
Manage Software with Application Streams
Learn to make smart decisions when choosing software packages enabled on a...

Learn to make smart decisions when choosing software packages enabled on a...
Learn how to use Red Hat Universal Base Images (UBIs) with Docker from a non-Red Hat system, such as a Windows or Mac workstation.

Explore the tech preview of OpenShift's memory-based horizontal pod autoscaling feature and how it autoscales your pods if the demands on memory increase.

In the second part of this series, we walk you through customizing Fedora CoreOS and making use of its immutable and atomic nature.

Learn how Fedora CoreOS helps you create an immutable, atomically-managed infrastructure, and then set up your own instance.

Now, application developers in the Red Hat Partner program can build their container apps and redeploy from the full set of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) user space packages (non-kernel).

Learn how to store credentials using Kubernetes secrets for connector configuration with Kafka Connect deployed using Strimzi or Red Hat AMQ Streams.

See how podman-machine (mostly) lets you run Buildah, Podman, and skopeo on your Mac without having to build your own Linux VM.

We preview the updates from Open Data Hub project that enable Kubeflow to run on Red Hat OpenShift.
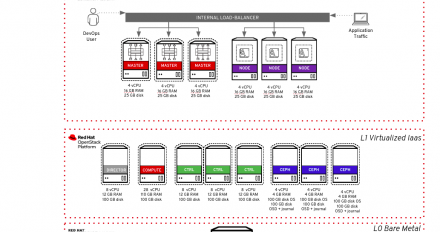
Learn how to test OpenShift 4.2 setup on OpenStack 13, and take advantage of OpenStack's programmatic API-driven approach.

Use OpenShift's projectRequestTemplate to add default controls for the resources that a project is allowed to consume.

We look at the OVN unidling issue and how the Controller_Event table can be used to forward events to a CMS, such as OpenStack Platform or OpenShift.
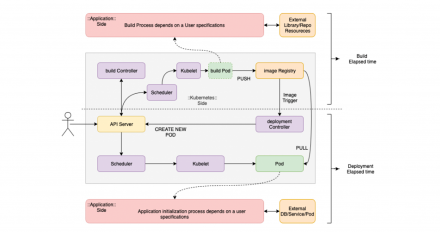
We introduce helpful, common tips for managing reliable builds and deployments on Red Hat OpenShift.
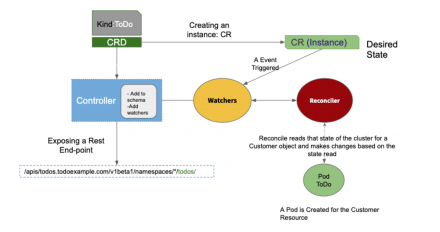
This article examines Kubernetes internals and Operator patterns by using a REST API example.

We provide a step-by-step visual tutorial describing how to create a simple virtual database using Red Hat Integration's data virtualization Operator.
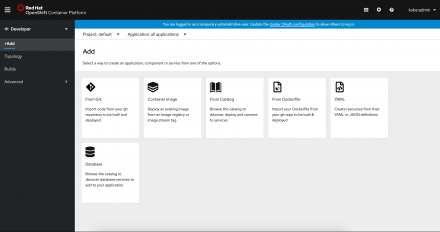
We take a look at user flow improvements for deploying applications in Red Hat OpenShift 4.3's Developer perspective.

We look at the various ways .NET Core is made available on Red Hat platforms, starting with an overview of the available platforms, and then showing how to install .NET Core on each of them.
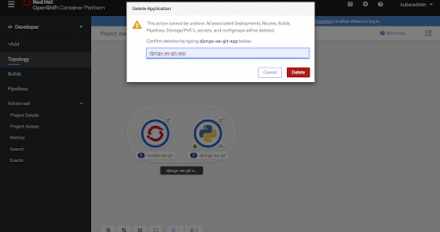
We explore the developer improvements added to OpenShift 4.3, which improves upon the features that were introduced in 4.2 and introduces new flows and features for the developer.

This article describes the oc-inject utility, which works on any Linux system that includes Python 3, the ldd utility, and the Red Hat OpenShift command-line tool oc.
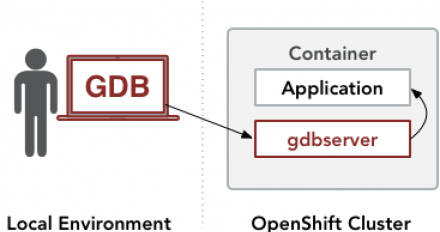
To successfully debug a containerized application, it is necessary to understand the constraints and how they determine which debugging tools can be used.

As a user, you would normally interact with OpenShift via the web console or oc command line client. When using either of these methods, under the covers they are talking to OpenShift via a REST API endpoint.
Moving Java applications to Red Hat OpenShift can seem daunting, but it can be worthwhile.

Red Hat AMQ Streams is a massively scalable, distributed, and high performance data streaming platform based on the Apache Kafka project. AMQ Streams provides an event streaming backbone that allows microservices and other application components to exchange data with extremely high throughput and low latency.
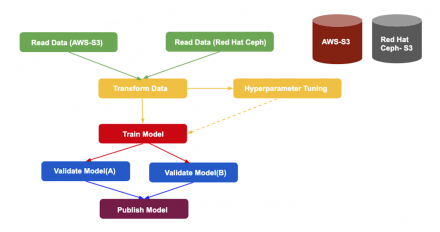
We describe how to use Open Data Hub and Kubeflow pipelines, both of which use Argo as the AI/ML pipeline tool.

This article will attempt to demystify the powerful and complex devfile.yaml in CodeReady Workspaces.