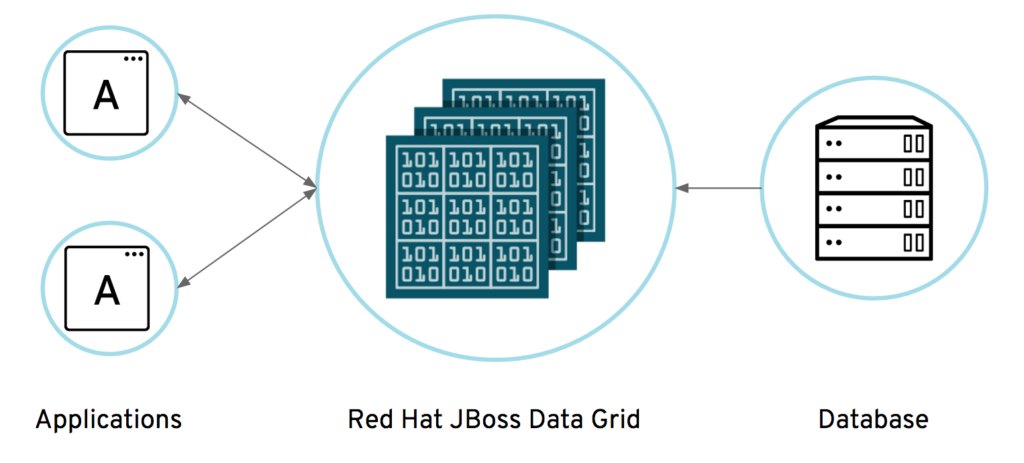
An in-memory data grid is a distributed data management platform for application data that:
- Uses memory (RAM) to store information for very fast, low-latency response time, and very high throughput.
- Keeps copies of that information synchronized across multiple servers for continuous availability, information reliability, and linear scalability.
- Can be used as distributed cache, NoSQL database, event broker, compute grid, and Apache Spark data store.
The technical advantages of an in-memory data grid (IMDGs) provide business benefits in the form of faster decision-making, greater productivity, and improved customer engagement and experience.
With Red Hat® JBoss® Data Grid (JDG) an enterprise open source in-memory data management store can be used as a distributed cache, NoSQL database, event broker, compute grid, and Apache Spark data store. JDG offers low latency, high-performance, elastic scalability and always available data store which makes it ideally suited for on-premise, web, Cloud, Big Data, and IoT applications. This article describes how one can offload your database data (PostgreSQL) into an in-memory data grid provided by JDG for fast processing, providing fast data for intelligent applications. The code provided here can be easily adapted to your database of choice and data of your choice to store in JDG.
Prerequisites
- JDG 7.0.0 environment
Download: Red Hat JBoss Data Grid 7.0.0 Server
Install: https://developers.redhat.com/products/datagrid/overview
We will refer to the installation directory of JDG 7.0.0 as $JDG_HOME - Maven 3.3.9
Download: Maven 3.3.9
Install: http://maven.apache.org/install.html
We will refer to the installation directory of Maven 3.3.9 as $M2_HOME - PostgreSQL 9.x
Download: PostgreSQL
Install: https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Detailed_installation_guides
Database
First, we need to create the PostgreSQL database called products, then we create a table called product and load the product data from a CSV file into the product table using the COPY command.
Setup PostgreSQL database.
Create a PostgreSQL database called products as depicted below.
$ psql psql (9.6.2) Type "help" for help. cvanball=# create database products; cvanball=# \q
Create the product table in PostgreSQL database products and load the data with the COPY command as depicted below.
$ psql -d products
products=# create table product
products-# (
products(# itemId numeric(10) CONSTRAINT itemid_pk PRIMARY KEY,
products(# name varchar(50),
products(# description varchar(1024),
products(# price decimal(10,2)
products(# );
CREATE TABLE
products=# COPY product FROM '<install-dir>/jboss-data-grid/jdg-cache-producer/src/main/java/com/redhat/jdg/producer/db/product-data.csv' ( FORMAT CSV, DELIMITER(','), HEADER(TRUE));
products=# \q
Change <install-dir> to match directory containing the GitHub repository. For your convenience, we provided a script.
The end result of the product table is depicted below.
$ psql -d products psql (9.6.2) Type "help" for help. products=# \d product Table "public.product" Column | Type | Modifiers -------------+-------------------------+----------- itemid | numeric(10,0) | not null name | character varying(50) | description | character varying(1024) | price | numeric(10,2) | Indexes: "itemid_pk" PRIMARY KEY, btree (itemid)
products=# select count(*) from product; count ------- 71 (1 row) products=#
Red Hat JBoss Data Grid
The only thing we need in JDG is configuring a cache. We name the cache productCache.
Start the JDG server, in the example below we are starting JDG in standalone mode.
$ cd $JDG_HOME/bin $ ./standalone.sh
Define and configure the productCache in the JDG server. For your convenience, we provide a Command Line Interface (CLI) script called configure_jdg.cli, which can be used with the ./cli.sh command as well.
$ cd $JDG_HOME/bin $ ./cli.sh --connect [standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=local/configurations=CONFIGURATIONS/local-cache-configuration=productCacheCfg:add(start=EAGER) [standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=datagrid-infinispan/cache-container=local/local-cache=productCache:add(configuration=productCacheCfg)
Application jdg-cache-producer
JDG Server comes with several different server endpoints, speaking in a variety of protocols. Here is a comparison of the protocols that can be used:
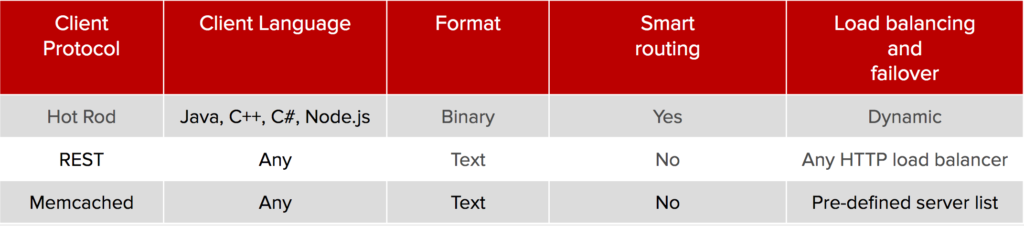
Hot Rod is a binary TCP client-server protocol used in JDG. The Hot Rod protocol facilitates faster client and server interactions in comparison to other text-based protocols and allows clients to make decisions about load balancing, failover, and data location operations.
If you need to share data among different languages/platforms, the use of a common marshaling format is recommended. While JDG does not impose a default, one option is ProtoBuf, a compact format with wide support. ProtoBuf aka Protocol Buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data – think XML, but smaller, faster, and simpler. You define how you want your data to be structured once, then you can use the special generated source code to easily write and read your structured data to and from a variety of data streams and using a variety of languages.
The application we are using demonstrates how to connect remotely to JDG to store the product data from the PostgreSQL database into the cache using the Hot Rod protocol and ProtoBuf. It's a maven based java application, which retrieves the data from the products ProgreSQL database and product table and stores the rows into the productCache cache of JDG using the Hot Rod based connector.
How to build java application jdg-cache-producer
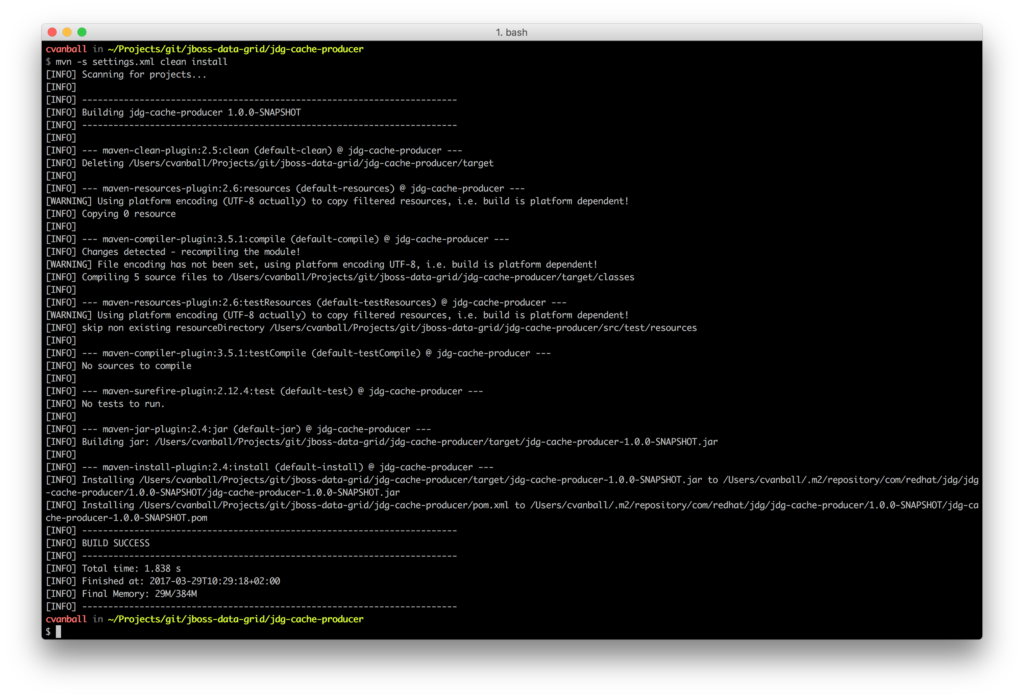
To build the java application jdg-cache-producer, use Maven with the command mvn -s settings.xml clean install as depicted below.
How to run java application jdg-cache-producer
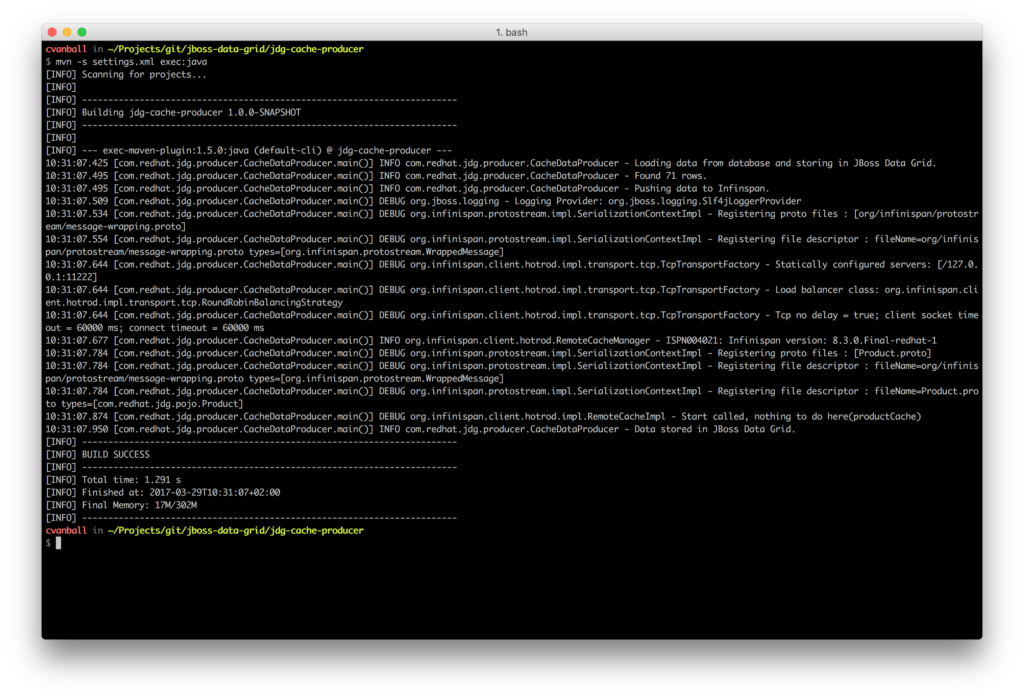
One needs to build the application first as shown previously to be able to run the application jdg-cache-producer using Maven with the command mvn -s settings.xml exec:java as depicted below.
In the jdg-cache-producer application we programmatically read the environment variables from the pom.xml to connect to the JDG environment and the database of your choice, see below:
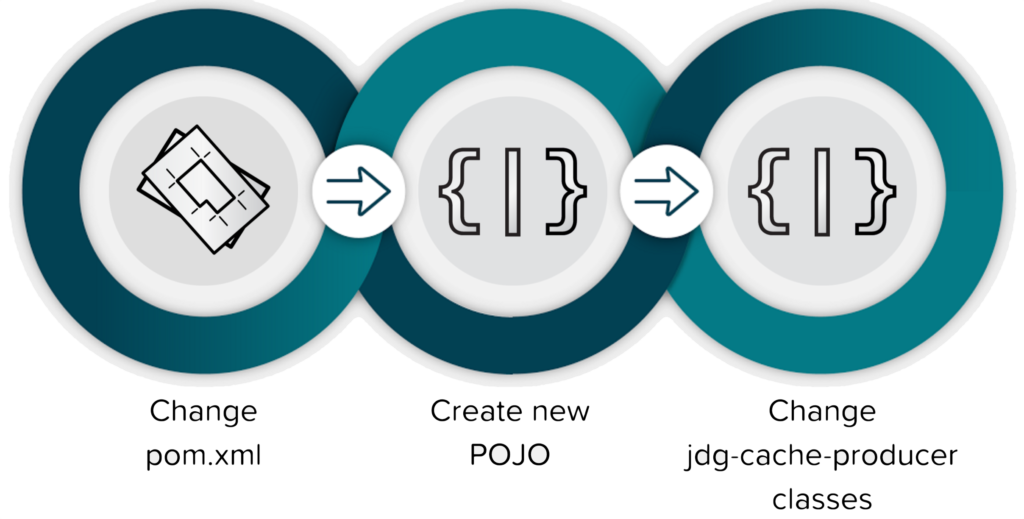
Developer flow
As mentioned earlier one needs to adapt the code to your database of choice and data of your choice to store in JDG. The following developer workflow as depicted and described below will show you how.
- Change pom.xml
The pom.xml contains configuration parameters to connect to the database of your choice and JDG. The table below explains the parameters.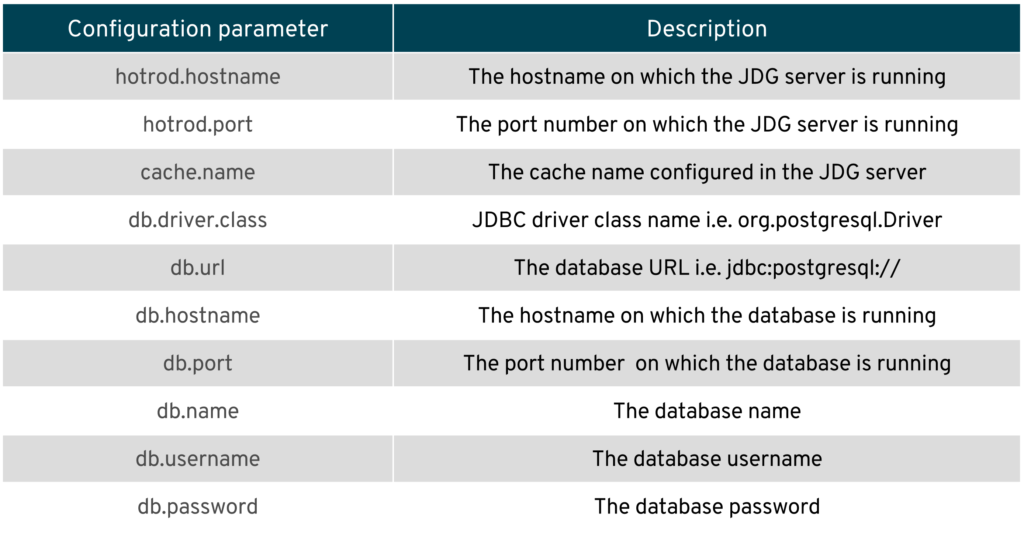
Note: Furthermore one need to add the dependency of the JDBC driver of the database of your choice. - Create new POJO class
Define a POJO class containing ProtoBuf annotations. See Defining Protocol Buffers Schemas With Java Annotations for more information on using ProtoBuf annotations.
See example Product.java. - Change jdg-cache-producer classes
Before we can run the jdg-cache-producer with the new POJO class we need to change some code. The following steps explain what needs to be created/changed.- Create a <POJO name>Repository class
See ProductRepository.java for inspiration. - Change CacheDataProducer class
In order to put the data into JDG, one needs to change the CacheDataProducer class to use the previously created POJO and Repository classes. See CacheDataProducer.java as depicted below for inspiration.
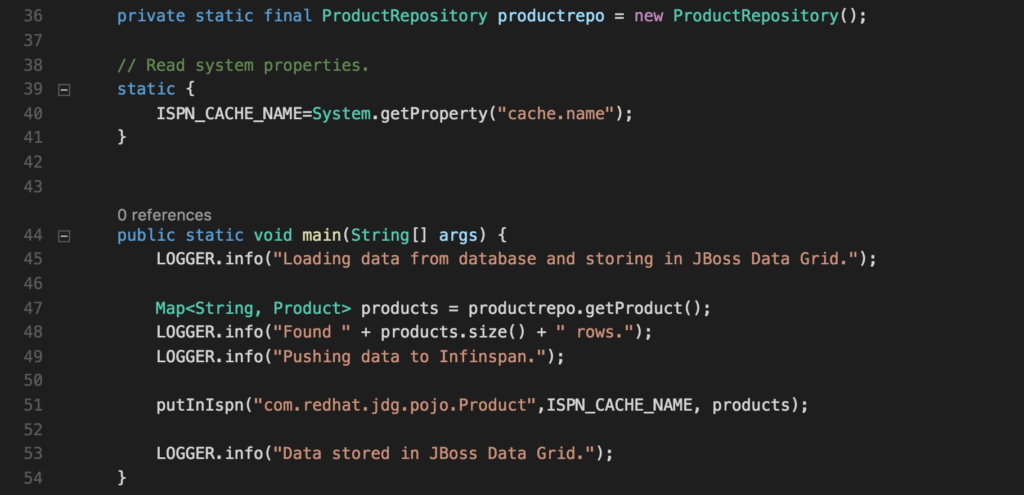 Line 36 needs to be changed to be able to use the new <POJO>Repository class.
Line 36 needs to be changed to be able to use the new <POJO>Repository class.
Line 47,48 and 51 needs to be changed to be able to use the new POJO class and new <POJO>Repository class.
- Create a <POJO name>Repository class
Conclusion
In this post, we’ve shown the steps one needs to perform in order to put database data into a Red Hat JBoss Data Grid cache for enabling extremely fast processing on your data residing in memory. See the following github repository for all source code: jdg-cache-producer
Special thanks to Red Hat's Duncan Doyle for sharing the initial bits of this clever jdg-cache-producer code while being in the Cloud with me flying to Boston and Red Hat's Thomas Qvarnström for his support.
For more information on PostgreSQL, ProtoBuf, and Red Hat JBoss Data Grid, please refer to the PostgreSQL, Protocol Buffers, and Red Hat JBoss Data Grid websites:
Download JBoss Data Grid for development use an intelligent, distributed caching solution.
Last updated: December 27, 2023