Red Hat Satellite 6.18 continues to deliver the value of Red Hat Lightspeed (formerly Red Hat Insights) to disconnected ("air-gapped") environments. These services assess your Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) environments to help you proactively identify and remediate threats, stop outages before they happen, and lower compliance risks.
The advisor service, powered by Red Hat Lightspeed and released in technology preview in May 2025, is now generally available. It offers a broad assessment of RHEL infrastructure health in four main areas: availability, stability, performance, and system security. This service gives you the details you need to plan updates and prioritize issues during your scheduled downtime.
The vulnerability service is also powered by Red Hat Lightspeed and now available on-premises in technology preview. It uses Red Hat’s expert knowledge to identify systems at risk, helping you do more than just scan for problems. You can view and triage alerts in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database. You get detailed CVE information, like the ID, description, publish date, severity, and CVSS score—all included with your Satellite subscription.
How do disconnected services work?
These tools are delivered in containers that include services, rules, remediations, frontends, and connectivity that are deployed on your Satellite installation. If your Satellite environment connects to the internet, you simply authenticate to the Red Hat registry and run a single enablement command.
In an air-gapped environment (one not connected to the internet), the container images are included in the installation ISO. You install the container images from that ISO and run the enablement command.
If you currently use Red Hat Lightspeed in a connected environment, do not enable the disconnected service. Stick with the full suite of services on the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console. Enabling the disconnected tools removes access to hosted features, including subscription tracking. Disconnected users can still submit subscription usage information to the console by following the inventory upload generation instructions.
Installation in a disconnected environment
The following installation instructions assume that you have installed Satellite 6.18 and have a valid Red Hat subscription. For full details, read the official documentation.
If you installed Satellite 6.18 in a disconnected environment, you already have the Satellite ISO image with the necessary container images. Download and mount the Satellite ISO image, then configure your local repositories.
Next, set up the container images on your Satellite server:
cd /media/sat6/
./setup_containersThen, enable the plug-in:
satellite-installer --enable-iopThe vulnerability service requires additional security data. From a separate internet-connected host, download and populate the CVE mapping file:
curl -o cvemap.xml https://security.access.redhat.com/data/meta/v1/cvemap.xmlTransfer the cvemap.xml file to your disconnected Satellite server and copy it to /var/lib/foreman/:
cp cvemap.xml /var/lib/foreman/Now you’re ready to register systems and start using these services in Satellite.
Registering systems
If a host is already registered to your Satellite server, make sure the insights-client package is installed and run the insights-client command:
sudo dnf install insights-client
sudo insights-clientYou must register new hosts to your Satellite server. Generate a registration script and enable the Setup Red Hat Lightspeed option (Figure 1).
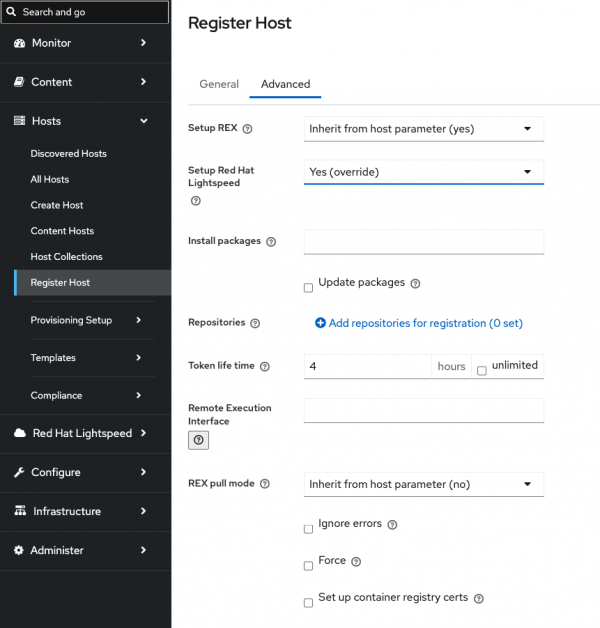
After registering your host, you can view the advisor and vulnerability analysis.
The advisor service is generally available in Satellite
To see all of the configuration issues impacting your environment, log in to the Satellite UI. Select Recommendations under Red Hat Lightspeed (Figure 2).
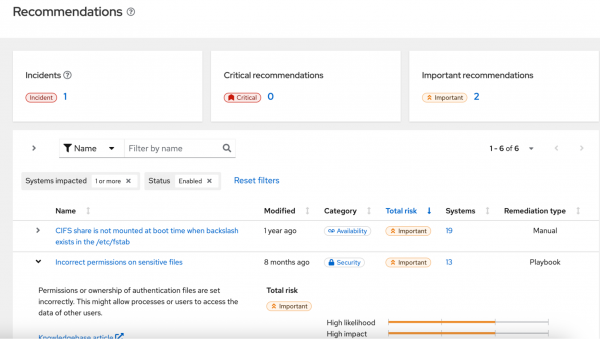
The Recommendations page lists configuration issues affecting your hosts, including risks to security, stability, availability, and performance. We organized this information to help you manage remediation more effectively. This updates the disconnected interface to look and feel like the hosted version.
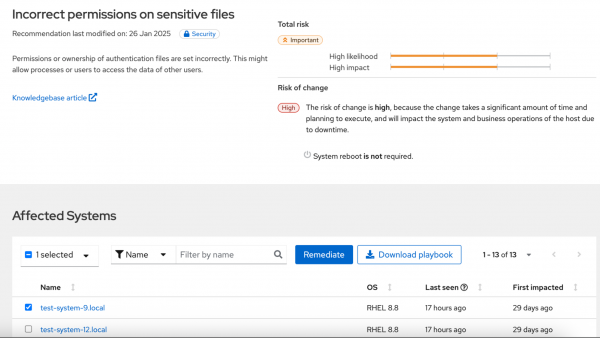
You can view an overview of each issue, including the risk level, the number of affected systems, and whether a resolution playbook exists, as shown in Figure 3. In fully disconnected environments, you will need to copy the Red Hat Knowledgebase article link and open it on a connected system. Alternatively, you can look up the article in the Red Hat Offline Knowledge Portal.
Select the recommendation title to see details, including the list of affected systems (Figure 4). If a playbook is available, you can select specific systems and remediate the issue directly through Satellite’s remote execution framework. You can also download the playbook to run in an automation tool like Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
The vulnerability service is now available in technical preview in Satellite
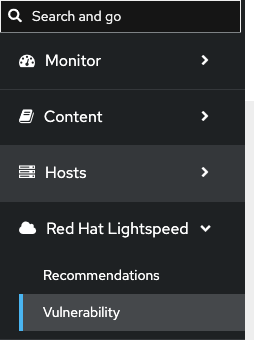
Before Satellite 6.18, you had to check errata views to see which CVEs were addressed. Now, the vulnerability service technology preview offers a security-focused view. To see it, select Vulnerability under the Red Hat Lightspeed menu (Figure 5).
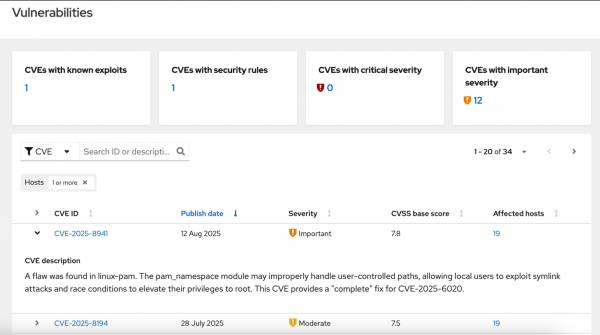
The Vulnerabilities page (Figure 6) shows the CVEs affecting your environment. It provides the severity, CVSS score, and number of affected systems so you can triage risks quickly.
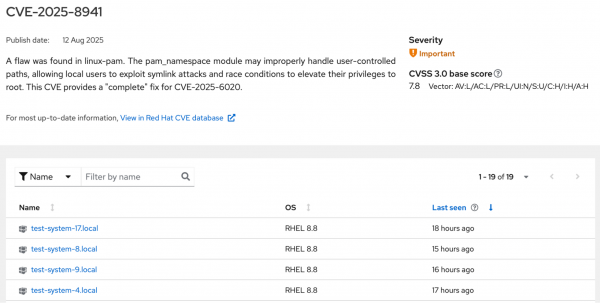
Select the CVE ID to see details, including the list of affected systems and a link to the CVE entry in the Red Hat CVE database. In fully disconnected environments, you will need to copy the CVE database link and open it on a connected system, or use the Red Hat Offline Knowledge Portal.
Try it
The advisor and vulnerability services are now available in Red Hat Satellite 6.18. For more details, visit the Red Hat Satellite home page and read the product documentation. To learn more about Red Hat Lightspeed, visit the home page or view the full documentation.
To provide feedback, visit the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and select the Feedback button in the lower-right corner of the screen (Figure 8).