate processed files to a sub-folder within the same bucket. - File-based components: (camel-file, camel-ftp, camel-azure-files, camel-smb) now use
PollDynamicAwarefor optimized dynamic polling, enabling faster poll and pollEnrich for endpoints (like fileName) computed at runtime. - camel-smb: Introduced
autoCreateto automatically create missing start directories and aligned URI syntax to use the path in the context-path instead of query parameters for consistency with other file components. - camel-xslt now accepts transformation input from message headers or variables.
- camel-micrometer: Introduced
app_infogauge exposing Camel context, runtime, and version details, and a newcamel_exchanges_last_timestampgauge to monitor how long the application has been idle. - camel-test: Added
@StubEndpointsto easily stub components (e.g., Kafka) for unit testing andAutoStartupExcludePatternto disable specific routes during test startup. - camel-platform-http: A component in SpringBoot based on Undertow can now expose extra Micrometer metrics as "undertow.sessions.*" and "undertow.threads.*"
Recipient list, split, multicast:
- In parallel mode, you can set
synchronous=trueto use bounded thread-pool execution (Camel 2 style). - With
synchronous=false, Camel’s reactive engine uses all available threads for sub-tasks.
Logging and diagnostics:
- Consumers now eagerly initialize MDC logging so details like routeId appear in logs during startup and creation.
- Intercept EIP now logs more context when intercepting messages (includes node id and related info).
- FailedToStartRouteException now shows
file:line-numberwhere the failure occurred.
Management and operations:
- You can now control routes by group (e.g., stop a set of routes at once).
- Stopped routes retain JMX MBeans for post-stop diagnostics.
- Added JSON dump methods for exporting route and processor statistics.
- Extended JMX management to BackOff, ForegroundTask, and BackgroundTask with richer logging.
- Management and observability services are exposed via dedicated management port (:9876, for security and isolation).
REST DSL validation:
- Enhanced request validator for both built-in and camel-openapi-validator.
- Added fine-grained validation control via camel.rest.validation-levels, allowing selective enforcement (e.g., ignore missing query params).
- Introduced response validation with
clientResponseValidation=true, ensuring responses comply with OpenAPI schema. - Improved payload validation based on OpenAPI definitions.
Code Camel Quarkus landing page
The original Code Quarkus landing page was split to clarify support differences between the Red Hat build of Quarkus and the Red Hat build of Apache Camel. Visit the new Code Camel Quarkus page.
Enhanced Kaoto advanced data mapping and productivity
The Kaoto Data Mapper now supports JSON alongside XML, allowing users to serialize and deserialize JSON structures, attach JSON schemas for tree-view mapping, and create cross-format mappings between JSON and XML (Figure 1). These enhancements make Kaoto more powerful, intuitive, and aligned with modern integration design workflows.
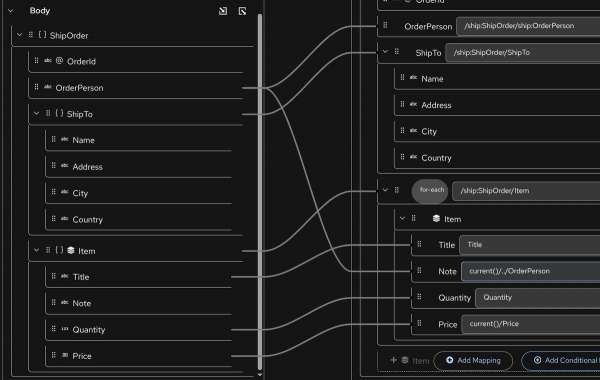
XML-schema improvements:
- Full support for
xs:extensionandxs:restriction. - Field type icons in the tree view.
- Display of
minOccursandmaxOccursattributes. - Better handling of relative XPath with parent (
..) notation andcurrent().
Designer usability improvements:
- Beans EIP now lists defined beans in Camel routes (Figure 2).
- JDBC component shows default and dataSource options with selectable beans.
- Enum-type options are now prefilled for quick selection.
- Drag and drop enabled by default for easy reordering and movement.
- Core editing tools: copy, paste, quick duplicate, undo, and redo.
- Automatic Maven dependency updates in
pom.xmlwhen saving new endpoints. - Intelligent form suggestions for configurations, expressions, and application.properties.
- New canvas menu to add routes, configurations, error handlers, and toggle node visibility.
- Quick step deletion via the delete key.
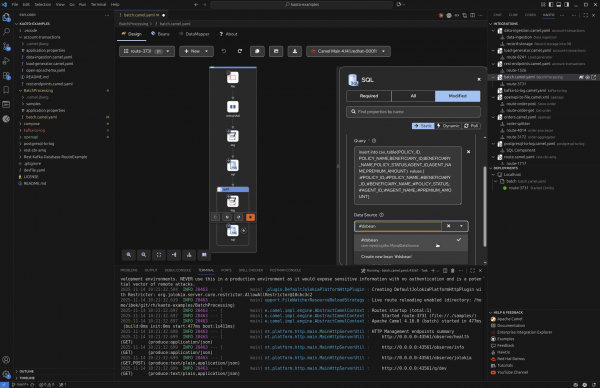
CLI integration accelerator enhancements
Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.14 delivers upgrades to Camel JBang for faster development, easier debugging, and better runtime control.
Modernized runtime and tooling:
- Camel JBang now defaults to JDK 21.
- The camel export
--verboseoption provides detailed export logs to simplify troubleshooting.
Improved commands and runtime control:
- The outputs of
camel getandcamel psare now cleaner by default. Use--remoteto show remote counters. - You can control entire route groups using
camel cmd start-groupandcamel cmd stop-group. You can dynamically enable or disable processors withcamel cmd enable-processorandcamel cmd disable-processor. - The
camel runcommand now supports--portfor Main, Spring Boot, and Quarkus, preventing port conflicts when running multiple instances.
Enhanced debugging and testing:
- The camel debug runs faster, supports Spring Boot projects directly (camel debug pom.xml), and can now step to a specific route index for targeted debugging.
- The new camel test plugin is for bootstrapping automated route tests (
camel test init,camel test run), using the Citrus framework.
Improved integration and YAML support:
- Route dumps to YAML are now compatible with Kaoto.
- The
camel cmd sendcommand can send messages without a running integration (specify integration name or PID to reuse one).
Camel dashboard on OpenShift
Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.14 introduces the Camel dashboard (developer preview), offering a unified view into the key metadata, health, and performance of your Camel applications running on OpenShift (Figure 3).
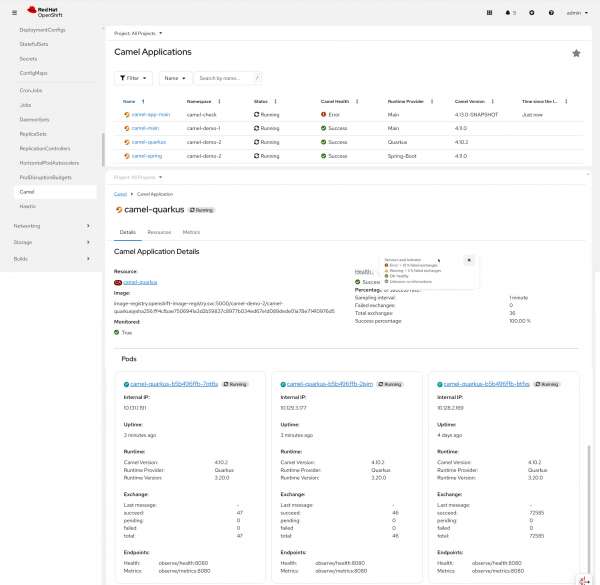
Designed for simplicity and efficiency, the dashboard provides near real-time insights into your caravan of integrations without requiring complex setup or heavy infrastructure. It focuses on the following key operational metrics:
- Message exchange counts (in-flight, total, failed)
- Success and failure rates
- Time since last successful message
- Resource usage (CPU, memory, network)
This lightweight tool enables quick visualization of system activity across multiple Camel instances, helping teams spot issues early, optimize performance, and maintain system reliability.
When a Camel application enables monitoring and management via Jolokia, the dashboard automatically provides a direct link to the HawtIO diagnostic console (Figure 4), enabling deeper inspection and troubleshooting without leaving the OpenShift environment.
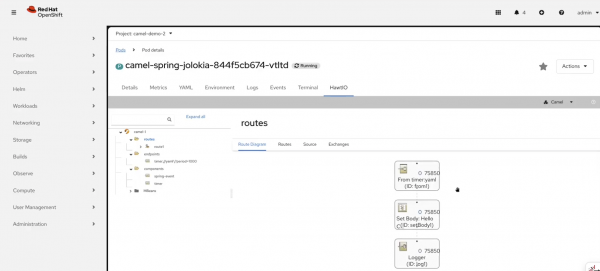
HawtIO Artemis plug-in and flight recorder
The recently reintroduced Artemis plug-in for HawtIO is now fully supported. Artemis plugin is purpose-built for managing the AMQ broker. The plug-in offers a web-based interface to monitor and control Artemis brokers directly from the HawtIO console. For example, it enables browsing and managing queues, sending and receiving test messages, inspecting connections and consumers, and performing administrative actions such as pausing, resuming, or purging queues. Designed for operational efficiency, the plug-in integrates with the latest AMQ broker (7.13) capabilities, giving users enhanced visibility and control over their messaging infrastructure.
This HawtIO release includes a refreshed diagnostics plugin (in tech preview). This plug-in allows developers to query and interact with the running JVM using the DiagnosticCommandMBean and HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean interfaces. A key feature of this plug-in is its Java Flight Recorder (JFR) utility (Figure 5).
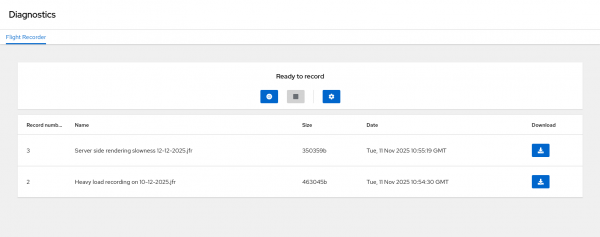
JFR is a low-overhead diagnostics and profiling tool built directly into the JVM. This utility allows you to:
- Configure and start new recordings.
- Check the history of previous recordings.
- Download .jfr files for analysis.
You can open downloaded JFR files using tools like Java Mission Control (JMC), available in the Upstream Eclipse Mission Control.
Summary
The Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.14, a lightweight, enterprise-grade integration toolkit, introduces several key enhancements for developers. This release expands its integration capabilities with newly supported components like OpenSearch, Azure Storage, and Mail Microsoft OAuth.
Developers will benefit from productivity boosts in the Kaoto integration designer, which now features visual data mapping for both JSON and XML. Operational visibility is also enhanced with the new Camel dashboard for real-time integration health on OpenShift, the fully supported HawtIO Artemis plug-in for managing AMQ brokers, and HawtIO Diagnostics plugin with Java Flight Recorder (JFR) utility for low-overhead diagnostics. Additionally, Camel CLI tools are modernized, and management features are improved with new route group controls and REST DSL validation enhancements. This update also includes enforcing camelCase in YAML DSL and replacing deprecated Spring Boot properties.
Additional resources:
- Try Camel in Developer Sandbox
- New examples and best practices
- HTTP Large File Streaming
- Platform HTTP act as reverse proxy
- Camel Observability Services
- Salesforce REST API and CDC Integration with Camel
- ActiveMQ Artemis broker using AMQP
- Upload a file to an AWS S3 bucket
- TCP communication with Netty using a custom codec to encode and decode the data over the wire
- Send and receive messages from Spring Redis in Quarkus
- Camel on SpringBoot Development Guide
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.14 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.13 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.12 (community)
- What’s new in Apache Camel 4.11 (community)
- What's new in Kaoto 2.8 (community)
- What's new in Kaoto 2.7 (community)
- What’s new in Red Hat build of Apache Camel 4.10 (previous release)
