Bunsen is a test log processing tool. It has a nice project page providing basic information about the tool, presentations, talks, etc. In this article, we’ll focus on recently implemented web interface features that make users' life easier.
New features in Bunsen
Let’s start with a feature visible right after opening the web interface: the project chooser. Earlier versions of Bunsen started with a relatively complex search form, where some users struggled with picking the right search criteria. The new UI defaults to a simple project chooser, as shown in Figure 1.

This feature allow you to pick one of the available projects, fill the search form with reasonable defaults, and it shows results close to what the user wants. Users can take it from there and modify the search criteria intuitively.
Another new convenience feature is support for cookies. With this feature, the search criteria can be optionally saved for future reuse. This speeds up repetitive searches using similar search criteria. Unchecking the cookies check box drops all the bunsen cookies and restores "factory settings".
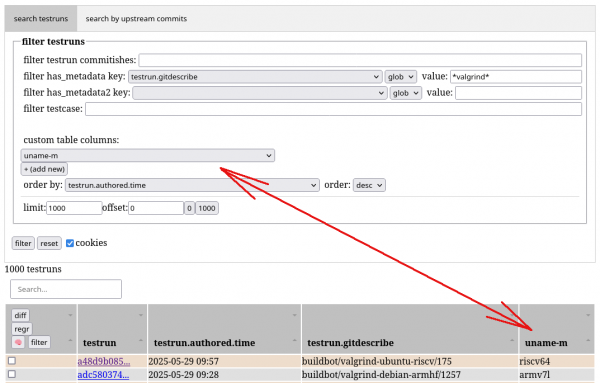
Additionally, the testrun overview now allows for customization. Additional columns may be shown, such as the uname -r column depicted in Figure 2. You can use these arbitrary columns for sorting by clicking their table header, like all the other columns.
Each testrun typically involves thousands of individual test results. One of the typical questions a Bunsen user may have is: "At what point did this break?" or "What’s the latest testrun where this testcase succeeded?" Bunsen may help answer such questions using the filter by testcase feature. Let’s use it to demonstrate how you can find a regression in the systemtap test results.
Demonstration: Filter by testcase
First, let’s assume there’s a regression somewhere among the available test runs, specifically in the const-value.exp testcase. Let’s list all the available test runs along with test results of const_value.exp, shown in Figure 3.
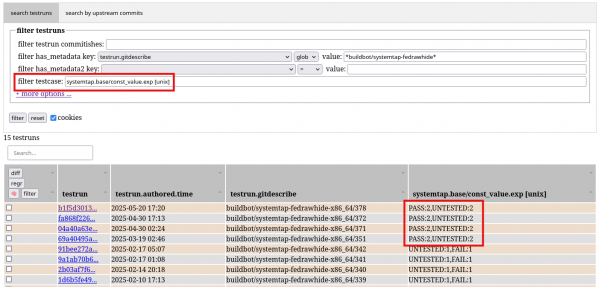
As you can see, starting from 2025-03-19, things improved. Now we can see there is a testrun hash. This identifies the Bunsen testrun. The upstream source VCS hash might be interesting too. To show that, you could use the previously introduced feature showing custom columns. The respective column name would be ‘source.gitname’. How do I know? The testrun detail shows the available metadata—just click the testrun hash (Figure 4).
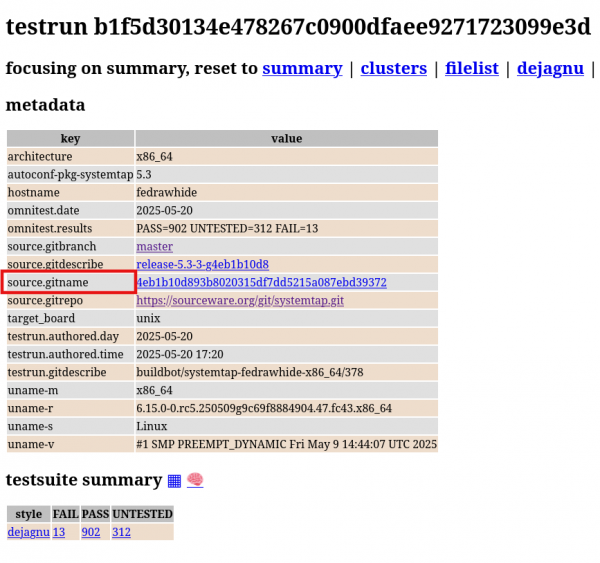
This overview shows test results coming from buildbot/systemtap-fedrawhide only. By relaxing this, more test results can be shown. It’s good to keep in mind, however, that test results coming from different sources might not be 100% comparable because the testing environment might be different.
Now, see how the search for header has two options: search testruns and search by upstream commits as depicted in Figure 5.
Let's switch to the second search by upstream commits tab. This is a new tab. It allows for focusing on upstream project Git commits and test results related to them.
Bunsen might not have test results for all the upstream commits available, but it knows the sequence of all the upstream commits within a project/branch, and can sort them and compute deltas as in the distance between commits.
To demonstrate this, let’s focus on the following systemtap commit that fixed the const_value.exp testcase at some point:
commit 22661ef175edd650cc76cc7ecd41481e72bbb489
Author: William Cohen <wcohen@redhat.com>
Date: Wed Feb 19 16:30:16 2025 -0500
Update const_value.exp C code to work with GCC15
GCC15 expects an argument declaration to match its actual use. If
they do not match, GCC15 flags that as an error. Made the function
pointer argument declarations match up with their use to eliminate
these errors.We can use this commit hash and search test results that are close to it. Specifically, we search systemtap upstream commits that are less than 35 upstream commits ("delta") far from the reference commit 22661ef1 in both directions (older and newer).
We can see that in our Bunsen database, we have testruns for upstream commits that are either 7+ days newer than the given upstream commit or 1+ day older. This way later on, we can significantly reduce the bisection iteration count on our way to get to commits that actually broke or fixed things (Figure 6).
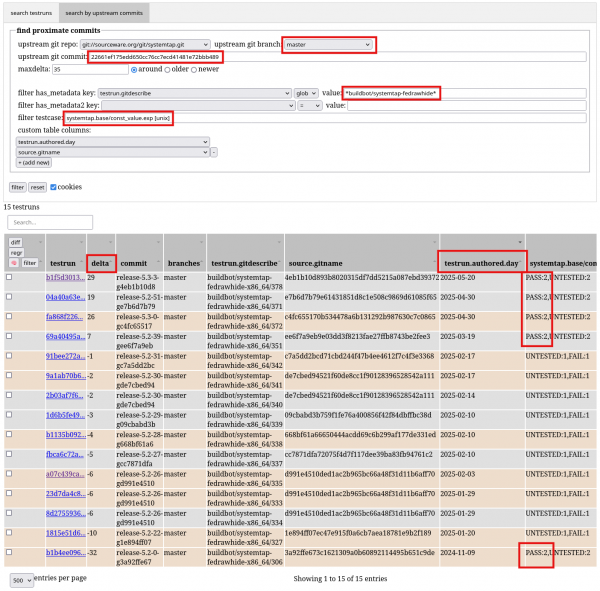
Note that under the hood this feature is based on the new r-find-testruns-with-commit command-line tool.
Wrap up
Hopefully this overview of new features was useful. Bunsen developers are focused on making the system responsive and easy to navigate and search. We expect future development on the responsiveness field, as well as using AI to analyze the test data. Your feedback is always welcome.
