Recently, the focus on the continuous delivery of value has created a lot of interest in microservices, CI/CD, and containers. The idea is that microservices are small and well defined enough to enable rapid innovation, automated testing, and frequent deployments with minimal risk. This is made possible by adopting continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines. CI/CD requires the ability to quickly, easily, reliably, and automatically create and tear down complete execution environments. Linux containers address this need by creating lightweight, portable, and isolated runtime environments. It becomes easy to reach the conclusion that the path to digital transform is continuous value delivery via microservices-based on containers and CI/CD.
To get started, you need an environment for CI/CD, so you need to download Jenkins, figure out where to run it, and climb the Jenkins learning curve. For CI/CD to be effective, you need to tie it into your processes so it gets kicked off when new code is committed. To have faith that your testing will be accurate you need to recreate your application environment in containers as part of each build. Once testing is complete, you might want to set up an approval process for deployment.
When it comes to deployments, you want to reduce downtime and mitigate risks while rolling out new code. Do you have enough resources, i.e., two identical production environments to be able to do blue-green or canary deployments? Do you have the infrastructure, such as load balancers, to easily route portions of your workload between your production environments?
It’s easy to get overwhelmed trying to implement deployment best practices. Wouldn’t it be nice if there were a development platform designed to take you from development to deployment?
Red Hat OpenShift.io: Continuous deployments without breaking a sweat
To help development teams get started quickly and be productive, Red Hat created OpenShift.io. OpenShift.io is an end-to-end development environment for planning, building and deploying cloud-native applications. Optimized for creating modern, container-based applications and microservices-based solutions in the cloud, OpenShifto.io is the ideal path to achieving deployment excellence.
OpenShift.io lets you get started writing actual, functional code right away. When you create a space in OpenShift.io for your project, you choose from a list of quick starts. When you do this, a lot more is happening than just importing some boilerplate code. All of the components of your selected stack are pulled into your space, along with the information to automatically build the whole project into Linux containers. With nothing more than a browser and an Internet connection, you now are ready to write the first method for your project, build it, test it, and deploy it. Getting to this point could have taken you days or longer if you had to assemble all of the pieces yourself.
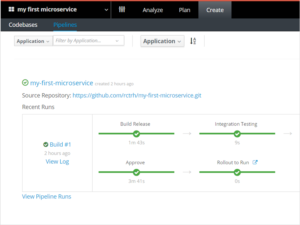
Build and deployment pipelines out of the box
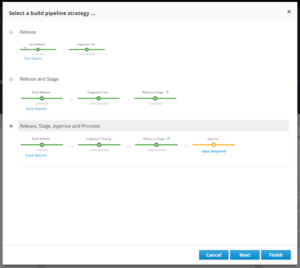
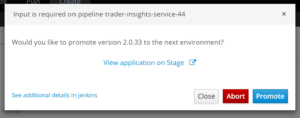
You can get started with CI/CD from day one on your project. When you select a quick start to bootstrap your development in OpenShift.io, you can choose from a list of ready-made build pipelines. These include sophisticated choices like canary deployments, with or without approval stages. There is no other setup required.
This is possible because you used a quick start that gave you a stack that your development environment knows how to build in containers. Jenkins for CI/CD is managed for you by OpenShift Pipelines running in your team’s OpenShift.io space. This means you don’t need to find resources to run your CI/CD server because you are running in the cloud on OpenShift Online.
For rolling deployments like blue-green or canary, you need multiple live environments with a way to route between them, which is a challenge if you manage your own infrastructure. Because you are running in the cloud with OpenShift.io, it’s easy to have multiple pods covering blue/green or previous build and canary, and the routes to direct traffic to the correct one. It’s even easier because you don’t have to edit any Kubernetes YAML files. You still get the power of Kubernetes, but OpenShift manages it for you.
OpenShift.io combines the innovations of a number of open source projects, including fabric8, Eclipse Che, Jenkins, JBoss Forge, WildFly Swarm, Vert.x, Kubernetes, and of course OpenShift. OpenShift.io itself is a container-based application delivered on Red Hat OpenShift Online.
Available for free, OpenShift.io is currently in a limited developer preview. Sign up at openshift.io to be notified when space becomes available.
Head over to openshift.io to start trying these and many more features today!
Last updated: February 26, 2024