Page
Architecture, design, and use case patterns
Palo Alto firewalls can be implemented in a number of configurations to suit your organization’s unique needs. Before we begin the deployment, let’s explore a handful of architectures that could be used for different environments.
Prerequisites:
- N/A
In this lesson, you will:
- Explore the different ways Palo Alto firewalls can be set within Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization to achieve different goals.
Virtualization protection
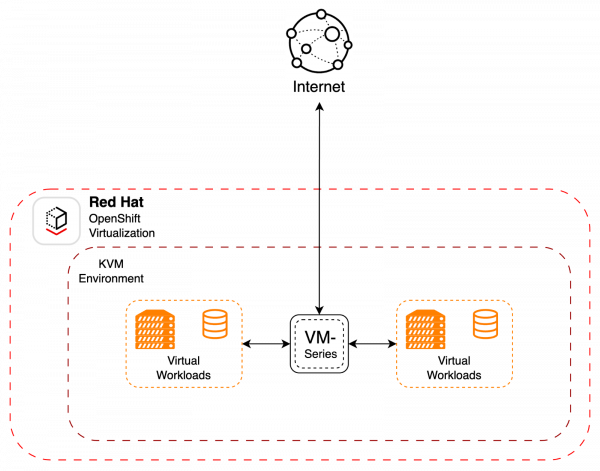
The first deployment model is fairly simple and straightforward. The Palo Alto VM-Series firewall can be deployed as a virtualized workload, which protects other virtual machines within the OpenShift environment from devices outside of the OpenShift cluster. This is shown in Figure 1.
Data center protection
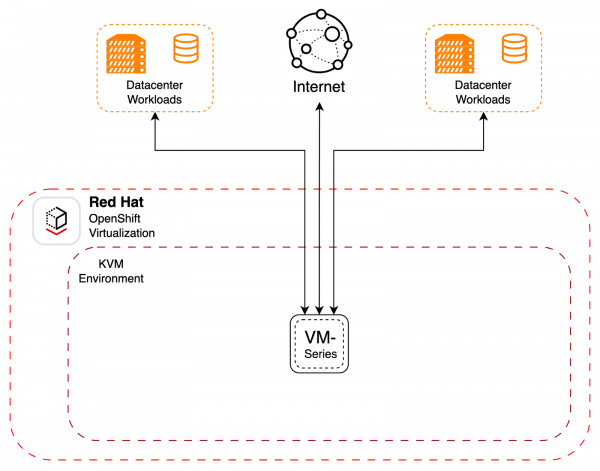
Additionally, you can run a virtualized firewall that’s connected to multiple outside networks through the use of a NetworkAttachmentDefinition (NAD), SriovNetwork, or a combination of the two. This deployment model uses the Palo Alto VM-Series firewall as a conduit between multiple externally attached networks, similar to a traditional network functions virtualization (NFV) workload. You can also configure OpenShift compute nodes for CPU pinning, NUMA, HugePages, or other performance and isolation scenarios, which are common security deployment considerations. See Figure 2.
UDN network namespace protection
OpenShift provides something that no other Kubernetes-based distribution can provide through what’s called User Defined Networking (UDN). You can think of UDN as similar to OpenStack tenant networks. These isolated networks allow namespaces to be on completely different network broadcast domains—and technically, a Palo Alto firewall can be added as a gateway between those isolated containerized network namespaces. This opens up opportunities that no other platform can achieve today. Figure 3 depicts this.
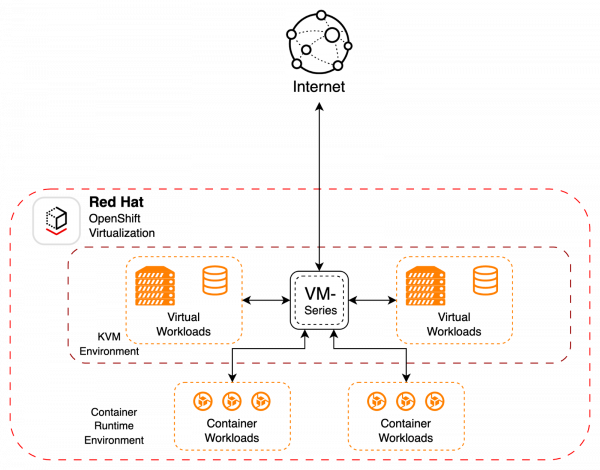
Mixed protection
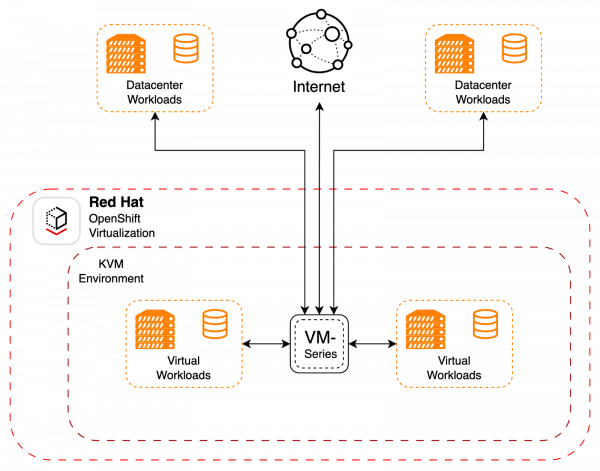
Figure 4 shows a mixed model with both data center and virtualized workloads protected with the Palo Alto VM-Series firewall. This is very similar to a traditional telco VNF deployment.
Now that we understand our architecture options, let’s examine the tools we’ll use to implement them.
