In this article, you will learn about kernel live patching for Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift environments. The year 2024 marked a significant milestone, with over 40,000 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) published, representing a 38% increase from the 28,818 CVEs in 2023. According to a lwn.net report, this continues a consecutive seven-year trend of record-high CVE publications since 2017. Experts predict another record-breaking year of CVE production in 2025, with estimates ranging from 48,675 to 58,956 new CVEs, which will likely bring the total number of CVEs above 300,000.
Given the escalating speed and sophistication of AI-powered attacks, as well as the continuous surge in CVEs, kernel live patching has become an indispensable practice, especially for critical systems and servers.
What is Linux kernel live patching?
Linux kernel live patching is a method for applying critical security patches to a running Linux kernel without the need to reboot or interrupt runtime.
Without live patching, applying a patch typically requires rebooting the patched service or app to load the new changes of the patched version. This is true even for patches applied to the Linux kernel itself, creating a conundrum for Linux system administrators. They need to apply imperative security updates, but that means unscheduled reboots to the Linux server, including latency and downtime.
Learn more about kernel live patch mechanics.
OpenStack Services on OpenShift environments
Starting with feature release 2, users can test a technology preview of kernel live patching support for OpenStack Services on OpenShift compute nodes. With this feature, users can apply critical security patches to a running Linux kernel in-memory, without needing to reboot or interrupt the runtime. This means you no longer need to drain the clusters and migrate the workload when applying CVE patches that require kernel updates, resulting in fewer maintenance windows.
The process would entail the operator creating a file kpatch-deployment.yaml OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment custom resource (CR) as follows:
apiVersion: dataplane.openstack.org/v1beta1
kind: OpenStackDataPlaneDeployment
metadata:
name: apply-kpatch
namespace: openstack
spec:
nodeSets:
- <nodeSet_name> 1
servicesOverride:
- update 2
ansibleExtraVars: 3
edpm_update_enable_kpatch: true
ansibleLimit: <node_hostname>,...,<node_hostname> 4- Lists the
OpenStackDataPlaneDeploymentNodeSetCRs that contain the nodes that you are applying kernel live patching. - Specifies the update as the only service to execute.
- Enables the flag of
kpatch edpm_update_enable_kpatch: true - Optional: Lists the individual nodes in the node set to apply the kernel live patch process. If not set, all the nodes in the node set are affected.
As shown in Figure 1, the operator would apply the kpatch-deployment.yaml file:
oc apply -f kpatch-deployment.yaml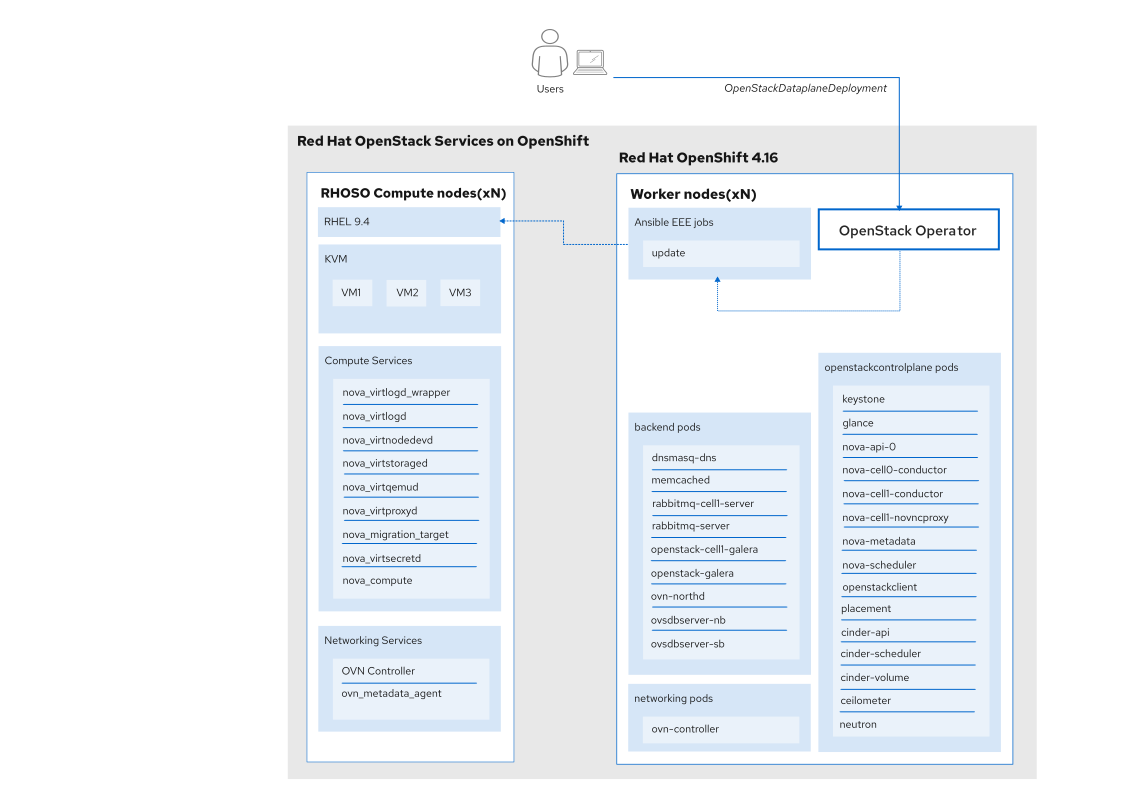
You can view the Ansible logs while the deployment executes as follows:
oc get pod -l app=openstackansibleee -w
oc logs update-apply-kpatch-openstack-edpm-2z6hbFinally, check that the kernel live patching process has been applied successfully:
oc get openstackdataplanedeployment
NAME NODESETS STATUS MESSAGE
edpm-deployment-post-ceph ["openstack-edpm"] True Setup complete
edpm-deployment-pre-ceph ["openstack-edpm"] True Setup complete
apply-kpatch ["openstack-edpm"] False Deployment in progress
----Redefine your maintenance windows
Kernel live patching offers significant operational advantages by fundamentally changing how you approach system maintenance and security updates:
- Allows you to apply critical and important security patches to a running Linux kernel, without the need to reboot or interrupt runtime.
- No need to drain the clusters and migrate the workload.
- Results in fewer maintenance windows.
Try it
Leveraging kernel live patching is a great way to keep your infrastructure updated and minimize the amount of manual work required. General Availability of kernel live patching for Red Hat OpenStack Services on OpenShift is targeted for feature release 4 and expected in November 2025.
You can learn more in the Linux Kernel's livepatch documentation and in Red Hat Enterprise Linux Applying patches with kernel live patching documentation.
