Migrating a large codebase from one language to another can be time-consuming. What if an AI tool could do the heavy lifting for you? Our team recently needed to migrate our Bash container test suite, container-common-scripts, to a new Python-based CI suite (container-ci-suite). I decided to experiment with the Cursor AI code editor to see if it could speed up the process. This article walks how easy it is to migrate a project from one programming or scripting language to another with Cursor.
Getting started
To get started, you first need to install the Cursor AI code editor. Then, log in with your Red Hat account.
Once you've logged in, let's run the editor. I enabled the following models in the Cursor AI code editor for the migration, as shown in Figure 1:
- claude-4-sonnet
- claude-4-sonnet-1m
- gpt-5
- grok-code-fast-1
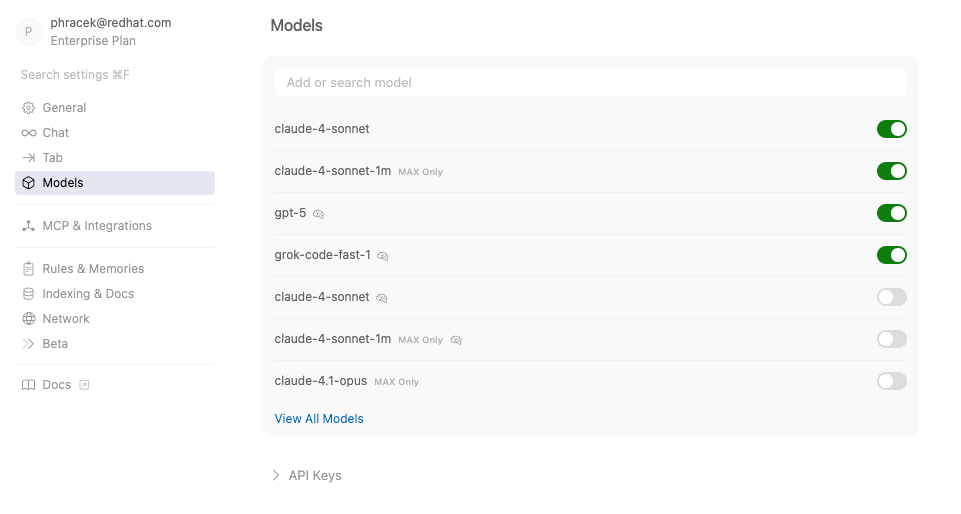
Starting the AI migration
First, clone the repository that will be migrated. For this example, we'll use the following command:
git clone git+https://github.com/sclorg/container-common-scripts.git
Next, open the project that you want to migrate in Cursor. The main Bash test suite is stored in container-common-scripts repository in the test-lib.sh file.
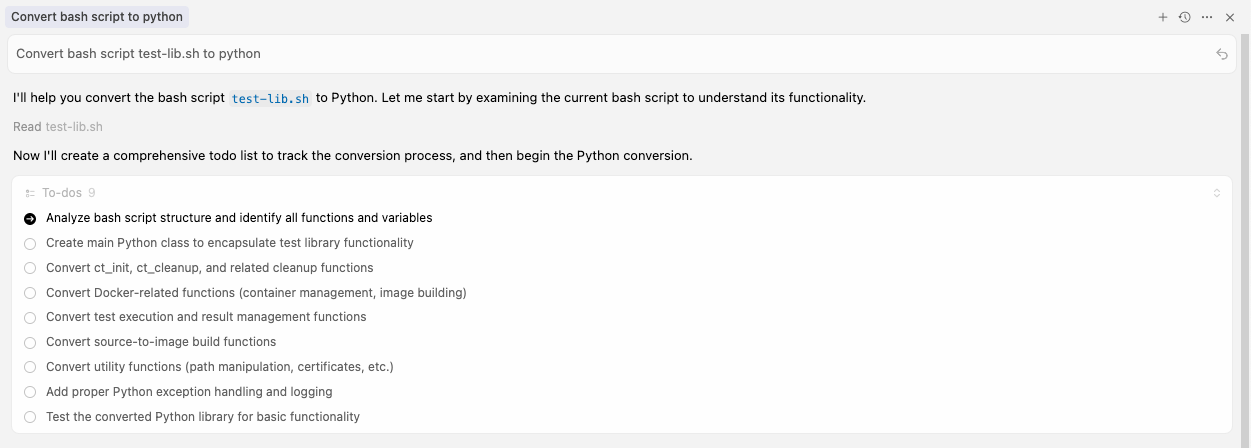
To start the conversion, you should tell Cursor what it needs to do. Now, we'll give the Cursor AI our aim for the migration:
Convert bash scripts test-lib.sh to Python
Figure 2 shows the output from Cursor.
Next, Cursor will analyze the Bash script and create a Python library, as shown in Figure 3.
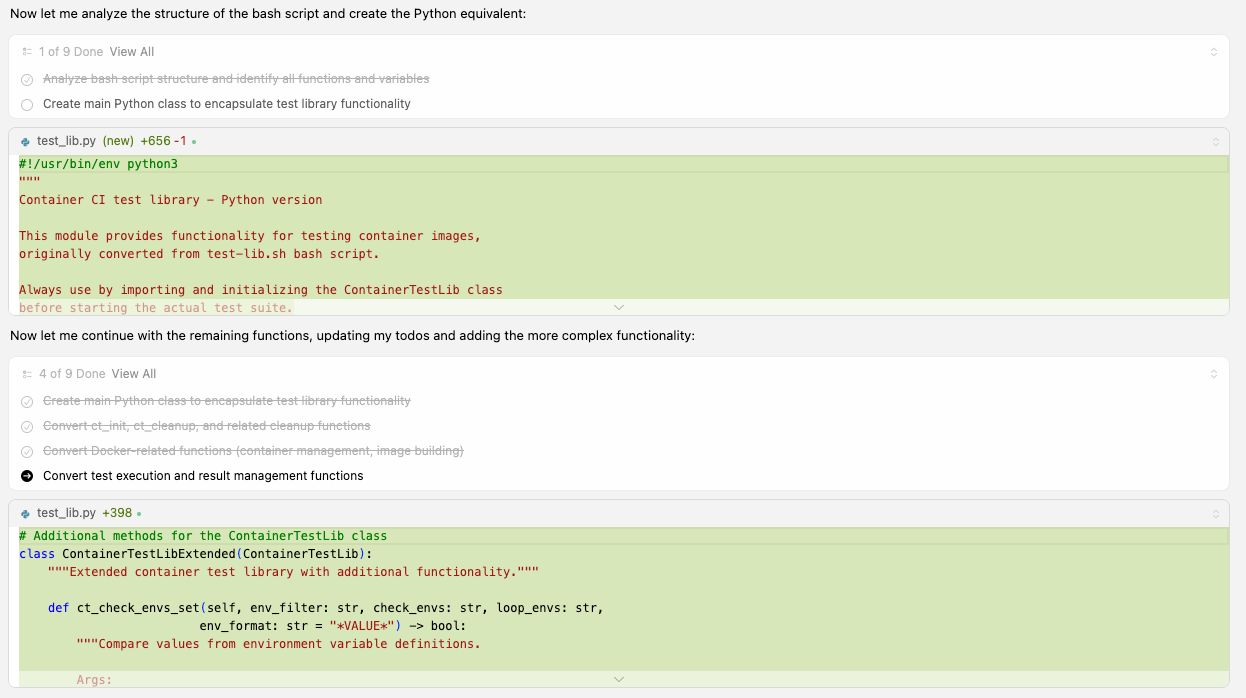
As a final task, the Cursor AI code editor automatically creates a basic test for this library (Figure 4).
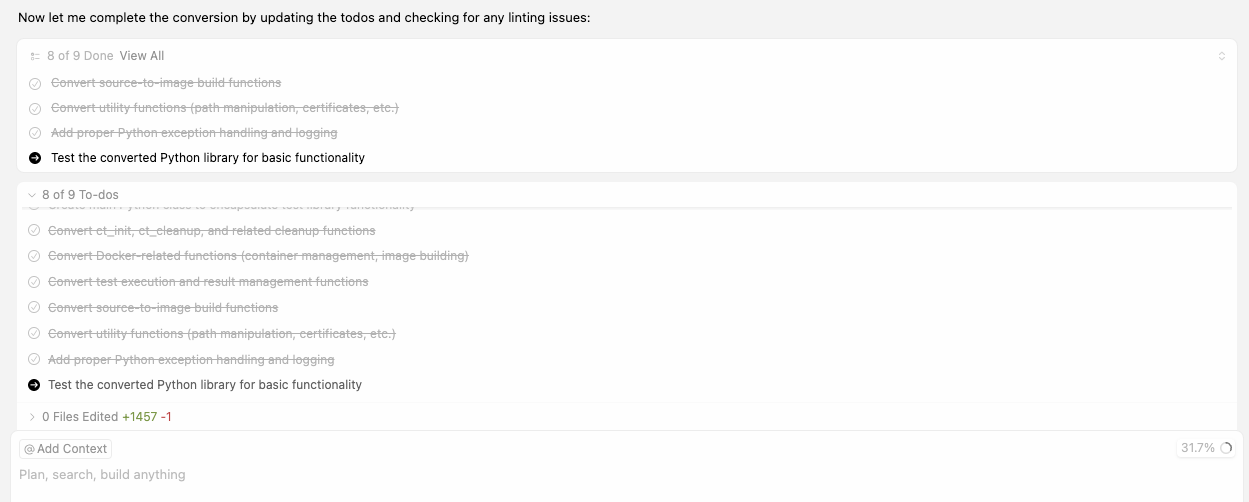
For the last step of the migration, Cursor provides a summary of what was accomplished (Figure 5).

The migration also includes a summarization of the integration and testing and a list of files that were created and modified (Figure 6).

Perfect. With that, everything is almost done.
Updating the created test suite with an existing one
Our Python-based suite is stored in container-ci-suite repository. Clone it using the following command.
git clone git+https://github.com/sclorg/container-ci-suite
The migration is complete from the Cursor side, but the container-ci-suite also includes a Python file called container_ci_suite/utils.py that contains a function called run_command. Let's use this one instead of using subprocess.run.
I asked Cursor to replace this functionality in the newly created test suite, as shown in Figure 7.
Cursor confirmed it would take on the job (Figure 8).

After executing the task, all subprocess.run commands should be replaced with utils.run_command.
As a developer, I shouldn't be fully satisfied with this migration. We also need to create a test suite for the migrated container suite. So, let's give the Cursor AI code editor a chance.
Create a PyTest suite for newly created suite
To create the test suite, let's prompt Cursor as follows:
Create PyTest suite for ContainerTestLib class
Here is Cursor's response:
**Cursor**
I'll create a comprehensive PyTest suite for the ContainerTestLib class. Let me start by creating a proper test structure.
First, let me create a tests directory and the main test configuration:First, Cursor creates a main unit test for core functionality. The next step is to create integration tests for more complex container operations. It's almost done. Cursor then creates error-handling and edge-case tests before generating a pytest configuration file and a simple test runner script.
Finally, Cursor summarizes all the tests, as shown in Figure 9.

It also summarizes the type of pytest markers, fixtures, and so on that were used (Figure 10).

Our real-world results
As soon as the migration was done, the converted library was pushed to the container-ci-suite GitHub repository by this pull request. The conversion itself was not so smooth; the library had a few issues that were fixed by pull request.
You might be wondering how the container testing went. The first container that used the new library was our httpd-container, specifically through this pull request. The tests are, in fact, passing.
Conclusion
As you can see, you can use the Cursor AI code editor with a specific AI model to migrate languages from one to the other. However, I strongly recommend having a human developer oversee the entire migration process.
This migration saved me a lot of development time; I would say around 1.5 months.
You can see the entire migration process in my GitHub documentation repository called documentation. The migration process itself is stored in a Markdown file exported from Cursor AI code editor, CURSOR_TEST_LIB_MIGRATION.md. The conversion document is stored in the CONTAINER_TEST_LIB_CONVERSION.md file.
