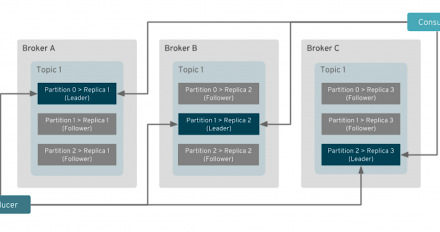
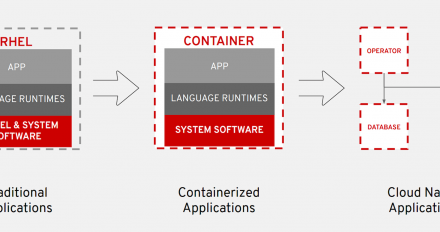
Develop with Django 2 and Python 3 in a container with Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Develop with Django 2 and Python 3 in a container with Red Hat Enterprise Linux - You can use Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Universal Base Images and application streams to develop in containers even if you are still running RHEL 7.