Overview: Simplify multi-cluster management: Auto-import of hosted clusters with RHACM
As organizations expand their hybrid cloud infrastructures, managing multiple Red Hat OpenShift clusters becomes an increasing challenge. With the arrival of Red Hat OpenShift HyperShift (Hosted Control Planes - HCP), companies can provision clusters faster and more efficiently, but this brings a new challenge: How do we manage dozens or hundreds of HCP clusters consistently and in an automated way?
This is where Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management (RHACM) shines. In this learning path, we'll explore how to fully automate the discovery and import process of HyperShift clusters using RHACM and the multi-cluster engine for Kubernetes (MCE), which eliminates repetitive manual tasks and accelerates governance standards adoption.
The challenge: Manual management at scale
Imagine the following scenario: Your organization regularly provisions new HCP clusters for different teams, projects, or environments. Each cluster needs to be:
- Discovered after provisioning.
- Registered in the RHACM management hub.
- Configured with security and compliance policies.
- Monitored to ensure availability and performance.
Doing this manually for each cluster is:
- Time-consuming: Each manual import can take 10 to 15 minutes.
- Error-prone: Forgotten steps or inconsistent configurations.
- Not scalable: The more clusters, the greater the operational overhead.
- Risky: Unmanaged clusters can violate security policies.
The solution: Intelligent auto-import with RHACM
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management offers powerful automation capabilities through:
1. Automatic discovery
The MCE can automatically discover HyperShift clusters provisioned in your infrastructure, identifying:
- Cluster type (MultiClusterEngineHCP)
- Operational status
- OpenShift version
- API endpoint
2. Policy-based import
Using RHACM's policy framework, you can define declarative rules that:
- Automatically select which clusters should be imported.
- Apply custom filters by name, label, or metadata.
- Handle credentials securely.
- Ensure configuration consistency.
3. Continuous governance
Once imported, clusters are automatically under governance:
- Compliance with corporate policies
- Centralized monitoring
- Coordinated updates
- Standardized add-on management
Solution architecture
The solution we'll implement involves the following components working together:
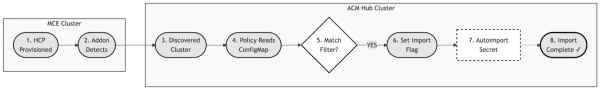
Workflow:
- Provisioning: A new HCP cluster is created on the MCE cluster.
- Discovery: The HyperShift add-on detects the new
HostedCluster. - Registration: A
DiscoveredClusterCRD is created in the RHACM Hub. - Evaluation: The auto-import policy evaluates the discovered cluster.
- Import: If criteria are met, import is initiated automatically.
- Completion: The cluster becomes a full
ManagedClusterin RHACM.
Prerequisites:
To implement the complete solution, you'll need:
- Red Hat OpenShift 4.16+ (recommended 4.18+)
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes2.11+ (recommended 2.14+)
- Multi-cluster engine for Kubernetes operator installed on the hosting cluster (MCE cluster)
- HyperShift operator configured on the MCE cluster
- Basic knowledge of:
- OpenShift/Kubernetes
- YAML and manifests
- RHACM concepts (policies, placements)
In this learning path, you will:
- Learn how to configure RHACM for discovery.
- Prerequisites and necessary tools
- Add-on configuration with namespace isolation
- Import the MCE cluster as a managed cluster
- HyperShift add-on activation and configuration
- Automatic discovery validation
- Learn how to use auto-import policies to automate with intelligence.
- Creating policies with dynamic Go templates
- Using
ConfigMapsfor custom filters - Common troubleshooting
- Scalability strategies
- Observability and metrics tips
- Next steps and extensions

