Scalability is the measure of a system's ability to increase or decrease in performance, cost, and availability in response to changes in application and system processing demands. In distributed systems, this can be done by scaling up/down existing server resources (vertical scaling), or scaling out/in entire servers (horizontal scaling). The former is much simpler but limited, while the latter is more expensive but enables very large scaling.
Dynamic scalability means that scaling can be done without requiring system downtime. In some environments, these systems can also scale autonomously based on the actual load. In this article, we're looking at the new dynamic quorum configuration and use cases.
Controllers in KRaft are Kafka nodes that use the Raft consensus algorithm to elect a leader (active controller), and replicate the cluster metadata. Before Kafka v3.9.0, KRaft based clusters only allowed static quorum configurations, where the set of controller nodes (a.k.a., voters) is fixed and cannot be changed without a restart.
Kafka v3.9.0 introduces support for dynamic quorum with KIP-853. This is one of the missing features required to reach feature parity with ZooKeeper-based clusters. From now on, the dynamic quorum should be the preferred way of configuring a KRaft based cluster, as it doesn't require cluster downtime.
Dynamic cluster scaling is important for a number of use cases:
- Scale: The operator wants to scale the number of controllers by adding or removing a controller (this is pretty rare in practice, as the controller quorum is set once and seldom changed).
- Replace: The operator wants to replace a controller because of a disk or hardware failure.
- Migrate: The operator wants to migrate the cluster from old to new machines, or change KRaft architecture (e.g., moving from dedicated controllers to combined mode nodes).
Implementation
The dynamic KRaft quorum extends the basic consensus algorithm. Specifically, it introduces three additional remote procedure calls (RPCs): AddRaftVoter, RemoveRaftVoter, and UpdateRaftVoter. Additionally, two new metadata records have been added: KRaftVersionRecord and VotersRecord.
In addition to the RPCs and metadata records, which enable this new feature, there are important safety and availability constraints to be considered.
Safety
Cluster metadata is replicated asynchronously through the __cluster_metadata single partition topic (a.k.a., metadata log), so it is not possible to atomically switch all controller configurations at once. For this reason, adding or removing many controllers in one go is not safe, as it can potentially split into two independent majorities (disjoint majorities). See Figure 1.
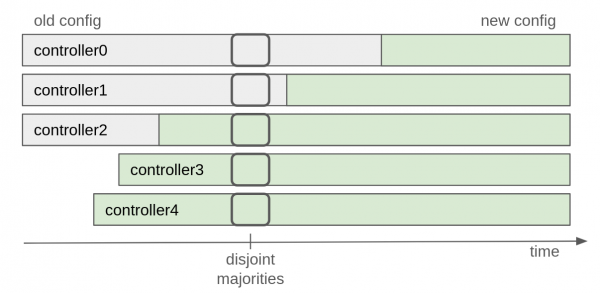
To address this issue, KIP-853 adds the following restriction: only one controller can be added or removed from the cluster at a time. In other words, it is only safe to start another quorum change once a majority of the old quorum has moved to operating under the new quorum. This rule ensures overlap between the majority of the old and new quorums, maintaining a controlling majority during the transition. The active controller acknowledges the configuration change by committing to the metadata log after hearing back from the new majority.
More complex quorum changes are implemented as a series of single-controller changes. In this case, it is preferable to add controllers before removing controllers. For example, to replace a controller in a three-controller cluster, adding one controller and then removing the other allows the system to handle one controller failure at all times throughout the whole process.
Availability
It's important to let new controllers catch up with the active controller's metadata log before joining the quorum. A three-controller cluster can tolerate one failure. However, if a fourth controller with an empty log is added to the same cluster, and one of the original three controllers fails, the cluster will be temporarily unable to commit new metadata entries. A similar availability issue can occur if many new controllers are added to a cluster in quick succession, where the new controllers are needed to form a majority of the cluster.
To avoid this issue, KIP-853 adds an additional phase before the quorum configuration change, in which a new controller always joins the cluster as an observer. This means that the new controller starts to replicate the metadata log, but does not yet count towards majorities. Once the new controller has caught up with the active controller, it can be added to the quorum set. The active controller aborts the change if the new controller is unavailable (e.g., hardware failure, configuration error), or it is so slow that it will never catch up.
Removing a controller can also be disruptive, as it could lead to unnecessary and repeated leader elections. Until KIP-996 has been implemented and released, it is recommended to shut down the controller to be removed before running the remove-controller command. If the removed controller is the active controller, it will only resign from the quorum when the new quorum is committed, but it won't count itself when computing the high watermark (commit check).
Practical examples
In the Kafka documentation, there are some basic command line examples to show how to scale up or down the controller set. Instead, here we present a couple of practical examples of how dynamic scaling can be used to perform some common maintenance tasks without cluster downtime.
- Replace a controller with a failed disk.
- Migrate to a different KRaft architecture.
In order to be able to configure a dynamic quorum, the kraft.version feature must be at version 1 or above for all cluster nodes. Note that downgrading is not supported. You can find out the cluster's finalized KRaft version by running the following command:
$ bin/kafka-features.sh --bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 describe | grep kraft.version
Feature: kraft.version SupportedMinVersion: 0 SupportedMaxVersion: 1 FinalizedVersionLevel: 1 Epoch: 5When using a static quorum, the configuration file for each node must specify all controllers in controller.quorum.voters. Instead, when using a dynamic quorum, you should set controller.quorum.bootstrap.servers, and either use the standalone flag or pass the initial controller set when formatting the disk. In the following examples, we'll use the initial controller set way to format the controllers for quickly forming a three node quorum.
Create a test cluster
Let's first create a brand new cluster with three controllers (0, 1, 2) and three brokers (7, 8, 9). In this case, we are running all cluster nodes on localhost. We show the configuration of the first controller and broker as a reference for creating the other nodes. The quorum bootstrap servers are configured similarly to the bootstrap servers configuration in Kafka clients. See below:
# controller
node.id=0
process.roles=controller
listeners=CONTROLLER://localhost:8000
listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT
controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER
controller.quorum.bootstrap.servers=localhost:8000,localhost:8001,localhost:8002
metadata.log.dir=/opt/kafka/server0/metadata
log.dirs=/opt/kafka/server0/data
# broker
node.id=7
process.roles=broker
listeners=REPLICATION://localhost:8007,CLIENT://localhost:9092
listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,REPLICATION:PLAINTEXT,CLIENT:PLAINTEXT
advertised.listeners=REPLICATION://localhost:8007,CLIENT://localhost:9092
controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER
inter.broker.listener.name=REPLICATION
controller.quorum.bootstrap.servers=localhost:8000,localhost:8001,localhost:8002
metadata.log.dir=/opt/kafka/server7/metadata
log.dirs=/opt/kafka/server7/dataBefore starting each controller node, we have to format the disk. This can be done via "standalone" mode or "initial controllers" mode. Here, we use the latter by passing the initial controller set. Both cluster and directory IDs can be generated using the storage tool. Dynamic controllers include a directory UUID within their meta.properties. This unique identifier helps to differentiate log directories in the controller (see disk replacement example below):
$ CLUSTER_ID="$(bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid)" \
DIR_ID_0="$(bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid)" \
DIR_ID_1="$(bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid)" \
DIR_ID_2="$(bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid)"
$ bin/kafka-storage.sh format \
--config /opt/kafka/server0/config/server.properties \
--cluster-id "$CLUSTER_ID" \
--initial-controllers "0@localhost:8000:$DIR_ID_0,1@localhost:8001:$DIR_ID_1,2@localhost:8002:DIR_ID_2"After that, there will be some files generated under the metadata log directory:
$ tree /opt/kafka/server0/metadata
/opt/kafka/server0/metadata
├── bootstrap.checkpoint
├── __cluster_metadata-0
│ ├── 00000000000000000000-0000000000.checkpoint
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.index
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.log
│ ├── 00000000000000000000.timeindex
│ ├── leader-epoch-checkpoint
│ ├── partition.metadata
│ └── quorum-state
└── meta.properties
2 directories, 9 filesThe meta.properties is a plaintext file that contains the metadata of the node, including node ID, directory ID, and cluster ID:
$ cat /opt/kafka/server0/metadata/meta.properties
#
#Thu Nov 07 15:19:01 CST 2024
node.id=0
directory.id=pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ
version=1
cluster.id=ucil9Sd9R7Ss8st7gV-KrgThe bootstrap.checkpoint file is a binary file that contains the metadata version of this node:
$ bin/kafka-dump-log.sh --cluster-metadata-decoder --files /opt/kafka/server0/metadata/bootstrap.checkpoint | grep metadata.version
| offset: 1 CreateTime: 1731059573622 keySize: -1 valueSize: 23 sequence: -1 headerKeys: [] payload: {"type":"FEATURE_LEVEL_RECORD","version":0,"data":{"name":"metadata.version","featureLevel":21}}The 00000000000000000000-0000000000.checkpoint snapshot file is new in v3.9.0, and its purpose is to store the above-mentioned records. Here we can see it contains the information for all of the controllers, including endpoints:
$ bin/kafka-dump-log.sh --cluster-metadata-decoder --files /opt/kafka/server0/metadata/__cluster_metadata-0/00000000000000000000-0000000000.checkpoint | grep "KRaftVersion\|KRaftVoters"
| offset: 1 CreateTime: 1731059573639 keySize: 4 valueSize: 5 sequence: -1 headerKeys: [] KRaftVersion {"version":0,"kRaftVersion":1}
| offset: 2 CreateTime: 1731059573639 keySize: 4 valueSize: 157 sequence: -1 headerKeys: [] KRaftVoters {"version":0,"voters":[{"voterId":0,"voterDirectoryId":"YQfYGinOSneT_INBzNf-Ew","endpoints":[{"name":"CONTROLLER","host":"localhost","port":8000}],"kRaftVersionFeature":{"minSupportedVersion":0,"maxSupportedVersion":1}},{"voterId":1,"voterDirectoryId":"bnbzYpVnQwGU10389c73eg","endpoints":[{"name":"CONTROLLER","host":"localhost","port":8001}],"kRaftVersionFeature":{"minSupportedVersion":0,"maxSupportedVersion":1}},{"voterId":2,"voterDirectoryId":"yHVmF0CFTtunPZU31gkobQ","endpoints":[{"name":"CONTROLLER","host":"localhost","port":8002}],"kRaftVersionFeature":{"minSupportedVersion":0,"maxSupportedVersion":1}}]}Once all cluster nodes are started, the quorum should be formed and in-sync:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh --bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 describe --re --hu
NodeId DirectoryId LogEndOffset Lag LastFetchTimestamp LastCaughtUpTimestamp Status
0 pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ 105 0 7 ms ago 7 ms ago Leader
1 QjRpFtVDTtCa8OLXiSbmmA 105 0 84 ms ago 84 ms ago Follower
2 slcsM5ZAR0SMIF_u__MAeg 105 0 84 ms ago 84 ms ago Follower
8 aXLz3ixjqzXhCYqKHRD4WQ 105 0 85 ms ago 85 ms ago Observer
7 KCriHQZm3TlxvEVNgyWKJw 105 0 85 ms ago 85 ms ago Observer
9 v5nnIwK8r0XqjyqlIPW-aw 105 0 86 ms ago 86 ms ago ObserverReplace a controller with a failed disk
When one of the controllers has a disk failure, the operator can replace this disk with a new one, as shown in Figure 2.
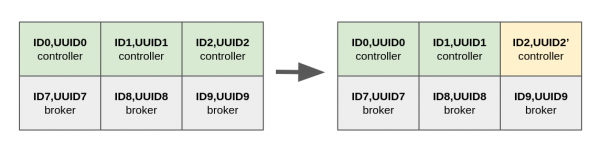
The replaced disk needs to be formatted with a new directory ID:
$ CLUSTER_ID="$(bin/kafka-cluster.sh cluster-id --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 | awk -F': ' '{print $2}')"
$ bin/kafka-storage.sh format \
--config /opt/kafka/server2/config/server.properties \
--cluster-id "$CLUSTER_ID" \
--no-initial-controllers \
--ignore-formatted
Formatting metadata directory /opt/kafka/server2/metadata with metadata.version 3.9-IV0.After restarting the controller, the quorum will have two nodes with an ID of 2: the original incarnation with a failed disk and an ever growing lag and follower status, plus a new one with a different directory ID and observer status. See below:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh --bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 describe --re --hu
NodeId DirectoryId LogEndOffset Lag LastFetchTimestamp LastCaughtUpTimestamp Status
0 pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ 535 0 6 ms ago 6 ms ago Leader
1 QjRpFtVDTtCa8OLXiSbmmA 535 0 283 ms ago 283 ms ago Follower
2 slcsM5ZAR0SMIF_u__MAeg 407 128 63307 ms ago 63802 ms ago Follower
2 wrqMDI1WDsqaooVSOtlgYw 535 0 281 ms ago 281 ms ago Observer
8 aXLz3ixjqzXhCYqKHRD4WQ 535 0 284 ms ago 284 ms ago Observer
7 KCriHQZm3TlxvEVNgyWKJw 535 0 284 ms ago 284 ms ago Observer
9 v5nnIwK8r0XqjyqlIPW-aw 535 0 284 ms ago 284 ms ago ObserverOnce the new controller is in sync with the leader (lag near zero), we scale down the quorum to remove the old controller, followed by a quorum scale up to add the new controller to the quorum set:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh \
--bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 \
remove-controller \
--controller-id 2 \
--controller-directory-id slcsM5ZAR0SMIF_u__MAeg
Removed KRaft controller 2 with directory id slcsM5ZAR0SMIF_u__MAeg
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh \
--bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 \
--command-config /opt/kafka/server2/config/server.properties \
add-controller
Added controller 2 with directory id wrqMDI1WDsqaooVSOtlgYw and endpoints: CONTROLLER://localhost:8002We have now successfully replaced the failed disk and restored the original quorum:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh --bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 describe --re --hu
NodeId DirectoryId LogEndOffset Lag LastFetchTimestamp LastCaughtUpTimestamp Status
0 pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ 3367 0 7 ms ago 7 ms ago Leader
1 QjRpFtVDTtCa8OLXiSbmmA 3367 0 229 ms ago 229 ms ago Follower
2 wrqMDI1WDsqaooVSOtlgYw 3367 0 230 ms ago 230 ms ago Follower
8 aXLz3ixjqzXhCYqKHRD4WQ 3367 0 230 ms ago 230 ms ago Observer
7 KCriHQZm3TlxvEVNgyWKJw 3367 0 230 ms ago 230 ms ago Observer
9 v5nnIwK8r0XqjyqlIPW-aw 3367 0 230 ms ago 230 ms ago ObserverMigrate to a different KRaft architecture
Migrating from a ZooKeeper-based cluster to a KRaft-based cluster requires three dedicated controller nodes. Once the migration is completed, the operator wants to reduce the resource usage to just three nodes, where each cluster node acts as controller and broker at the same time (combined mode). See Figure 3.
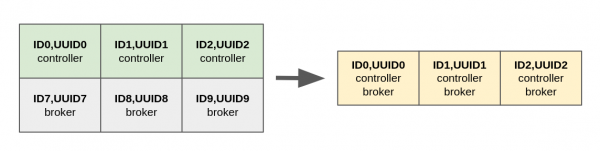
First, we update all controllers adding the broker role and missing configuration. Here we are reporting the diff output with the previous configuration of the first controller:
$ diff prev.properties updated.properties
2,4c2,5
< process.roles=controller
< listeners=CONTROLLER://localhost:8000
< listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT
---
> process.roles=controller,broker
> listeners=CONTROLLER://localhost:8000,REPLICATION://localhost:8010,CLIENT://localhost:9095
> listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,REPLICATION:PLAINTEXT,CLIENT:PLAINTEXT
> advertised.listeners=REPLICATION://localhost:8010,CLIENT://localhost:9095
5a7
> inter.broker.listener.name=REPLICATIONThis configuration change requires a rolling update where you restart all controllers one at a time. In order to minimize the number of leader elections, you can restart the current active controller last:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh --bootstrap-controller :8000 describe --re --hu
NodeId DirectoryId LogEndOffset Lag LastFetchTimestamp LastCaughtUpTimestamp Status
2 wrqMDI1WDsqaooVSOtlgYw 10009 0 6 ms ago 6 ms ago Leader
0 pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ 10009 0 362 ms ago 362 ms ago Follower
1 QjRpFtVDTtCa8OLXiSbmmA 10009 0 362 ms ago 362 ms ago Follower
8 aXLz3ixjqzXhCYqKHRD4WQ 10009 0 363 ms ago 363 ms ago Observer
7 KCriHQZm3TlxvEVNgyWKJw 10009 0 363 ms ago 363 ms ago Observer
9 v5nnIwK8r0XqjyqlIPW-aw 10009 0 363 ms ago 363 ms ago ObserverNow, we have to move all topic replicas from nodes 7, 8, and 9 to nodes 0, 1, and 2 using the partition reassignment tool. In our cluster we only have a few topics, but on a real cluster we recommend using the remove broker endpoint from the Cruise Control project, which moves all topics while keeping the cluster balanced. Once the reassignment is completed, the topics should have partitions spread among the combined nodes, like in the following example:
$ bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9095 --describe --topic my-topic Topic: my-topic TopicId: RHzP92QGSwy-RTcm5a5IpA PartitionCount: 5 ReplicationFactor: 3 Configs:
Topic: my-topic Partition: 0 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1,0 Isr: 0,1,2 Elr: LastKnownElr:
Topic: my-topic Partition: 1 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0,2 Isr: 0,1,2 Elr: LastKnownElr:
Topic: my-topic Partition: 2 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,1 Isr: 0,1,2 Elr: LastKnownElr:
Topic: my-topic Partition: 3 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0,2 Isr: 0,1,2 Elr: LastKnownElr:
Topic: my-topic Partition: 4 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1,0 Isr: 0,1,2 Elr: LastKnownElr:At this point, all data has been moved to the combined nodes, so we can stop the dedicated brokers, scaling down the cluster. Before stopping, we have to first unregister the broker to avoid issues like newly created partitions still being assigned to the removed replicas, or errors when the metadata version is updated after a cluster upgrade:
$ bin/kafka-cluster.sh unregister --bootstrap-server localhost:9095 --id 7 \
&& pkill -SIGKILL -ef "server7" && sleep 5
Broker 7 is no longer registered.
$ bin/kafka-cluster.sh unregister --bootstrap-server localhost:9095 --id 8 \
&& pkill -SIGKILL -ef "server8" && sleep 5
Broker 8 is no longer registered.
$ bin/kafka-cluster.sh unregister --bootstrap-server localhost:9095 --id 9 \
&& pkill -SIGKILL -ef "server9" && sleep 5
Broker 9 is no longer registeredThis is the final result with only three cluster nodes:
$ bin/kafka-metadata-quorum.sh --bootstrap-controller localhost:8000 describe --re --hu
NodeId DirectoryId LogEndOffset Lag LastFetchTimestamp LastCaughtUpTimestamp Status
2 wrqMDI1WDsqaooVSOtlgYw 13840 0 6 ms ago 6 ms ago Leader
0 pbvuBlaTTwKRxS5NLJwRFQ 13840 0 387 ms ago 387 ms ago Follower
1 QjRpFtVDTtCa8OLXiSbmmA 13840 0 387 ms ago 387 ms ago FollowerLimitations and future work
At the time of writing, the dynamic controller quorum feature has the following limitations:
- It is not possible to convert KRaft based clusters using a static controller quorum to a dynamic controller quorum configuration (KAFKA-16538).
- To avoid disrupting or slowing down leader elections and metadata changes, the operator needs to ensure that the new controller is able to keep up with the leader before adding it to the quorum set.
In future releases, the Kafka community will focus on the following improvements:
- Converting KRaft-based clusters using a static controller quorum to a dynamic controller quorum configuration. This is important because it allows the KRaft quorum formatted in v3.8.1 or earlier to upgrade to the dynamic controller quorum.
- Add new metrics for the dynamic controller quorum. During membership change, it is helpful to have metrics to help the operator know the current status, like the number of uncommitted voters change and number of voters.
- Implement the
controller.quorum.auto.join.enableconfiguration to control whether a KRaft controller should automatically join the cluster metadata partition based on its cluster ID. This helps ensure that the new controller is synchronized with the leader and adds it to the quorum set automatically.
Conclusion
Dynamic scaling Kafka clusters offer significant improvements in flexibility and efficiency, especially for handling changing workloads, hardware failures, and cluster migrations. By introducing the dynamic quorum configuration in Kafka v3.9.0, KRaft clusters can now scale controller nodes without downtime.
This new functionality enables Kafka operators to scale and manage clusters more effectively, whether by adding or removing controllers to meet demand or by conducting maintenance tasks like disk replacement and KRaft architecture migration.
While there are limitations and safety precautions, such as the inability to migrate from static to dynamic quorum, and ensuring new controllers synchronize before joining the quorum, the dynamic KRaft quorum greatly enhances Kafka's resilience and adaptability.
