
Handling Angular environments in continuous delivery with Red Hat OpenShift
We show how to configure Angular environments for continuous delivery, so you can build an image once and then promote it to other environments.

We show how to configure Angular environments for continuous delivery, so you can build an image once and then promote it to other environments.

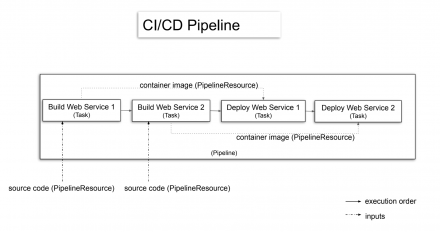
Learn how to combine various building blocks of Tekton to build and deploy a cloud-native application.

Using OpenShift image streams with Kubernetes Deployments allows automatic updates without sacrificing compatibility with standard Kubernetes.

Nicolas Massé continues the series on using the 3scale toolbox with an introduction to the Jenkins Shared Library.

In this article, Nicolas Massé shows how to use the 3scale toolbox to deploy your API from a Jenkins pipeline.
In this article, Nicolas Massé covers the overarching principles and key steps for deploying your API from a CI/CD pipeline.
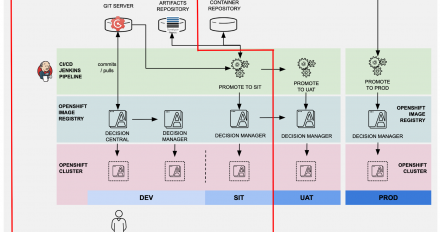
This article shows how to fully utilize the capabilities of Red Hat Decision Manager and Red Hat OpenShift to enable a smooth CI/CD process.
Watch Nikhil Thomas work with Tekton at the command line in this presentation from KubeCon Shanghai 19 CD Summit
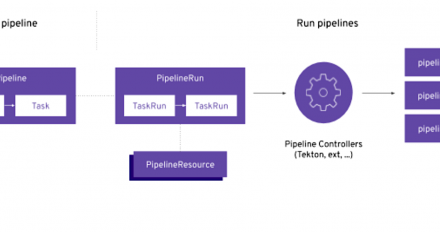
Learn more about OpenShift Pipelines, which enable the creation of cloud-native, Kubernetes-style CI/CD pipelines based on the Tekton project.
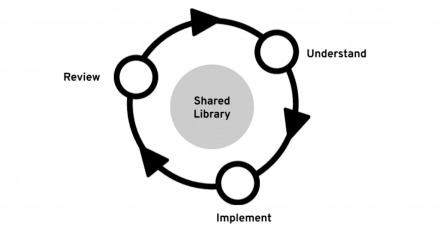
Decentralizing both the application lifecycle management process as well as the related tooling is key to scaling development and meeting changing needs.
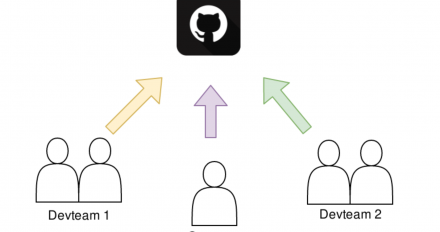
This article explores the service model of Red Hat AMQ Online 1.1 and how it maps to a GitOps workflow for different teams in your organization.
Learn how to build an automated integration and delivery pipeline using Jenkins CI/CD and Red Hat OpenShift 4.0 in this tutorial.
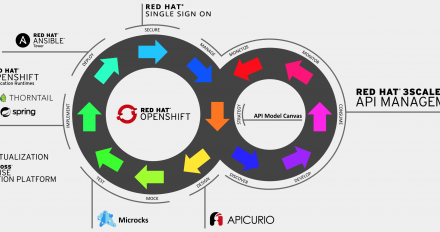
This article describes a set of full API lifecycle management activities that can guide your API initiatives from an idea to the realization, from the inception of an API program up to management at scale throughout your whole company.

Part 2 of this series, explores a way to handle IoT edge application development: multi-architecture containers on a PaaS like OpenShift. Building and running an ARM container on X86_64 is shown.

Part 1 of a two-part series, explores techniques that enable the portability of containers across different environments.Through these techniques, you may be able to use the same language, framework, or tool used in your datacenter straight to the IoT edge, even with different CPU architectures.
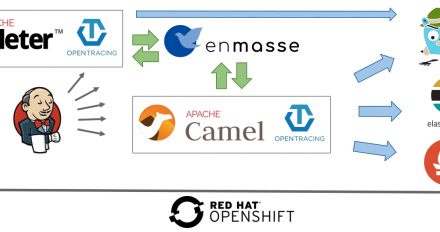
Part 3 of a series about using a container platform for automated performance testing. It covers how to automate and orchestrate the provisioning of an environment and the execution of performance tests.

Part 2 of a series about using a container platform for automated performance testing. It describes how to build an observability stack that can be used during automated performance tests.

This article discusses a fast and easy way to get Java apps running in a cloud by using OpenShift’s Source-to-Image (S2I) builder with Maven, Gradle,or Java 11.

This article describes how to build .NET Core container images using source-to-image (S2I). The container images can be built directly from a git repository, from local sources, or from a pre-built application on, which can be useful on your development machine or as part of a CI/CD pipeline.

Part 1 of a series about leveraging OpenShift or Kubernetes for automated performance tests. It provides an overview of the setup for automated performance testing using a container platform. Points to consider when executing and analyzing performance tests are covered.
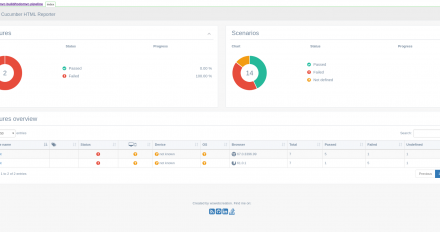
It can be complex to set up an end-to-end integration test infrastructure, but the process can be simplified by using an infrastructure-as-code approach. In addition, running integration tests for multiple OS/browser combinations can waste resources and time, but a container orchestrator and ephemeral workloads can help mitigate that. This article shows how to build behavior-driven development (BDD) container-native integration tests and run them in OpenShift to overcome these obstacles.

The next online DevNation Live is July 19th at 12pm EDT for "Container pipeline master: Continuous integration + continuous delivery with Jenkins", presented by Red Hat principal technical product marketing manager, Siamak Sadeghianfar.

Using Meta Test Family, writing tests for containers is really easy. Container testing helps you guarantee that a container is working properly just as an RPM package would.

The Eclipse MicroProfile project is moving fast with four releases and eight subspecs having at least two implementations each. This post provides an overview of MicroProfile 1.3, which was released on September 30th, and helps you to get started with the specification.