KServe is a standard Model Inference Platform on Kubernetes built for highly scalable use cases. It is a popular open source platform available as a community project, as well as a core component of Red Hat OpenShift AI. It provides a Kubernetes custom resource definition (CRD) for serving machine learning (ML) models on arbitrary frameworks. It aims to solve production model-serving use cases by providing performant, high-abstraction interfaces for common ML frameworks and model formats like TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, Scikit-learn, and ONNX.
It simplifies the deployment process by abstracting the complexities associated with serving ML models at scale in production. KServe is framework-agnostic, supporting various ML frameworks, and it leverages Kubernetes' scalability features for dynamic scaling based on demand. It facilitates canary deployments for controlled model version updates, offers advanced metrics and monitoring for performance insights, and allows users to serve multiple models concurrently. KServe’s versatility, versioning support, and customizable inference pipelines make it a powerful tool for deploying, scaling, and managing ML models in production environments. Figure 1 illustrates these components.
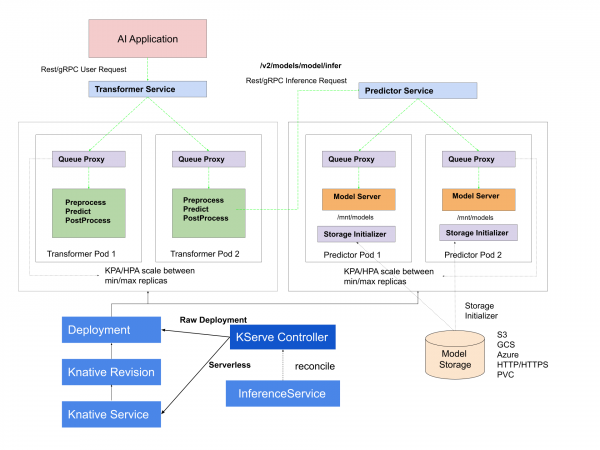
Why KServe?
- KServe is a standard, cloud-agnostic Model Inference Platform on Kubernetes, built for highly scalable use cases.
- Provides performant, standardized inference protocol across ML frameworks.
- Supports modern serverless inference workloads with request-based auto-scaling including scale-to-zero on CPUs and GPUs.
- Provides high scalability, density packing, and intelligent routing using ModelMesh.
- Offers simple and pluggable production serving for inference, pre/post processing, monitoring, and explainability.
- Supports advanced deployments for canary rollout, pipeline, and ensembles with InferenceGraph.
KServe’s ModelServer is built on top of FastAPI, which brings out-of-box support for OpenAPI specification and Swagger UI. KServe supports the Open Inference Protocol (OIP) specification that defines a standard protocol for performing ML model inference across different serving runtimes, promotes standardization, and improves interoperability between different model-serving runtimes. It enables the creation of cohesive inference experience, empowering the development of versatile client or benchmarking tools that can work with all supported serving runtimes. This will enable users to easily migrate from one platform to another.
Popular API specs
OpenAI
OpenAI provides an API interface that empowers end users with AI capabilities, facilitating the smooth integration of their applications with robust ML models. Hosted in OpenAI’s cloud, these pre-trained models are accessible through APIs, presenting substantial cost savings for organizations. OpenAI further supports model fine-tuning by allowing dataset uploads via APIs. These models are deployable on a scalable infrastructure, and their adoption has increased because of their user-friendly API interface.
HuggingFace
Starting with version 1.4.0, Text Generation Inference (TGI) offers an API compatible with the OpenAI Chat Completion API. The new Messages API allows customers and users to transition seamlessly from OpenAI models to open LLMs. The API can be directly used with OpenAI’s client libraries or third-party tools like LangChain or LlamaIndex.
Open Inference Protocol (OIP)
This specification enables the creation of a cohesive inference experiences, empowering the development of versatile client or benchmarking tools that can work with all supported serving runtimes. KServe’s OIP has been widely adopted by popular runtimes like KServe, NVIDIA Triton Inference Server protocol, Seldon MLServer, Seldon Core v2 inference protocol, OpenVino RESTful API and gRPC API, AMD Inference Server and the TorchServe Inference API. By adopting OIP, developers can build applications that are not tied to a single platform and are able to swap out inference servers and even deploy different AI models such as Mistral or Llama2 without modifying the application layer.
NVIDIA and Red Hat
KServe has recently added support for generate endpoint to support additional runtimes like HuggingFace and vLLM to work with large models.
With the launch of NVIDIA NIM, NVIDIA is providing a industry-standard set of inference applications including support for optimized LLM models such as Nemotron, Llama2, and Mistral through an OpenAI API compliant interface. Along with the tooling to download and optimize these models, NVIDIA also provides the TensorRT-LLM and the NVIDIA Triton Inference Server both as a contribution to the open source community, as well as in its NVIDIA AI Enterprise offerings. KServe is a powerful inferencing platform that can complement inference services built on Triton and other engines.
To benefit from open standards, NVIDIA is working with Red Hat to improve KServe OIP’s compatibility with OpenAI schema. The addition of this feature will allow standards-based portability in applications leveraging generative AI models, including the integration of such inference services into Red Hat OpenShift AI, which uses KServe for model serving, as well as interoperability with current and future services by NVIDIA converging on the OpenAI Specifications and making locally deployed LLMs more accessible.
Last updated: March 25, 2024