macOS imposes strict limitations on the places from which you can download commands. Many of the Linux-related tools you want to use come from sites other than the App Store, so you have to change your preferences in macOS to use the commands. In this article, I show how to install a command that is not from the App Store, using the popular Helm client as an example.
Download a binary onto your Mac
Download the binary for the client you need. For example, Helm offers a variety of binaries at its GitHub repository.
Unpack the binary and add it to your PATH. I prefer to add commands in the /usr/local/bin directory. Here's how to install the current version of Helm:
$ tar xf helm-v3.9.0-rc.1-darwin-amd64.tar
$ cd darwin-amd64/
$ sudo mv helm /usr/local/bin
At this point, the warning in Figure 1 appears if you try to execute the helm command.
helm list
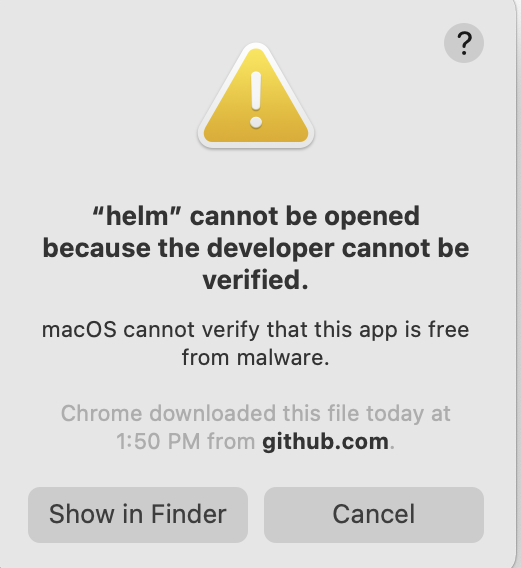
You get the same error if you try to open the application from the Finder. The problems arise because macOS keeps track of the sources for applications and is wary of applications that don't come from the App Store. You can expand the range of sources that your computer will accept, however.
Changing preferences for downloads
You can change your range of sources for applications in the System Preferences application, which is usually in your Dock on your desktop. The option you want is on the Security & Privacy pane, which by default allows downloads only from Apple's App Store. You have to click the lock icon at the bottom left of the page, enter your admin password, and then change the option to App Store and identified developers.
If App Store and identified developers is already checked but helm did not run, select Allow anyway (Figure 2).

After you change the security setting, installation starts:
Helm stores cache, configuration, and data based on the following configuration order:
- If a HELM_*_HOME environment variable is set, it will be used
- Otherwise, on systems supporting the XDG base directory specification, the XDG variables will be used
- When no other location is set a default location will be used based on the operating system
By default, the default directories depend on the Operating System. The defaults are listed below:
| Operating System | Cache Path | Configuration Path | Data Path |
|------------------|---------------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------|
| Linux | $HOME/.cache/helm | $HOME/.config/helm | $HOME/.local/share/helm |
| macOS | $HOME/Library/Caches/helm | $HOME/Library/Preferences/helm | $HOME/Library/helm |
| Windows | %TEMP%\helm | %APPDATA%\helm | %APPDATA%\helm |
Usage:
helm [command]
Available Commands:
completion generate autocompletion scripts for the specified shell
create create a new chart with the given name
....
....
saving session....completed
[Process completed]
Once installation has completed, run the helm command again:
$ helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.8.2", GitCommit:"6e3701edea09e5d55a8ca2aae03a68917630e91b", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.17.5"}
This output shows that Helm has been installed successfully. A similar process should allow you to install other command-line tools on macOS, such as the oc client for RedHat OpenShift.
