Prior to Red Hat OpenShift GitOps 1.10, the Operator supported setting the number of desired shards via a first-class setting in the Argo CD custom resource using the variable controller.sharding.replicas. The user still had to decide on the number of shards they wanted to have running. To make this an informed decision, users needed to consider the number of managed clusters per shard.
Although this functionality helps define the number of replicas of Argo CD application controllers needed, it does not necessarily end up having the optimal use of the compute resources across all shards. For example, setting 2 shards may be too small for handling 10 clusters, while setting 50 shards will leave 40 shards unused and still consume the assigned compute resources.
To solve this problem, OpenShift GitOps 1.10 introduced dynamic scaling of replicas. This article describes the properties introduced to enable dynamic scaling and explains how dynamic scaling works.
Enabling the dynamic scaling feature
The Operator introduced the following properties in the ArgoCD custom resource definition (CRD) to enable the dynamic scaling feature:
Sharding.dynamicScalingEnabled: Whether to enable dynamic scaling of the Argo CD application controller component. This will ignore the configuration ofSharding.enabledandSharding.replicas.- Default value:
true
- Default value:
Sharding.minShards: The minimum number of replicas of the Argo CD application controller component.- Default value:
1
- Default value:
Sharding.maxShards: The maximum number of replicas of the Argo CD application controller component.- Default value:
1
- Default value:
Sharding.clustersPerShard: The number of clusters that need to be handled by each shard. If the replica count has reached themaxShards, the shards will manage more than one cluster.- Default value:
1
- Default value:
Setting the property Sharding.dynamicScalingEnabled will enable the dynamic scaling feature and will override the behavior of existing properties Sharding.enabled and Sharding.Replicas.
The number of replicas is computed based on the following condition:
Number of Replicas = (Total Number of Clusters managed by ArgoCD) / (Sharding.clustersPerShard)
If the result of the above formula, that is, the computed number of replicas, is less than the value of property Sharding.minShards, the Operator sets the replicas equal to the value of Sharding.minShards. Similarly, if the computed value of replicas exceeds Sharding.maxShards, then the number of replicas is set as the value of Sharding.maxShards.
Dynamic scaling example
Step 1: Let's install GitOps Operator and add the configuration below to the pre-installed Argo CD configuration.
spec:
controller:
sharding:
dynamicScalingEnabled: true
minShards: 1
maxShards: 3
clustersPerShard: 1
In this example, we are only taking clustersPerShard as 1 for easier demonstration. This means one shard will manage only one cluster before increasing the number of replicas of the application controller. The shard will manage more than 1 cluster when the replicas of the application controller match the value of maxShards.
Step 2: Once the Operator is up and running, install the argocd CLI following the instructions here. We will use argocd CLI to add clusters to the Argo CD instance.
Step 3: Connect the argocd CLI to the Argo CD instance using the below command:
$ argocd login <argocd_server_url>
username: admin
password: <secret openshift_gitops_cluster>
The argocd server URL can be found in the from the route of openshift-gitops-server pod, as shown in Figure 1.
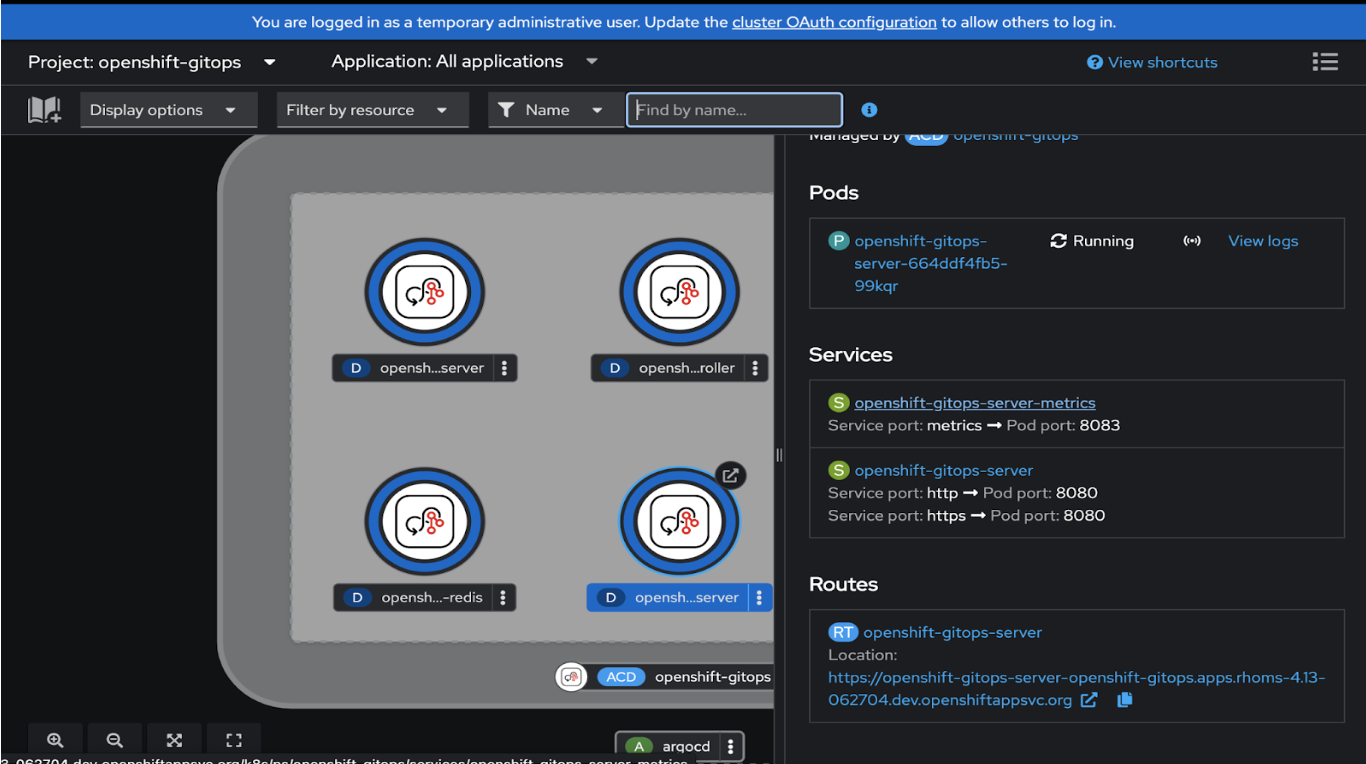
We can get the password from the secret openshift-gitops-cluster in namespace openshift-gitops.
Let’s check the number of application controller replicas created by default:
$ kubectl get pods -n openshift-gitops | grep application-controller
openshift-gitops-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 35s
Step 4: Now, add the clusters to Argo CD using the following command:
$ argocd cluster add CONTEXT [flags]
More details about the command can be found at on the Argo CD project website.
For this example, I have added 1 cluster that I created using kind. Once the clusters are added, you can see the number of application controller replicas increasing. You can view the number of replicas using the kubectl command below.
$ kubectl get pods -n openshift-gitops | grep application-controller
openshift-gitops-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 4m21s
openshift-gitops-application-controller-1 1/1 Running 0 14s
Step 5: You can remove the clusters from Argo CD using the below command. More details about the command can be found here.
$ argocd cluster rm SERVER/NAME
Once the cluster is deleted, we can see the replicas of the application controller decrease:
$ kubectl get pods -n openshift-gitops | grep application-controller
openshift-gitops-application-controller-0 1/1 Running 0 7m36s
One thing to note is that the number of replicas of the application controller would never go below the value of sharding.minShards field and would never exceed the value of sharding.maxShards field.
Conclusion
The OpenShift GitOps operator's auto-scaling feature will provide a fire-and-forget mechanism when adding or removing managed clusters to an Argo CD instance. This also reduces the manual intervention by the operators and automates scaling of the application controller.
