
Three ways to containerize .NET applications on Red Hat OpenShift
Developers looking to containerize .NET applications have options. Get an overview of the three paths forward using Linux, Windows, or Red Hat OpenShift CNV.

Developers looking to containerize .NET applications have options. Get an overview of the three paths forward using Linux, Windows, or Red Hat OpenShift CNV.

Now generally available on Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Red Hat OpenShift, .NET 5.0 includes language updates, improved garbage collection, and more.
Learn how to deploy Microsoft SQL Server 2019 on Red Hat OpenShift, use SQL Server from an OpenShift-deployed ASP.NET Core application, and more.
Ever wanted to set up CI for .NET Core in a cloud-native manner and didn’t know where to start? This is the guide you were looking for!

Learn how to use OpenAPI to describe the APIs provided by an ASP.NET Core service, then use the API description to generate a strongly-typed client.
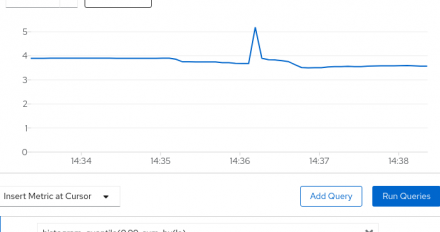
Learn how to use Prometheus to monitor a .NET Core application running on Kubernetes, and use PromQL to run queries and generate metrics.
Learn how to fix a "It works on my machine" NET Core (C#) "Unable to obtain lock file access" error on Red Hat OpenShift.

In the final articles of this series, explore C# 8's new static local functions, indices and ranges, and using declarations.

Explore how C# 8 lets us express whether a variable shouldn’t be null, and when it can be null.
Explore how C# 8 allows developers to extend an interface and provide a default implementation, then check out the rest of this C# 8 series.

We explore C# 8's extended pattern matching support and compare it to pattern matching in C# 7.

Explore the new C# 8 asynchronous streams feature in this first article in our series covering the new features available in C# 8.

We look at the various ways .NET Core is made available on Red Hat platforms, starting with an overview of the available platforms, and then showing how to install .NET Core on each of them.

Tom Deseyn shows how you can capture events from the .NET Core runtime and BCL using EventListener, dotnet-trace, and EventPipe environment variables.

.NET Core 3.1 for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 is now available; it is a long-term supported (LTS) release, which will be supported for three years.

We cover installing .NET Core RPMs and using the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Universal Base Image (UBI) container images.

We'll go over the basics of the .NET process class in .NET Core 3.0 and cover a few differences in usage between Windows and Linux.

.NET Core 3.0 for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 is now available; learn more about new features and improvements.
We look at new features of .NET Core for Linux, including improved performance and support for building Windows desktop applications.

We walk through the steps of implementing a CI/CD process for .NET Core in Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (OCP).

We explore Eclipse Che 7 and highlight some of the ways .NET developers can use it to their advantage.

We examine the new NativeLibrary class in .NET Core 3.0 and show how you can use it instead of the DllImport attribute.

We show how to execute .NET Core code easily in a separate process using Tmds.ExecFunction and explain why doing so is useful.

We explain how to significantly reduce build times for .NET Core applications by creating a custom build image that includes common dependencies.

Learn how the new incremental build feature of the S2I .NET Core builder can reduce build times by reusing packages from a previously built image.