Page
Explore the JupyterLab environment

Explore the JupyterLab environment
You are now inside your JupyterLab environment (Figure 11). It's a web-based environment, but everything you do here is actually happening on the OpenShift AI cluster. This means that, without having to install and maintain anything on your own computer, and without disposing of lots of local resources such as CPU and RAM, you can conduct your data science work in this powerful and stable managed environment.
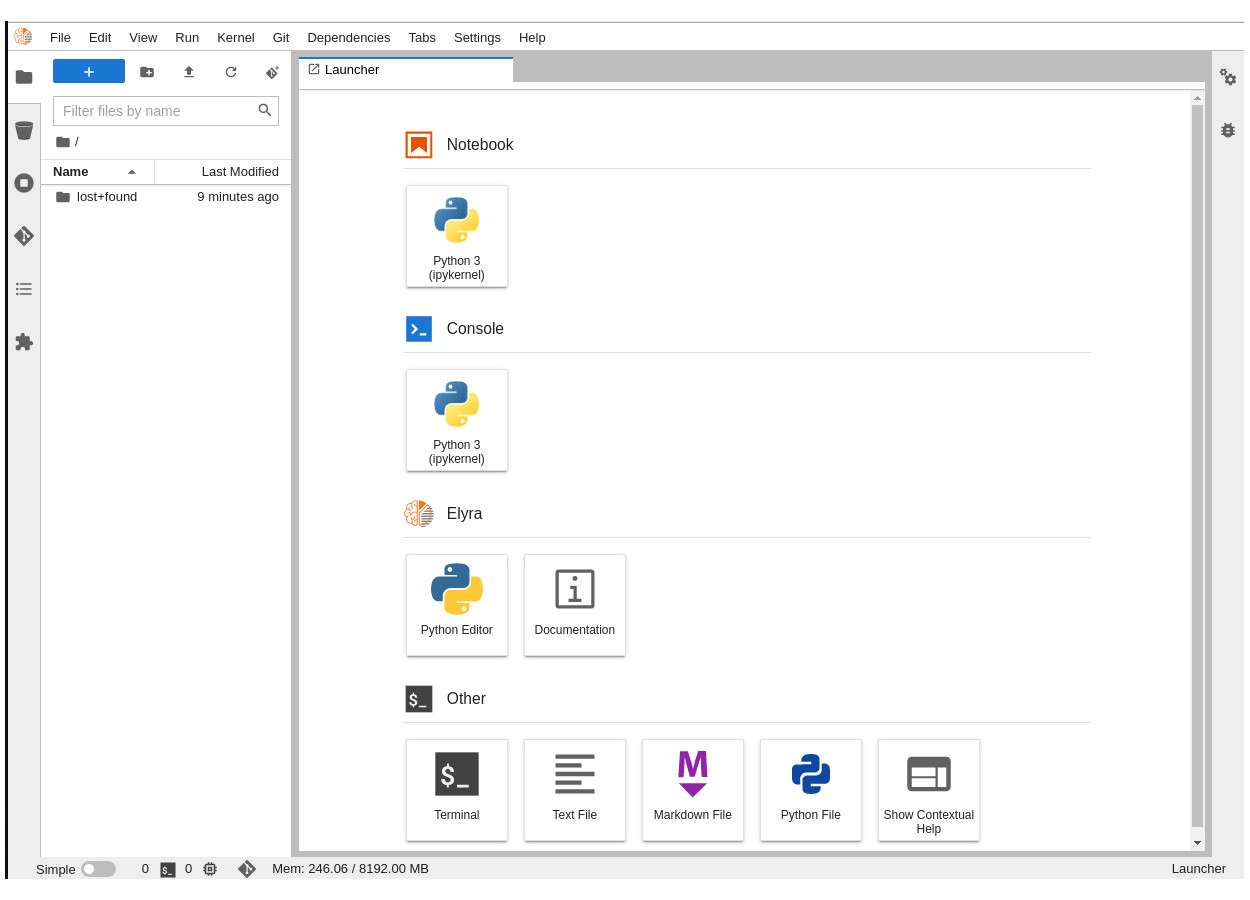
You are now in a window that resembles a file browser on a desktop. The window displays the files and folders that are saved inside your own personal space inside OpenShift AI. It's pretty empty right now, though. So the first thing we will do is add content into this environment by using Git.
Clone a Git repository
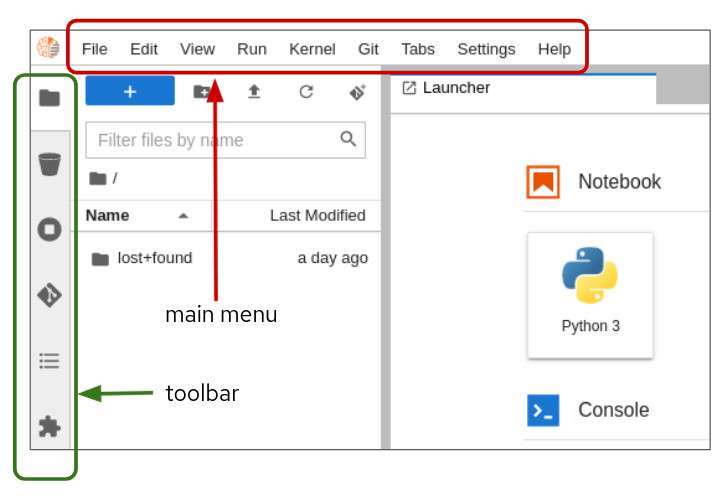
You can clone a Git repository in JupyterLab through the left-hand toolbar or the Git menu option in the main menu (Figure 12).
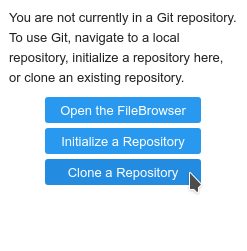
Let's clone a repository using the left-hand toolbar. Click on the Git icon, shown in Figure 13.

Then click on Clone a Repository (Figure 14).
Enter your git repository URL, which for this learning path is https://github.com/rh-aiservices-bu/firstJupyterNotebook.git. Then click CLONE (Figure 15).
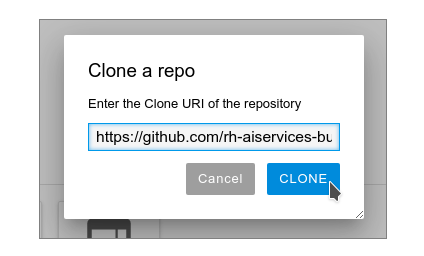
Cloning takes a few seconds, after which you can double-click and navigate to the newly-created folder that contains your cloned Git repository.
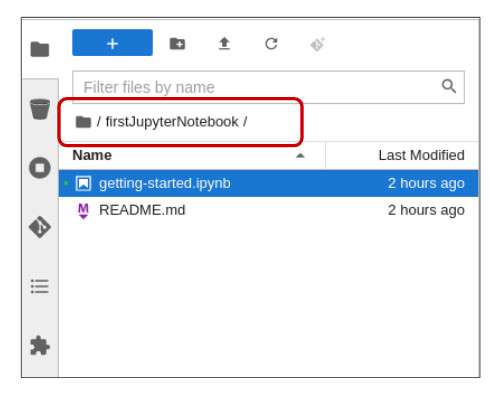
For this learning path, double-click and navigate to the newly-created folder, named firstJupyterNotebook. The Git repository contains two files: getting-started.ipynb and README.md (Figure 16).