Page
Initiate and optimize your model server

Let’s begin by setting up Podman Desktop and the AI Lab extension. Once installed and verified, we’ll download an AI model and demonstrate how you can start experimenting with it.
Prerequisites:
- Basic understanding of Python.
- Basic understanding of containerization concepts.
- Basic awareness of cloud-native concepts.
- The latest version of Podman Desktop installed on your laptop.
- Podman Desktop 1.10.3+ and Podman 5.0.1+.
- At least 12GB RAM, 4+ CPUs (more is better for large models).
In this lesson, you will:
- Set up Podman Desktop.
- Set up the AI lab extension.
- Download an AI model.
- Learn about recipes and playgrounds.
Set up Podman Desktop and the AI Lab extension
Here are detailed installation instructions for Podman Desktop and the AI Lab extension. Familiarize yourself with the primary features and interface of the extension.
Follow these steps to install the extension directly from Podman Desktop:
Download and install Podman Desktop if you haven’t already done so. Then open it on your machine to view the dashboard (Figure 1).
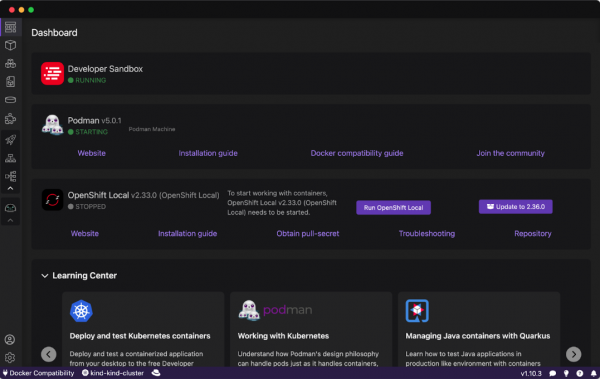
Figure 1: Open the Podman Desktop dashboard. From the left-hand menu, navigate to Extensions > Catalog (Figure 2).
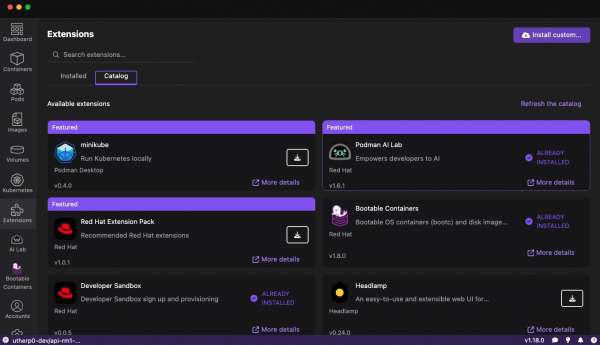
Figure 2: From the Podman Desktop dashboard, select Extensions in the left-hand menu, then select the Catalog tab. - Search for the Podman AI Lab and click Install.
Note: You can also install the Podman AI Lab by using the Red Hat Extension pack available in Podman Desktop.
Verify the installation
After installation, the Podman AI Lab icon appears in the left navigation bar of Podman Desktop, as shown in Figure 3.
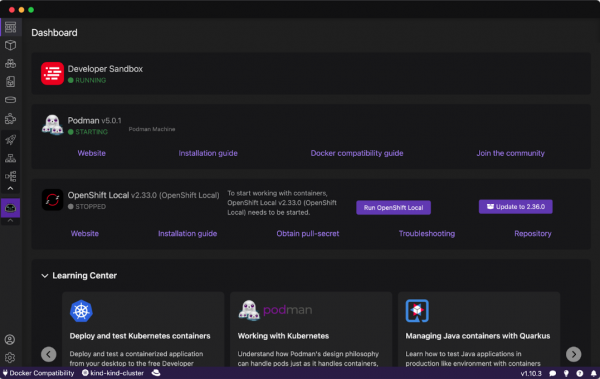
After clicking the AI Lab icon in the left menu, the Podman AI Lab dashboard opens and shows the Extension details page in Figure 4.
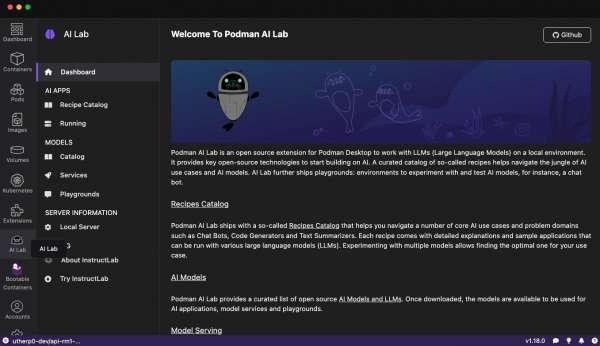
Download an AI model
Podman AI Lab provides a catalog of recipes showcasing common AI use cases (Figure 5). Choose a recipe, configure it with your preferred settings, and run it to see the results. Each recipe includes detailed explanations and sample applications that you can run using different large language models (LLMs).
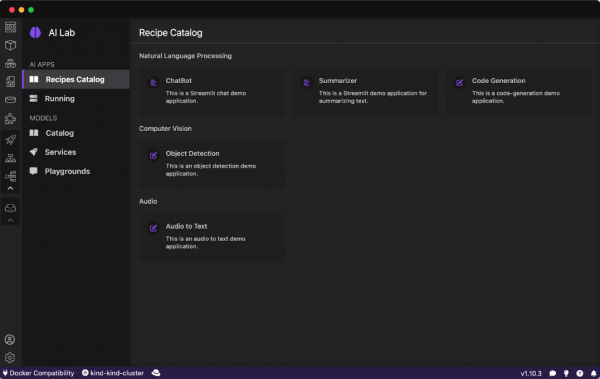
You can use a curated set of open source AI models also included in the Podman AI Lab (Figure 6).
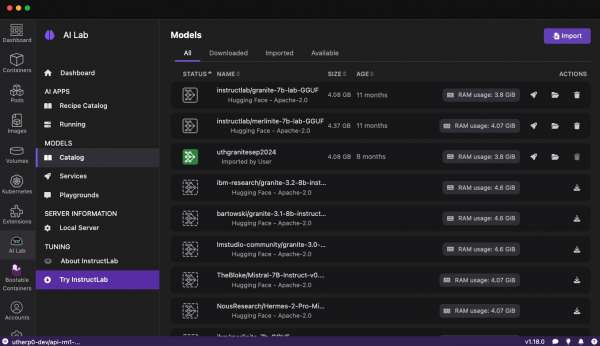
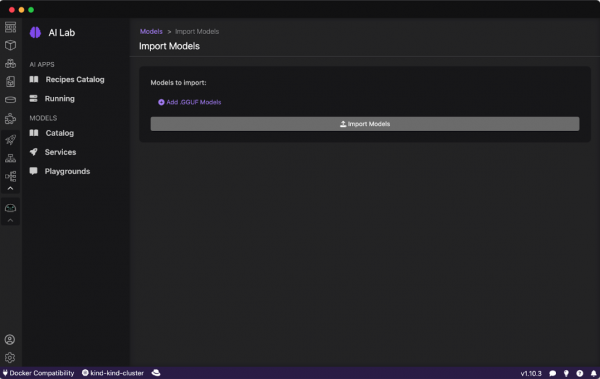
Custom models
You can also import your own AI models to run within the Podman AI Lab. For example, you can import a quantized GGUF model directly into your Podman Desktop AI Lab environment (Figure 7).
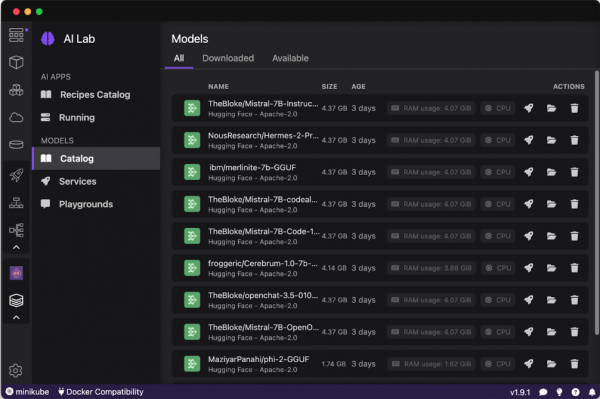
Select a model from the catalog and download it locally to your workstation. Users can download AI models in widely used formats, including GGUF, PyTorch, and TensorFlow. For this example, we have downloaded the Mistral-7B model from Hugging Face (Figure 8).
Start a playground with a model
Open the Podman Desktop AI Lab interface by selecting Playgrounds from the left-hand sidebar. In the Playgrounds area, click New Playground to set up a new experimental environment. Here you can name your new environment and choose a downloaded model to utilize (Figure 9).
Once configured, the Podman Desktop AI Lab will initiate a containerized model server. This setup includes an interactive interface that allows you to send queries and view the responses. You will find the playground housed within an isolated Podman pod, which simplifies the underlying infrastructure, enabling straightforward model inference using an OpenAI-compatible API.
After the environment is ready, you can access the playground dashboard. This dashboard serves as your interactive interface for sending prompts to the model and viewing the outputs (Figure 10).
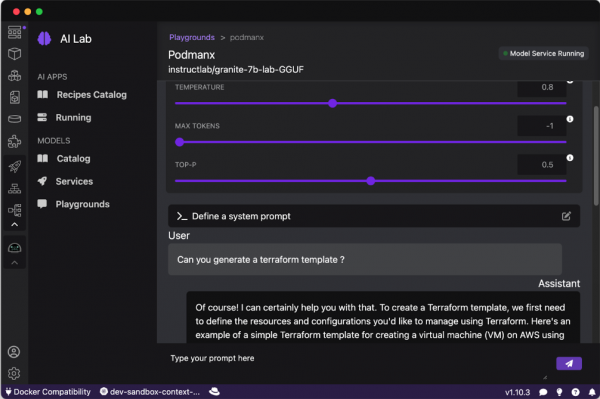
The playground provides the following adjustable parameters designed to tailor model behavior to specific development and data science applications:
- Temperature: This setting modulates the degree of stochasticity in the model's responses. Lower temperature values result in outputs that are more deterministic and focused, which is useful for tasks requiring high accuracy. Higher values introduce more randomness, enhancing creativity and potentially leading to novel insights or solutions.
- Max tokens: This parameter sets the upper limit on the length of the model's output, thereby controlling verbosity. It’s crucial for managing both the computational cost of generating responses and the practicality of their analysis in data-heavy environments.
- Top-p: This configuration influences the model's token selection process by adjusting the trade-off between relevance and diversity. It's key for fine-tuning the precision versus novelty aspect of the responses, especially in exploratory data analysis or when generating content.
You can leverage these settings within the Podman AI Lab's Playground to systematically optimize your model according to specific criteria.
Recipes Catalog
Recall the Recipes Catalog illustrated in Figure 5, these containerized AI recipes allow developers to quickly set up and prototype AI applications directly on their local machines. Recipes are built with at least two fundamental components: a model server and an AI application. The AI recipes cover a wide range of AI functionalities including audio processing, computer vision, and natural language processing. The sample applications rely on the llamacpp_python model server by default.
For a model of your choosing, click Start AI App (Figure 11).
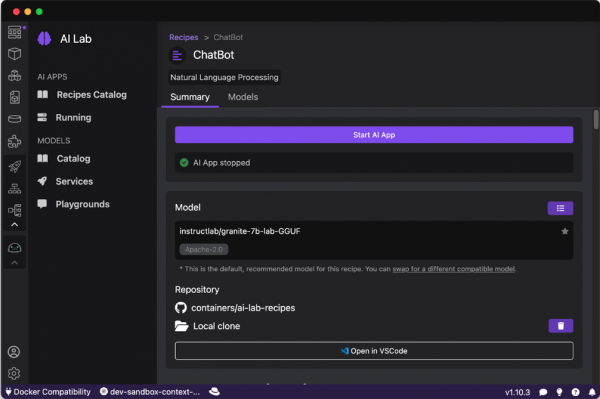
The sample application dashboard will appear (Figure 12).
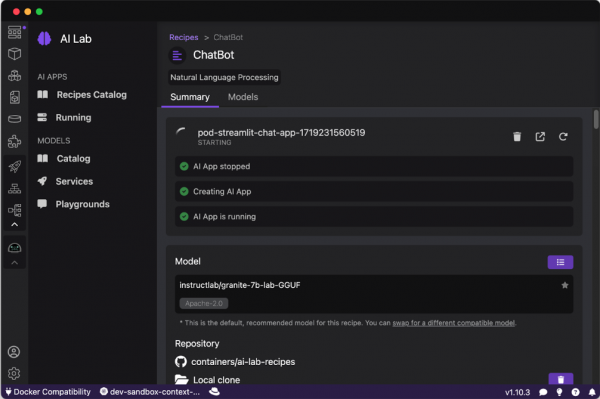
Then you can run an AI application (Figure 13).
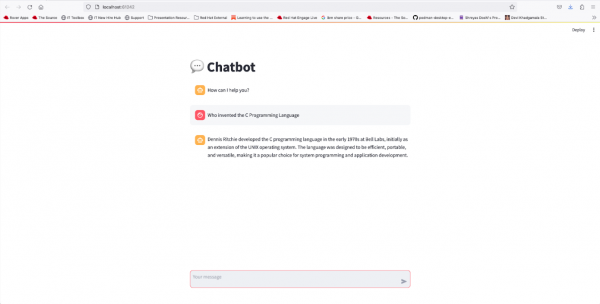
That’s it! Now you know how to experiment with LLMs using the AI Lab extension in Podman Desktop.
Summary
The Podman Desktop AI Lab extension simplifies developing with AI locally. It offers essential open source tools for AI development and a curated selection of recipes that guide users through various AI use cases and models. Podman AI Lab also includes playgrounds where users can experiment with and evaluate AI models, such as chatbots.
Learn more
Learn more about Podman:
- Learning path: Install Podman Desktop and connect it to your Developer Sandbox
- Learning path: Container development using Podman, Podman Desktop, and Kubernetes
- E-book: Podman in Action
- Cheat sheet: Podman
