
How to use Kubernetes dynamic client with Fabric8
Learn how to use Fabric8 Kubernetes dynamic client and easily interact with Kubernetes API using GenericKubernetesResource API. (Part 3 of 5)

Learn how to use Fabric8 Kubernetes dynamic client and easily interact with Kubernetes API using GenericKubernetesResource API. (Part 3 of 5)

Learn how to program Kubernetes REST API in Java using Fabric8 Kubernetes client in this quick demonstration. (Part 1 of 5)

Learn how to interact with Kubernetes custom resources using its REST API in Java and the Fabric8 Kubernetes Java client. (Part 2 of 5)
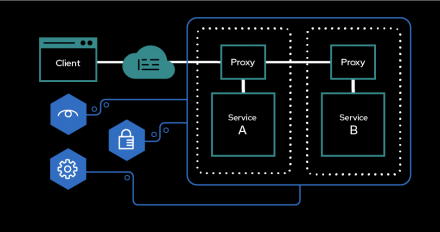
The common "no healthy upstream" message is usually caused by configuration errors. Knowing these errors and how to find them leads to quicker fixes.
The developers of Operators have found a new, flexible technique for allowing application developers to alter Operator behavior.

Learn the components of the control plane and workers nodes, along with Kubernetes resources that developers should know.
Get an overview of the GitOps principles and learn why they are essential for new IT projects in this excerpt from the GitOps Cookbook.
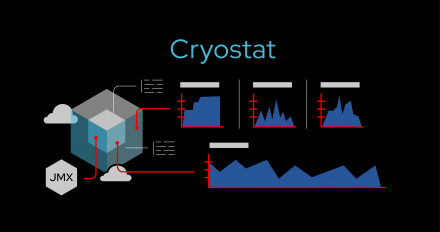
With the introduction of new security context constraints, pods must be properly configured under the enforced security standards defined globally or on a namespace level to be admitted to launch. Learn how Cryostat Operator 2.2.0 accommodates these changes.

When deployed on Kubernetes or OpenShift, Cryostat uses a default permission configuration that maps Kubernetes resources to Cryostat-managed resources to authorize a user to perform certain actions. Since a single set of mappings does not always fit all, with Cryostat Operator 2.2.0, we allow this mapping to be configurable via the Cryostat custom resource.

We've rounded up some of our favorite Kubernetes and OpenShift content from 2022, including stories about microservices and container optimization, along with top announcements.
Assess, prioritize, and modernize applications at scale with the migration toolkit for applications from Red Hat. Explore what's new in version 6.

Discover the evolution of open source application development and how Red Hat OpenShift meets the demand for containerized applications.

Learn how to use odo to set up a database to interact with an application's REST API. A demo sets up the environment and installs the necessary tools.

Integration using Apache Camel K makes it possible to build services that are scalable and reliable even when they depend on rapid interaction with data sources.

Learn about regex, Kubernetes storage concepts, and more.
Learn about the advantages and types of Kamelets configuration files which simplify connections to external systems.

Learn about Podman Desktop, a GUI dedicated to managing containers and Kubernetes for application developers.
Discover six ways the odo command-line interface (CLI) for Red Hat OpenShift and Kubernetes improves the developer experience.

Red Hat will contribute developer tools and expertise to backstage.io, making it easier for teams to use Kubernetes to build services and applications.

Write a Kubernetes Operator in Java to automate deployment and control of your application through a Custom Resource Definition.

See Red Hat experiment with running RHEL 9 as a virtual machine on Apple's macOS Ventura beta release and an M1-based MacBook Pro, along with single node OpenShift.
Red Hat Summit: Connect brought updated topics and tech from Red Hat’s annual

Learn how to easily generate Helm charts using Dekorate, how to map properties when installing or updating your charts, and how to use Helm profiles.

Discoverability is key to a successful API strategy. Learn how to improve API discovery, usability, and developer experience with a dynamic inventory.

Discover how Kubernetes improves developer agility by managing storage for containerized applications. (Part 1 of 3)