In this series of article, I will present several ways to deploy an application on an EAP Domain. The series consists of four parts. Each one will be a standalone article, but the series as a whole will present a range of useful topics for working with JBoss EAP.
- Part 1: Set up a simple EAP 7.0 Domain (this article).
- Part 2: Domain deployments through the new EAP 7.0 Management Console
- Part 3: Introduction to DMR (Dynamic Model Representation) and domain deployments from the Common Language Interface CLI
- Part 4: Domain deployment from the REST Management API
In part one of this series, we set up a simple JBoss EAP Domain. In part two, we reviewed the EAP Management Console deployment Mechanism and deployed the helloworld-html5 EAP Quickstart on the main-server-group ( Server11 and Server21). In part three, we deployed helloworld-html5 on secondary-server-group using the CLI Command line.
In this tutorial, part four, we are going to explore another deployment option: the REST Management API. To do so, we will upload a file in the EAP content repository and then deploy it.
Management Interfaces
On the master domain controller, we set up two management interfaces: the native on port 9999, and the HTTP management interface on port 9990.
While the CLI uses the native management port, and the EAP management console and the REST API are available on the HTTP management port, all these management interfaces also share common XML configuration files: host.xml/domain.xml. They also send commands to EAP using an intermediate representation called DMR ( Dynamic Model Representation).
DMR
DMR stands for Dynamic Model Representation, and it is a new syntax introduced with EAP 6 to denote Java objects associated with EAP Management interfaces. DMR is flatter than XML files and all the items are at the same level. Let's check out a sample:
The domain.xml configuration section containing EAP profiles and server groups looks like this:
<profiles> <profile name="default"> .... </profile> <profile name="ha"> .... </profile> <profile name="full"> ... </profile> <profile name="full-ha"> ... </profile> </profiles> <server-groups> <server-group name="primary-server-group" profile="full"> ... </server-group> <server-group name="secondary-server-group" profile="full"> ... </server-group> <server-group name="singleton-server-group" profile="default"> ... </server-group> </server-groups>..
And the DMR representation of this same XML looks like this:
...
"profile" => {
"default" => undefined,
"ha" => undefined,
"full" => undefined,
"full-ha" => undefined
},
"server-group" => {
"primary-server-group" => undefined,
"secondary-server-group" => undefined,
"singleton-server-group" => undefined,
},
...
The EAP Configuration is made up of a DMR tree, and using the CLI you can navigate through the entire configuration: deployments, server-groups, subsystems and modules, hosts... you can even update the DMR tree with specific operations.
For example, to read the whole configuration:
[domain@localhost:9990 /] :read-resource
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => {
"domain-organization" => undefined,
"management-major-version" => 4,
"management
...
To check the undertow subsystem configuration on ha profile:
[domain@localhost:9990 /]/profile=ha/subsystem=undertow:read-resource
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => {
"default-security-domain" => "other",
"default-server" => "default-server",
"default-servlet-container" => "default",
"default-virtual-host" => "default-host",
"instance-id" => expression "${jboss.node.name}",
"statistics-enabled" => false,
"buffer-cache" => {"default" => undefined},
"configuration" => {
"filter" => undefined,
"handler" => undefined
},
"server" => {"default-server" => undefined},
"servlet-container" => {"default" => undefined}
}
}
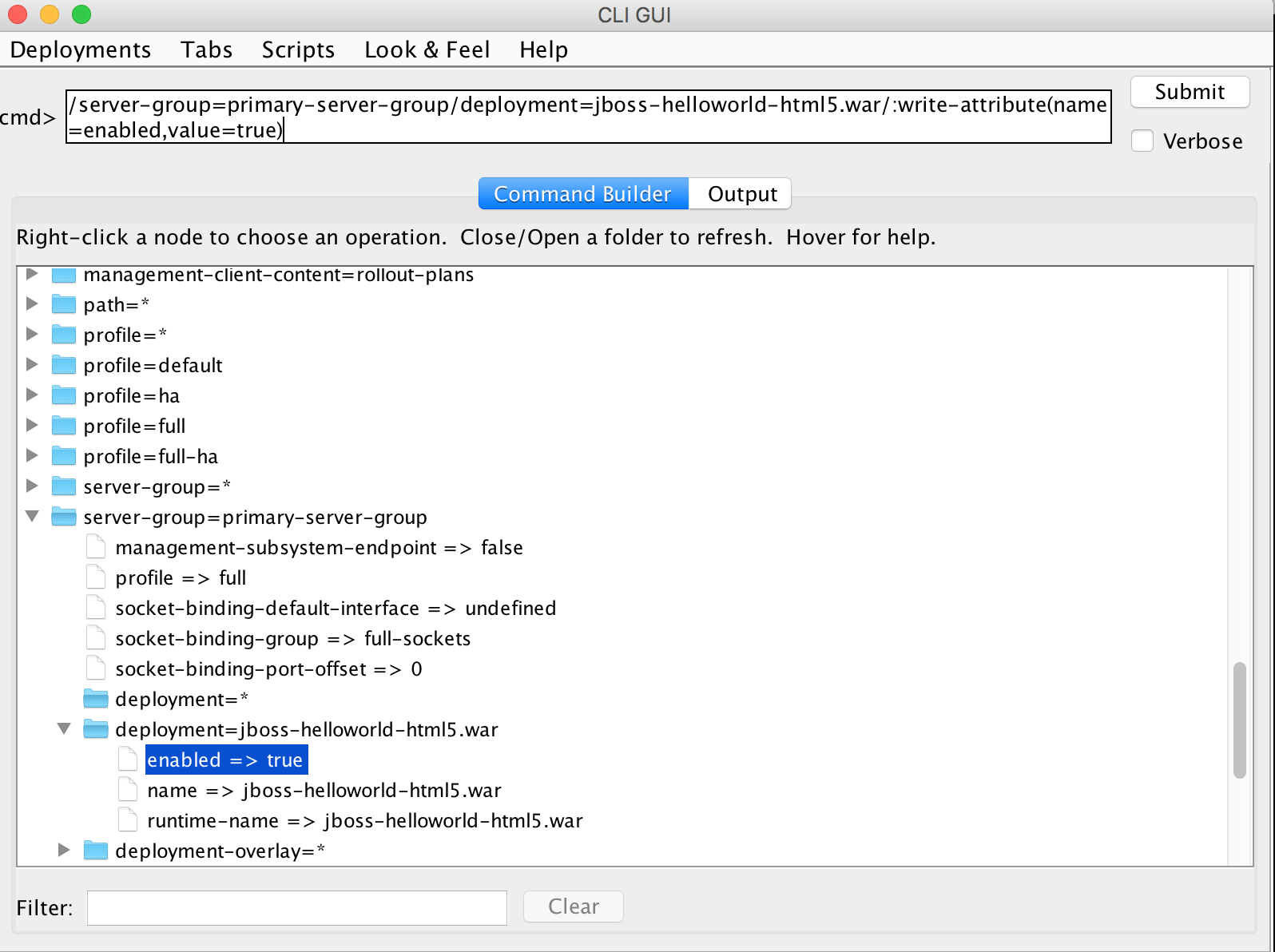
Generate DMR Queries with CLI gui
The command builder in the CLI console can be used to generate queries in DMR Syntax. Start the CLI in a graphical tool by adding the --gui option:
enonowog-OSX:bin enonowog$ ./jboss-cli.sh --gui
DMR to REST
All the management interfaces rely on JBoss DRM to read/update the configuration; the REST API is based on this feature.
The mangement API is available at http://127.0.0.1:9990/management, and this endpoint accepts JSON POST requests of the format:
data:operation:the operation to be performed:address:the path on which the operation should be performed
This is an array with all the path items and finally the operation parameters ( names and values). The authentication type is DIGEST.
To check the status of server 11, for example, we use the following DMR:
/host=host1/server=Server11:read-attribute(name=server-state)
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => "STOPPED"
}
With the REST API, we would do this instead:
$ curl --digest 'http://localhost:9990/management' --header "Content-type:application/json"-d '{"operation":"read-attribute", "address":["host","host1","server","Server11"],"name":"server-state","json.pretty":1}' -u admin:Admin01#
{
"outcome" : "success",
"result" : "STOPPED"
}
REST API Deployment
To deploy the helloworld-html5 application on the singleton server group using the REST management API, we simply have to add the helloworld-html5-war on the server group.
This is the DRM command to complete our operation:
/server-group=singleton-server-group/deployment=jboss-helloworld-html5.war:add(enabled=true)
From this we can build API parameters, and the REST query can be deduced from DMR:
operation=add
address=["server-group","singleton-server-group","deployment","jboss-helloworld-html5.war"]
parameters=("enabled":"true")
And our REST command:
$ curl --digest 'http://localhost:9990/management' --header "Content-type:application/json"-d '{"operation":"add", "address":["server-group","singleton-server-group","deployment","jboss-helloworld-html5.war"],"enabled":"true","json.pretty":1}' -u admin:Admin01#
{
"outcome" : "success",
"result" : null,
"server-groups" : {"singleton-server-group" : {"host" : {"host2" : {"Server23" : {"response" : {
"outcome" : "success",
"result" : null
}}}}}}
}
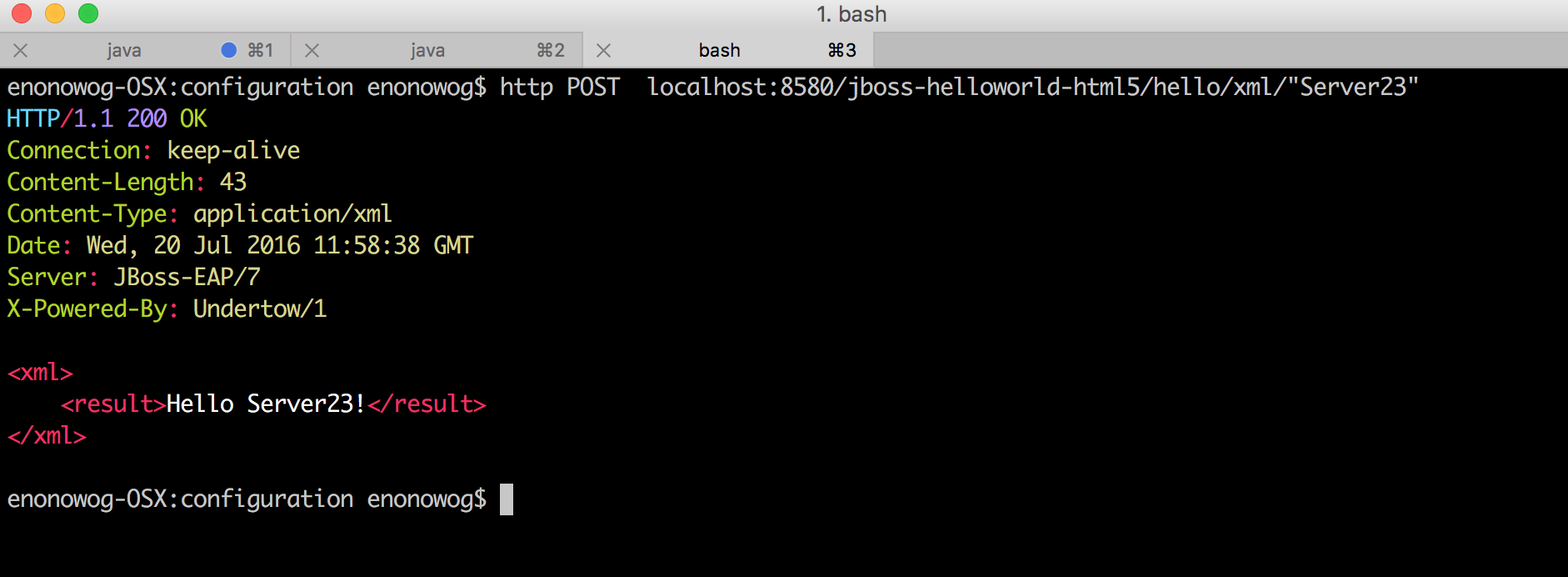
This command deploys the application on instance server 23, the only member of the singleton-server-group, and enables it. Remember server 23's HTTP port is 8580
The application is now deployed on the five servers, and this concludes our chapter on deployment. We now know how the different deployment options can be used, depending on our projects requirements.
The REST API is interesting if we have a continuous integration tools like Jenkins on some WebHooks to trigger deployments after the builds, but DMR is clearly easier for scripting and the command line.
Last updated: March 16, 2023