
In the learning path Overview, we explored the benefits of auto-importing HyperShift clusters with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (RHACM). Now it's time to prepare the environment to make this automation a reality.
In this learning path, you'll learn how to correctly configure RHACM to automatically discover HyperShift clusters provisioned in your environment. We'll cover everything from tool installation to complete discovery validation.
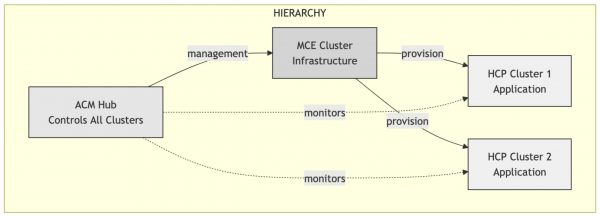
Understand the terminology
Before we begin, let's clarify the terms we will use throughout the lessons:
Term | What it is | Function | Practical example |
RHACM hub cluster | Cluster where RHACM is installed | Manages all other clusters | Your main management cluster |
MCE cluster | Cluster where multicluster engine for Kubernetes (MCE) runs | Provisions and hosts HCP clusters | Infrastructure cluster |
Managed cluster | Any cluster managed by RHACM | Receives policies and is monitored | Production, dev, etc. clusters |
HCP cluster | HyperShift Cluster (HostedCluster) | Cluster with control plane in pods | Lightweight application cluster |
local-cluster | The RHACM Hub itself seen as managed | Hub's self-reference | RHACM managing itself |
Think of it this way:
- RHACM hub = Airport control tower
- MCE cluster = Hangar where planes are built
- Managed clusters = Planes in operation
- HCP clusters = Lightweight and quick-to-provision planes
Workflow
Note
Unless otherwise indicated, all configurations must be performed on the ACM cluster.
In this lesson, you will:
- Install the
clusteradmCLI. - Configure an add-on with namespace isolation.
- Create a custom
KlusterletConfig. - Add labels for RHACM backup.
Step 1: Install the clusteradm CLI
The clusteradm is an essential tool for RHACM management via the command line.
On the RHACM Hub cluster bastion, execute:
curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/open-cluster-management-io/clusteradm/main/install.sh | bashValidate the installation:
/usr/local/bin/clusteradm versionExpected output:
client version : v1.0.2-0-gea3fc6d server release version : v1.32.8 default bundle version : 1.0.0
Step 2: Add-on configuration with namespace isolation
One of the challenges when integrating MCE with RHACM is avoiding add-on conflicts. This is very important! The solution is to configure namespace isolation for critical add-ons.
Why namespace isolation? When you import an MCE cluster, which already has its own operators, as a managed cluster in RHACM, some add-ons may conflict. Isolating them in different namespaces prevents these conflicts.
The add-ons that need isolation are:
cluster-proxymanaged-serviceaccountwork-manager
2.1 Create an AddOnDeploymentConfig
This resource defines where the add-ons will be installed on the managed cluster (MCE).
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: AddOnDeploymentConfig
metadata:
name: addon-ns-config
namespace: multicluster-engine
spec:
agentInstallNamespace: open-cluster-management-agent-addon-discovery
EOFThis defines that add-ons should be installed in the open-cluster-management-agent-addon-discovery namespace instead of the default open-cluster-management-agent-addon.
2.2 Configure ClusterManagementAddOns
Now let's update each add-on to use this custom configuration.
Work manager:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterManagementAddOn
metadata:
name: work-manager
spec:
addonMeta:
displayName: work-manager
installStrategy:
placements:
- name: global
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
rolloutStrategy:
type: All
type: Placements
EOF
oc get ClusterManagementAddOn
NAME DISPLAY NAME CRD NAME
application-manager Application Manager
cert-policy-controller Certificate Policy Addon
cluster-proxy cluster-proxy
config-policy-controller Config Policy Addon
gitops-addon gitops-addon
governance-policy-framework Governance Policy Framework Addon
governance-standalone-hub-templating Governance Standalone Hub Templating
hypershift-addon Hypershift Addon Agent
managed-serviceaccount managed-serviceaccount
search-collector Search Collector
submariner Submariner Addon
volsync VolSync
work-manager work-managerAdd the add-on DeploymentConfigs to the ClusterManagementAddOn. See the following example:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterManagementAddOn
metadata:
name: work-manager
spec:
addonMeta:
displayName: work-manager
installStrategy:
placements:
- name: global
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
rolloutStrategy:
type: All
configs:
- group: addon.open-cluster-management.io
name: addon-ns-config
namespace: multicluster-engine
resource: addondeploymentconfigs
type: Placements
EOFManaged ServiceAccount: Add the AddOnDeploymentConfig to the managed-serviceaccount. Here’s an example:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterManagementAddOn
metadata:
name: managed-serviceaccount
spec:
addonMeta:
displayName: managed-serviceaccount
installStrategy:
placements:
- name: global
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
rolloutStrategy:
type: All
configs:
- group: addon.open-cluster-management.io
name: addon-ns-config
namespace: multicluster-engine
resource: addondeploymentconfigs
type: Placements
EOFCluster proxy: Do the same here.
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterManagementAddOn
metadata:
name: cluster-proxy
spec:
addonMeta:
displayName: cluster-proxy
installStrategy:
placements:
- name: global
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
rolloutStrategy:
type: All
configs:
- group: addon.open-cluster-management.io
name: addon-ns-config
namespace: multicluster-engine
resource: addondeploymentconfigs
type: Placements
EOFUse the following commands to verify that your resources have been configured correctly.
oc get deployment -n open-cluster-management-agent-addon-discovery
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
cluster-proxy-proxy-agent 1/1 1 1 39s
klusterlet-addon-workmgr 1/1 1 1 3m28s
managed-serviceaccount-addon-agent 1/1 1 1 2m40sStep 3: Custom KlusterletConfig
To avoid klusterlet name conflicts on the MCE cluster, we need to create a custom configuration.
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
kind: KlusterletConfig
apiVersion: config.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
metadata:
name: mce-import-klusterlet-config
spec:
installMode:
type: noOperator
noOperator:
postfix: mce-import
EOFThis creates a klusterlet with the -mce-import suffix, avoiding conflict with the existing MCE klusterlet.
Validate:
oc get KlusterletConfigExpected output:
NAME AGE
mce-import-klusterlet-config 2sStep 4: Labels for RHACM backup
If you use RHACM's backup feature, add labels to critical resources:
oc label addondeploymentconfig addon-ns-config -n multicluster-engine \
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=true
oc label addondeploymentconfig hypershift-addon-deploy-config \
-n multicluster-engine cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=true
oc label clustermanagementaddon work-manager \
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=true
oc label clustermanagementaddon cluster-proxy \
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=true
oc label clustermanagementaddon managed-serviceaccount \
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=true
oc label KlusterletConfig mce-import-klusterlet-config \
cluster.open-cluster-management.io/backup=trueBest practice
Always add backup labels to critical configuration resources to ensure disaster recovery.
