Page
Automate the import for discovered hosted clusters

Now it's time to configure the automated import process by defining the policy and Go template, creating the placement definition, and binding the resources to ensure automatic detection and import of discovered hosted clusters into Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (RHACM).
In this lesson, you will:
- Configure the policy.
- Understand the Go template.
- Create the placement definition.
- Bind the import policy to a placement definition.
- Validate the policy.
- Verify cluster discovery.
- Check HyperShift add-on logs.
- Import existing HCP clusters (optional).
Step 1: Configure the policy
To configure your policy to import all your discovered hosted clusters, create a YAML file for your DiscoveredCluster custom resource and edit the configuration that is referenced in the following example:
Note
You MUST create the file. Don't use "cat EOF".
cat policy-mce-hcp-autoimport.yaml
apiVersion: policy.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: Policy
metadata:
name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
annotations:
policy.open-cluster-management.io/standards: NIST SP 800-53
policy.open-cluster-management.io/categories: CM Configuration Management
policy.open-cluster-management.io/controls: CM-2 Baseline Configuration
policy.open-cluster-management.io/description: Discovered clusters that are of
type MultiClusterEngineHCP can be automatically imported into ACM as managed clusters.
This policy configure those discovered clusters so they are automatically imported.
Fine tuning MultiClusterEngineHCP clusters to be automatically imported
can be done by configure filters at the configMap or add annotation to the discoverd cluster.
spec:
disabled: false
policy-templates:
- objectDefinition:
apiVersion: policy.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ConfigurationPolicy
metadata:
name: mce-hcp-autoimport-config
spec:
object-templates:
- complianceType: musthave
objectDefinition:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: discovery-config
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
data:
rosa-filter: ""
remediationAction: enforce
severity: low
- objectDefinition:
apiVersion: policy.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: ConfigurationPolicy
metadata:
name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport
spec:
remediationAction: enforce
severity: low
object-templates-raw: |
{{- /* find the MultiClusterEngineHCP DiscoveredClusters */ -}}
{{- range $dc := (lookup "discovery.open-cluster-management.io/v1" "DiscoveredCluster" "" "").items }}
{{- /* Check for the flag that indicates the import should be skipped */ -}}
{{- $skip := "false" -}}
{{- range $key, $value := $dc.metadata.annotations }}
{{- if and (eq $key "discovery.open-cluster-management.io/previously-auto-imported")
(eq $value "true") }}
{{- $skip = "true" }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- /* if the type is MultiClusterEngineHCP and the status is Active */ -}}
{{- if and (eq $dc.spec.status "Active")
(contains (fromConfigMap "open-cluster-management-global-set" "discovery-config" "mce-hcp-filter") $dc.spec.displayName)
(eq $dc.spec.type "MultiClusterEngineHCP")
(eq $skip "false") }}
- complianceType: musthave
objectDefinition:
apiVersion: discovery.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: DiscoveredCluster
metadata:
name: {{ $dc.metadata.name }}
namespace: {{ $dc.metadata.namespace }}
spec:
importAsManagedCluster: true
{{- end }}
{{- end }}This policy seems a little scary. But don't worry. It's already set up and ready to go. Just create it.
oc apply -f policy-mce-hcp-autoimport.yamlUnderstand the Go template
Let's dissect the template to understand each part:
Loop over all
DiscoveredClusters:{{- range $dc := (lookup "discovery.open-cluster-management.io/v1" "DiscoveredCluster" "" "").items }}lookup queriesallDiscoveredClustersin the cluster.$dcis the iteration variable.
Previous import check:
{{- $skip := "false" -}} {{- range $key, $value := $dc.metadata.annotations }} {{- if and (eq $key "discovery.open-cluster-management.io/previously-auto-imported") (eq $value "true") }} {{- $skip = "true" }} {{- end }} {{- end }}- Avoid re-importing already imported clusters.
- Use annotation to mark processed clusters.
Import conditions:
{{- if and (eq $dc.spec.status "Active") (contains (fromConfigMap "..." "mce-hcp-filter") $dc.spec.displayName) (eq $dc.spec.type "MultiClusterEngineHCP") (eq $skip "false") }}Cluster will be imported IF:
- Status is Active.
DisplayNamecontains the filter fromConfigMap.- Type is
MultiClusterEngineHCP. - Not previously imported.
Import action:
- complianceType: musthave objectDefinition: apiVersion: discovery.open-cluster-management.io/v1 kind: DiscoveredCluster metadata: name: {{ $dc.metadata.name }} namespace: {{ $dc.metadata.namespace }} spec: importAsManagedCluster: true- Sets
importAsManagedCluster: trueon theDiscoveredCluster. - Triggers RHACM's import process.
- Sets
Step 2: Placement definition
Create the placement definition that selects only the local-cluster, which is a managed hub cluster. Use the following YAML sample:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: Placement
metadata:
name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport-placement
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
spec:
tolerations:
- key: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unreachable
operator: Exists
- key: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/unavailable
operator: Exists
clusterSets:
- global
predicates:
- requiredClusterSelector:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: local-cluster
operator: In
values:
- "true"
EOFWhy local-cluster? DiscoveredClusters are created on the hub, so the policy needs to run there to query them.
Step 3: Bind the import policy to a placement definition
Connect the resources by using a PlacementBinding resource. See the following example where placementRef references the placement that you created, and subjects references the policy that you created:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: policy.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: PlacementBinding
metadata:
name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport-placement-binding
namespace: open-cluster-management-global-set
placementRef:
name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport-placement
apiGroup: cluster.open-cluster-management.io
kind: Placement
subjects:
- name: policy-mce-hcp-autoimport
apiGroup: policy.open-cluster-management.io
kind: Policy
EOFStep 4: Policy validation
Verify if the policy was created and is compliant.
Go to Governance > Policies, click
policy-mce-hcp-autoimportthenResults. If everything is correct, there will be no violations.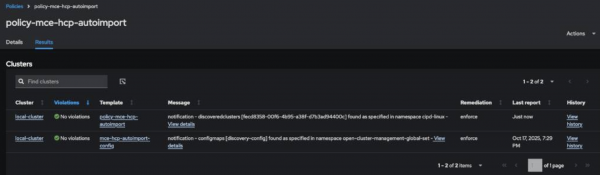
Figure 1: MCE HCP Autoimport policy results. Or use the CLI:
oc get policies.policy.open-cluster-management.io policy-mce-hcp-autoimport -n open-cluster-management-global-setExpected output:
NAME REMEDIATION ACTION COMPLIANCE STATE AGE policy-mce-hcp-autoimport enforce Compliant 2mYou're now ready to go! All new hosted clusters that you create in your imported MCE cluster will be automatically detected and imported into RHACM!
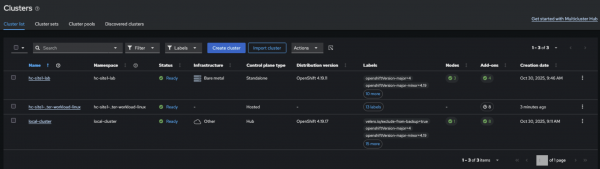
Figure 2: Hosted cluster autoimporting.
Step 4: Check discovery in RHACM
Wait a few minutes and verify if the cluster was discovered:
oc get discoveredcluster -AExpected output:
NAMESPACE NAME DISPLAY NAME CLOUD PROVIDER STATUS AGE
hc-site1-lab f74a752d-6209-4bd2-8978-9374e437445b hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux agent Active 15mInspect the discovered cluster details:
oc get discoveredcluster -n hc-site1-lab f74a752d-6209-4bd2-8978-9374e437445b -o yaml
apiVersion: discovery.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: DiscoveredCluster
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2025-10-30T15:58:48Z"
generation: 2
labels:
hypershift.open-cluster-management.io/hc-name: cluster-workload-linux
hypershift.open-cluster-management.io/hc-namespace: hc-site1-lab
name: f74a752d-6209-4bd2-8978-9374e437445b
namespace: hc-site1-lab
resourceVersion: "145526"
uid: 900f11b2-e7b6-4e88-9204-b8c33229675c
spec:
apiUrl: https://X.X.X.X:6443
cloudProvider: agent
creationTimestamp: "2025-10-30T15:57:05Z"
credential: {}
displayName: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux
importAsManagedCluster: true
isManagedCluster: false
name: f74a752d-6209-4bd2-8978-9374e437445b
openshiftVersion: 0.0.0
status: Active
type: MultiClusterEngineHCPStep 5: Check HyperShift add-on logs
Confirm the add-on is working correctly:
oc logs -n open-cluster-management-agent-addon-discovery \
deployment/hypershift-addon-agent -fYou should see something like this:
INFO agent.controller-manager-setup agent/agent.go:257 starting manager
INFO agent.agent-reconciler agent/agent_helper.go:48 local cluster name is local-cluster
INFO agent.agent-reconciler.addon-status-controller agent/addon_status_controller.go:66 reconciling Deployment hypershift/operator
INFO agent.agent-reconciler.addon-status-controller agent/addon_status_controller.go:104 done reconcile Deployment hypershift/operator
INFO agent.agent-reconciler install/upgrade.go:75 hypershift operator management is disabled. Skip installing or upgrading the hypershift operatorPerfect! The add-on is configured to discover clusters, but not manage the operator, which already exists on MCE.
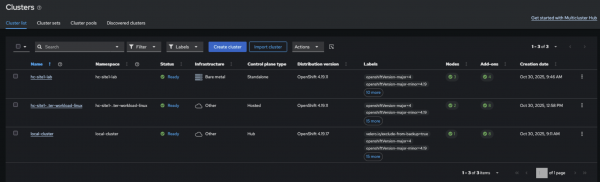
Bonus step: Import existing HCP clusters
To import existing HCP clusters, go to Infrastructure > Clusters > Import Cluster.
Enable YAML view, and customize your manifest as indicated.
For this learning path, we are using the following cluster names:
- Hosting Cluster Name (your MCE cluster):
hc-site1-lab - Hosted Cluster Agent Nodes:
cluster-workload-linux
- Hosting Cluster Name (your MCE cluster):
The imported hosted cluster name must be a concatenation of
<managed-cluster-name>-<hosted-cluster-name>, as stated in Lesson 3.Example name:
hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux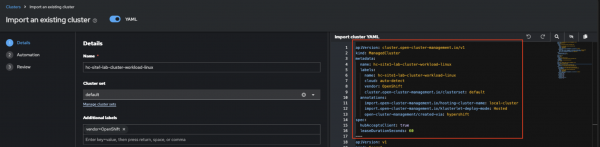
Figure 4: Hosted cluster manual import. For reference, here is the example YAML used in this lab.
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1 kind: ManagedCluster metadata: name: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux labels: name: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux cloud: auto-detect vendor: OpenShift cluster.open-cluster-management.io/clusterset: default annotations: import.open-cluster-management.io/hosting-cluster-name: local-cluster import.open-cluster-management.io/klusterlet-deploy-mode: Hosted open-cluster-management/created-via: hypershift spec: hubAcceptsClient: true leaseDurationSeconds: 60 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: auto-import-secret namespace: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux stringData: kubeconfig: "********************" type: Opaque --- apiVersion: agent.open-cluster-management.io/v1 kind: KlusterletAddonConfig metadata: name: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux namespace: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux spec: clusterName: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux clusterNamespace: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux clusterLabels: name: hc-site1-lab-cluster-workload-linux cloud: auto-detect vendor: OpenShift cluster.open-cluster-management.io/clusterset: default applicationManager: enabled: true policyController: enabled: true searchCollector: enabled: true certPolicyController: enabled: true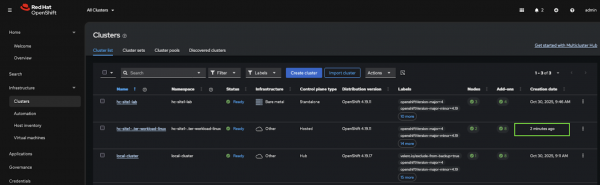
Figure 5: ACM hub showing successful manual import. Figure 5: RHACM hub showing successful manual import.
Success! The hosted cluster has been manually imported into RHACM.
